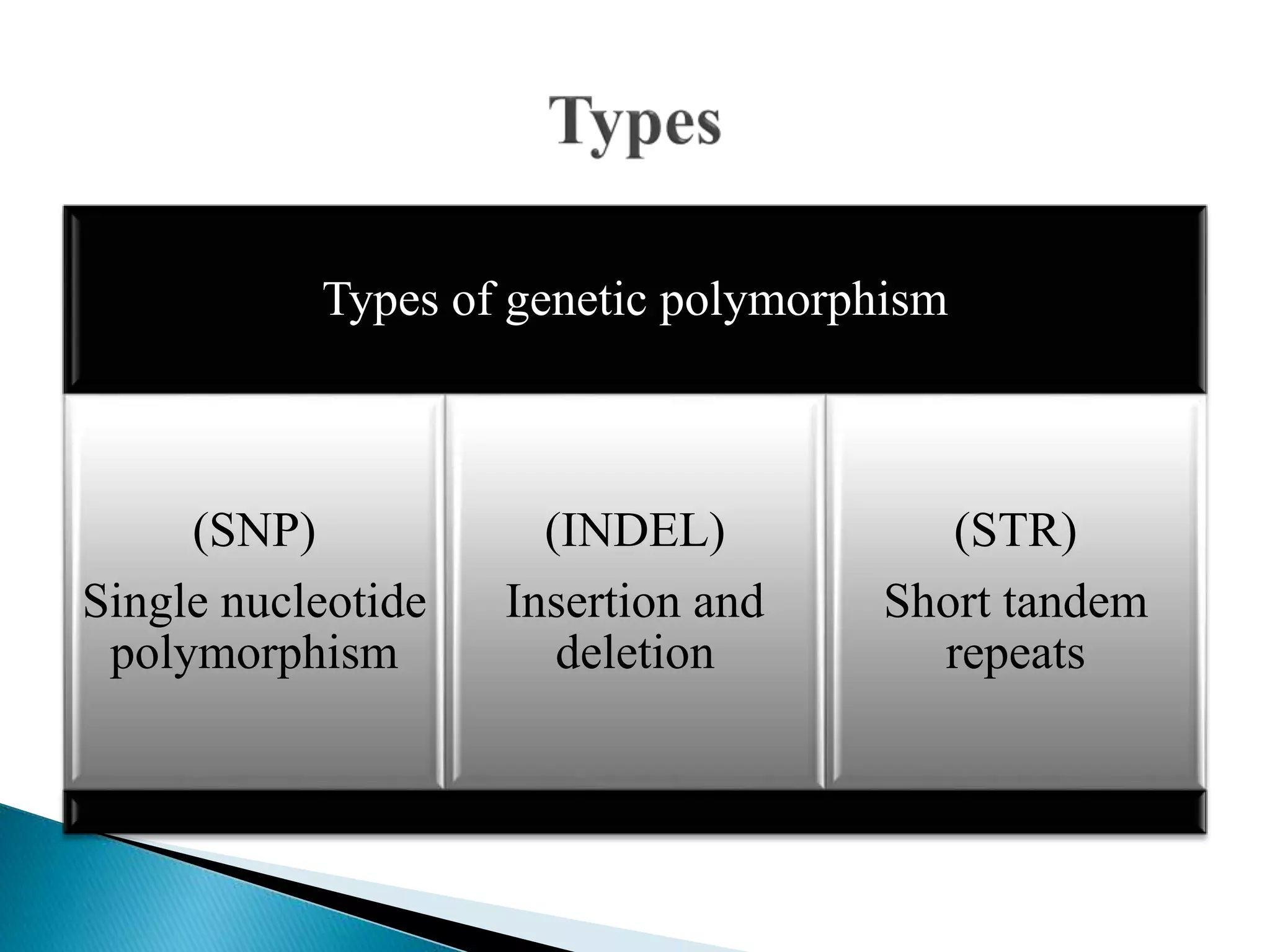
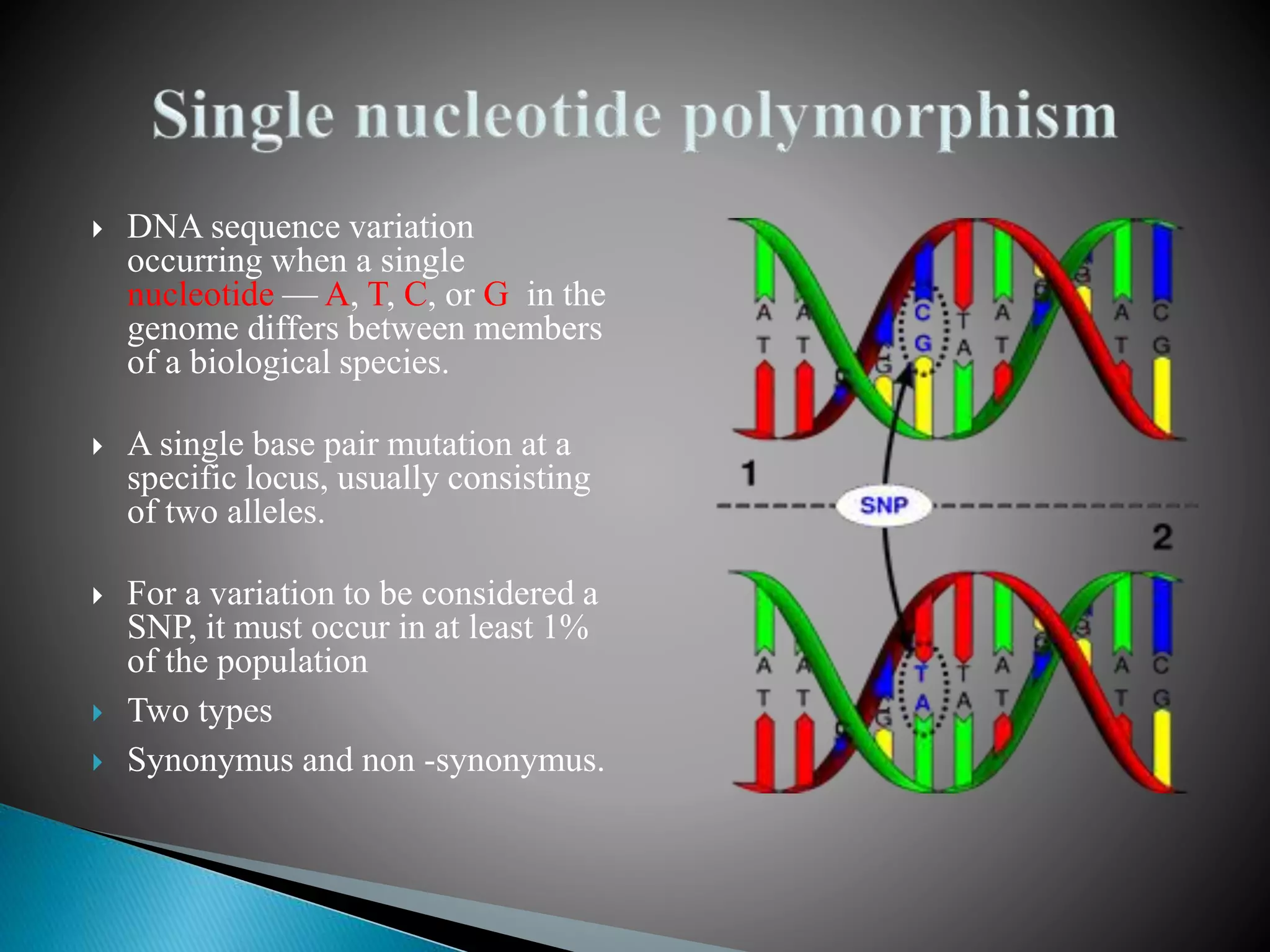
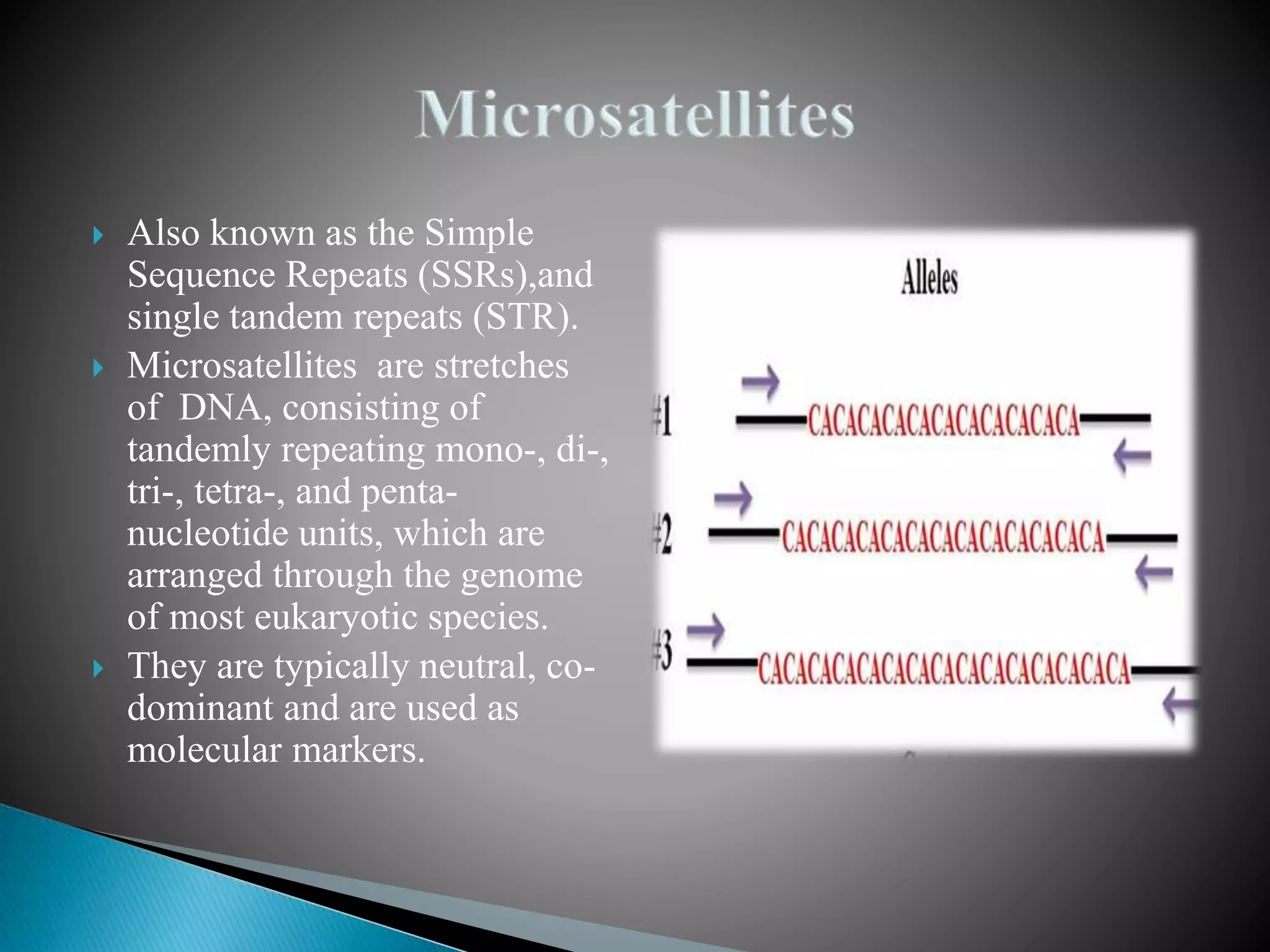
The document discusses genetic polymorphisms in Plasmodium falciparum, the parasite that causes malaria. It defines key terms like locus, allele, and genome. It then describes different types of genetic polymorphisms like single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), insertions and deletions (INDELs), and short tandem repeats (STRs). The document focuses on polymorphisms related to drug resistance in P. falciparum, discussing genes associated with resistance to chloroquine (pfcrt) and other antimalarial drugs, along with specific mutations in those genes linked to resistance.