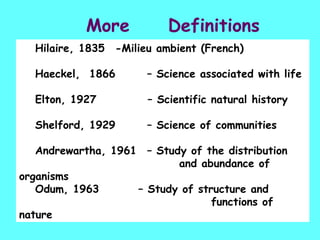
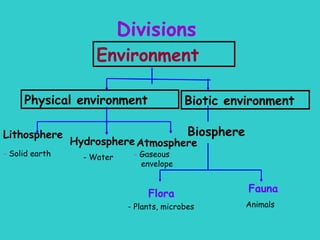
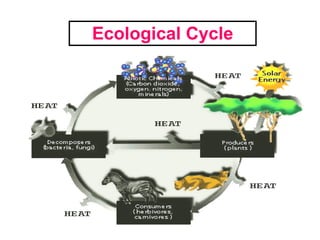
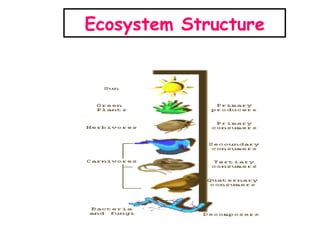
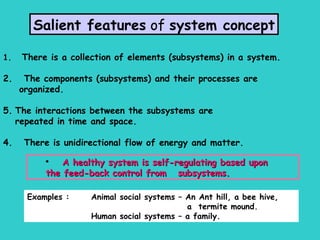
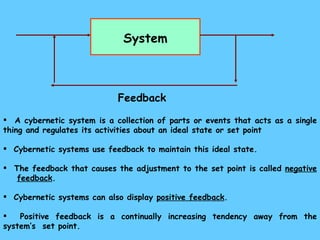
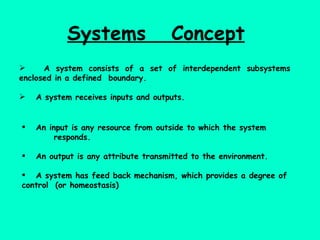
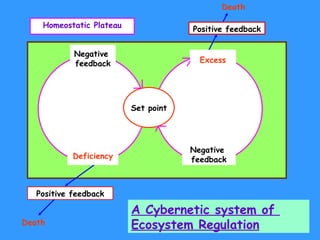
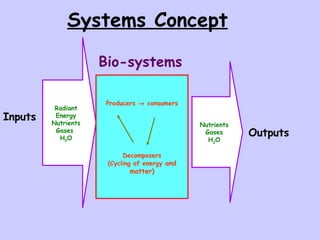
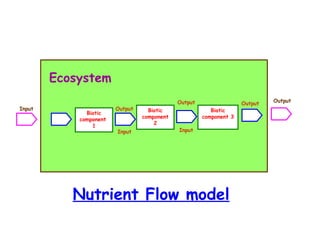
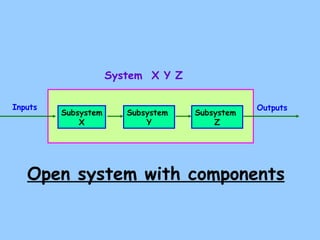
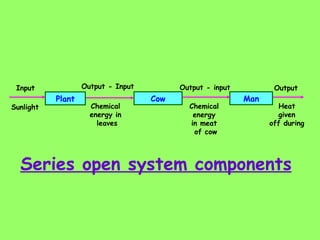
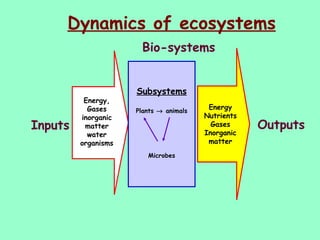
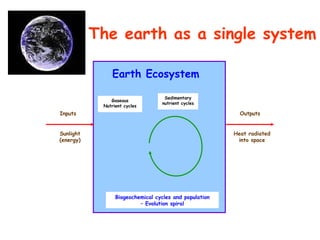
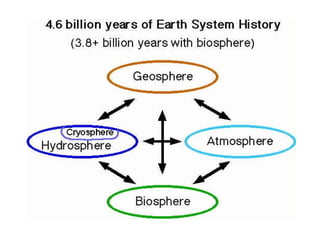
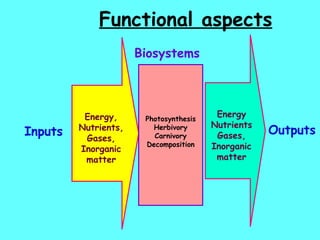
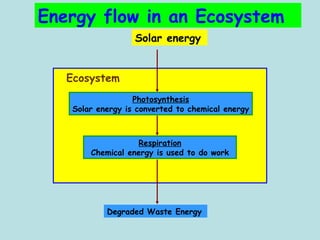
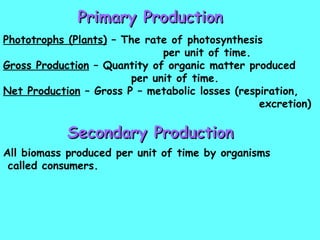
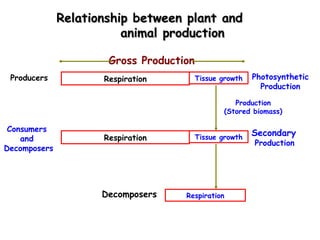
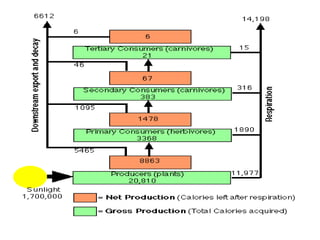
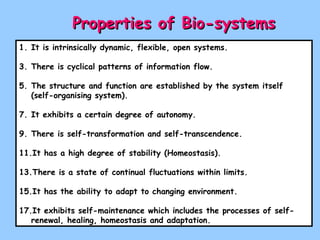
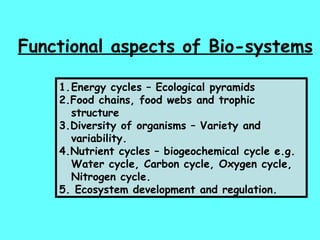
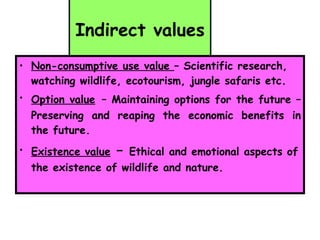
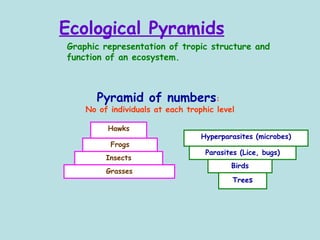
