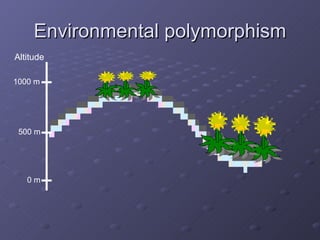
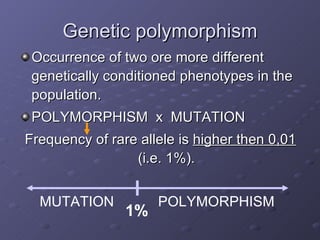
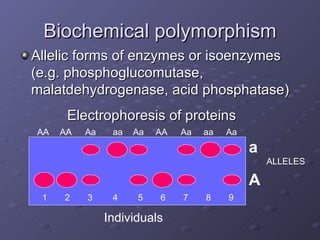
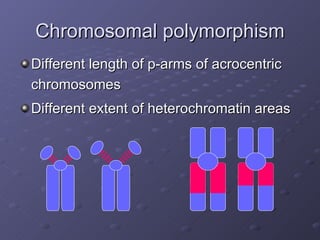
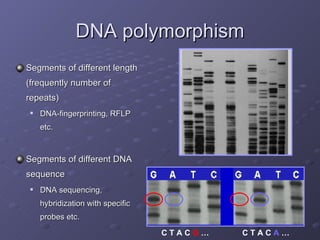
The document discusses genetic and environmental polymorphism, which refers to differences in DNA sequences or phenotypes induced by environmental factors. It provides examples of various types of genetic polymorphism, including phenotypic, biochemical, immunological, chromosomal, and DNA polymorphisms. The manifestation of these polymorphisms can include variations in traits, proteins, antigens, blood groups, length of chromosomes, and DNA sequences. The importance of polymorphism studies is also highlighted for applications like forensics, transplantation, epidemiology, taxonomy, and understanding susceptibility to environmental factors and drugs.