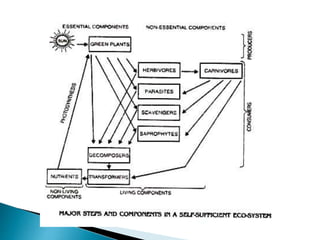
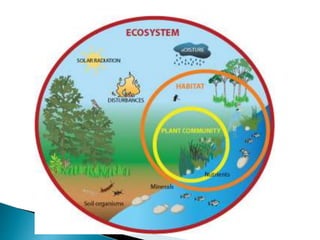
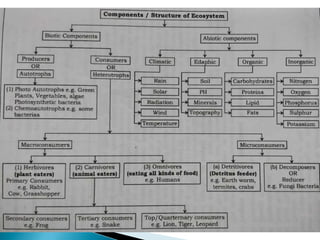
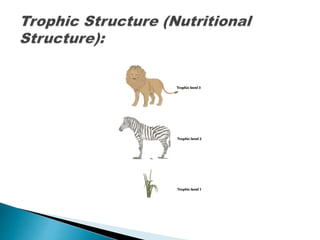
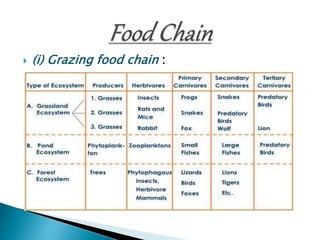
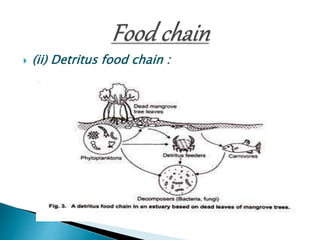
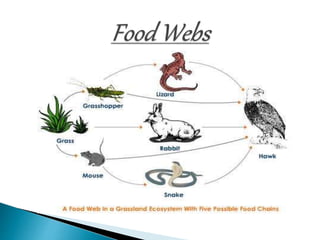
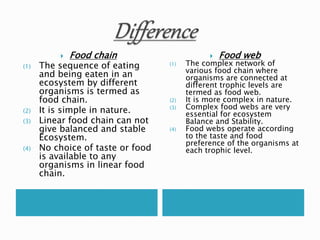
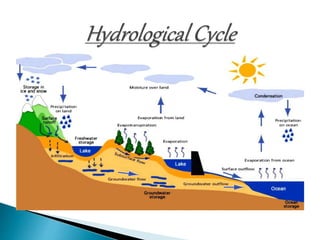
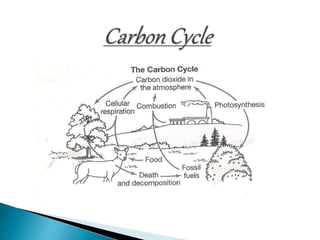
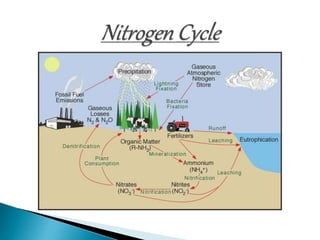
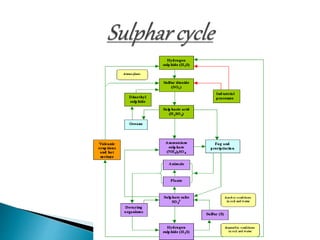
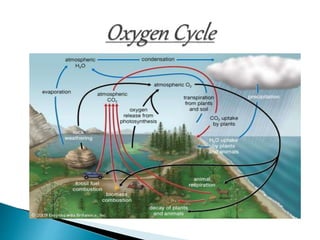
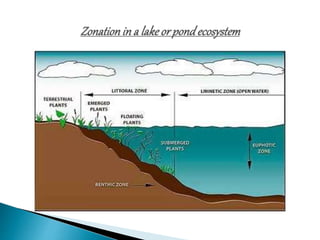
The document defines ecology and describes various ecological concepts and components. Ecology is defined as the scientific study of the interactions between organisms and their physical environment. It discusses the components of different ecosystems including producers, consumers, decomposers and their interactions through food chains, food webs and nutrient cycles. Major ecosystem types described are forests, grasslands, deserts, freshwater and marine systems.