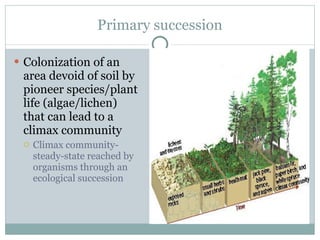
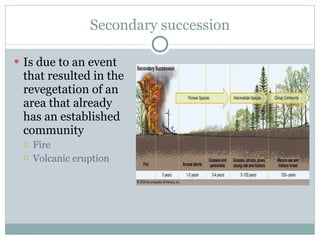
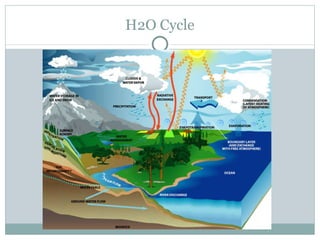
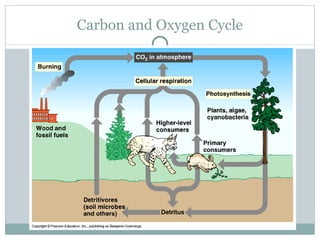
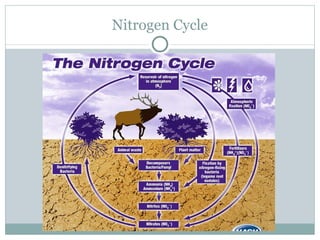
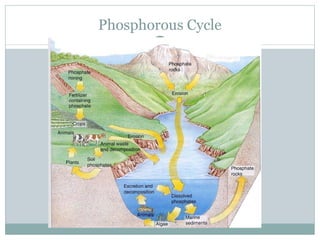
This document provides an introduction to key concepts in ecology, including biomes, ecological niches, succession, energy and biomass pyramids, and nutrient cycles. It defines ecology as the study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment. It also describes the main biomes like tundra, taiga, grasslands, and rainforests. Primary and secondary succession are discussed as ways communities develop over time.