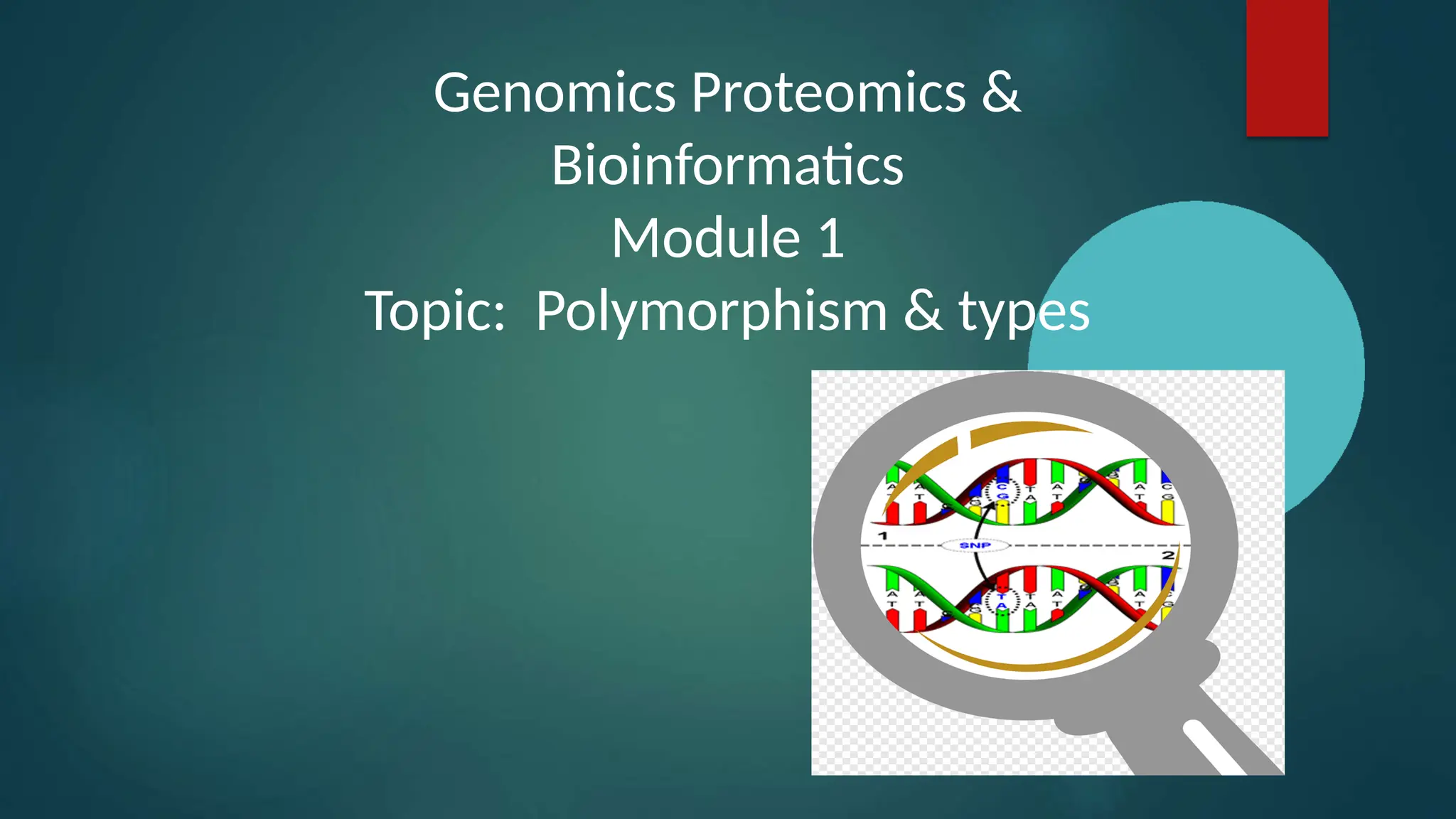
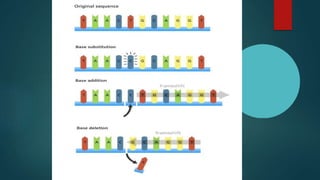
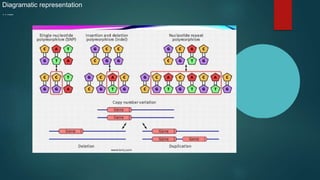
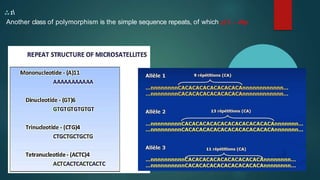
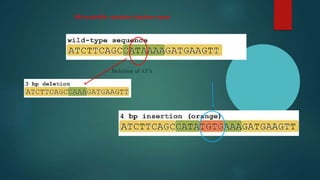
The document discusses genetic polymorphism, defined as the presence of multiple forms of a gene in a population, particularly when variations exceed 1% frequency. It explains the structure and function of chromosomes, mutations, and the various types of polymorphisms such as single nucleotide polymorphisms and insertion-deletion polymorphisms. Key examples include the ABO blood group system and the HLA system, highlighting how genetic variations influence traits and biological functions in humans.