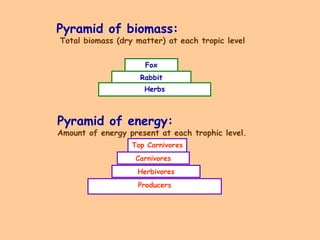
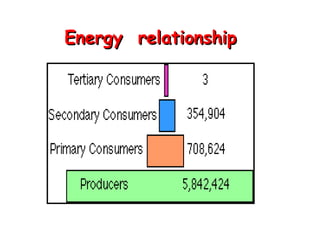
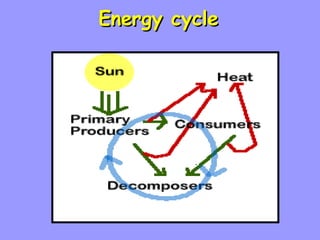
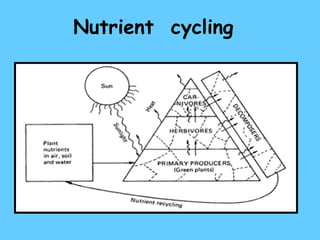
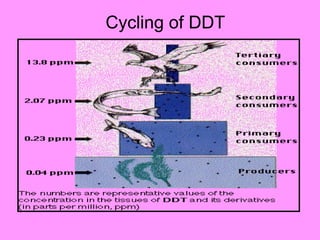
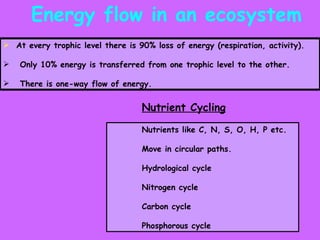
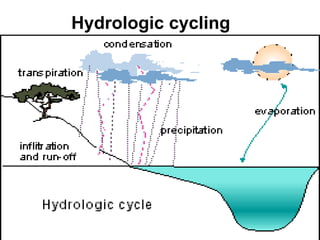
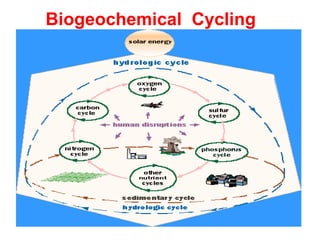
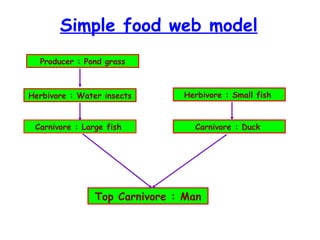
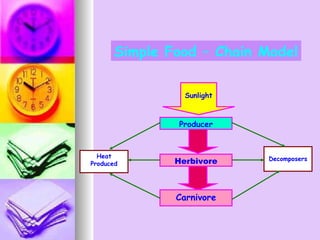
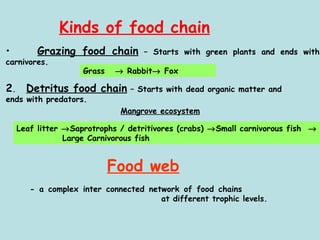
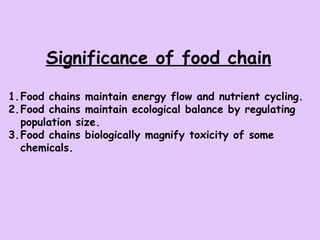
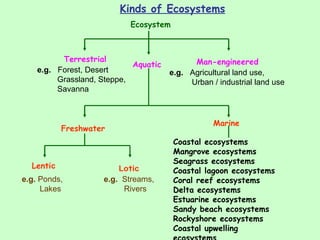
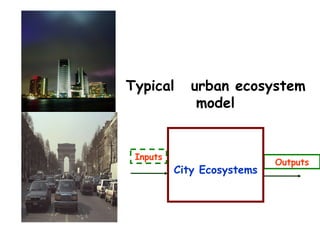
The document defines ecology as the scientific study of the interaction between living organisms and their environment. It discusses key concepts in ecology like ecosystems, biotic and abiotic components, energy flow, nutrient cycling, and trophic structure. Some key types of ecosystems mentioned are forests, grasslands, deserts, aquatic, urban, and agricultural ecosystems.