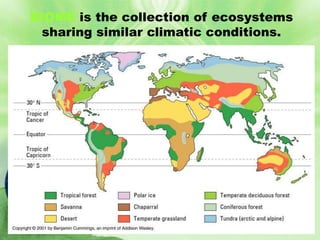
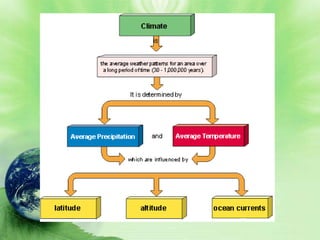
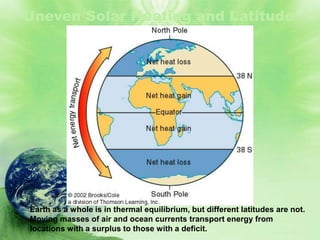
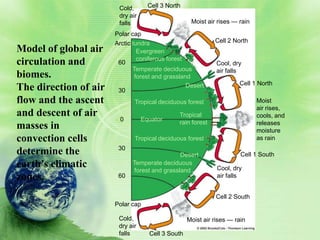
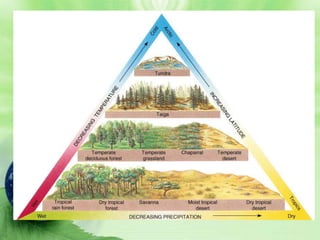
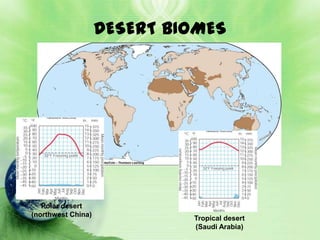
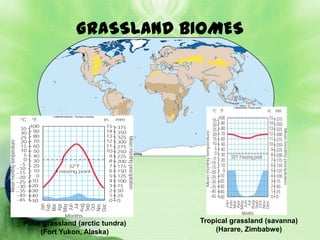
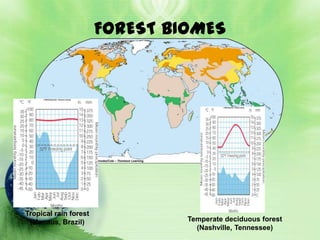
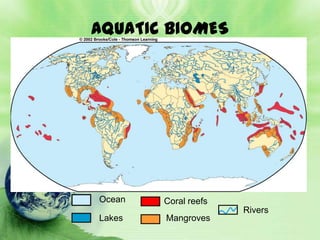
1. Biomes are defined as large regions with similar climates and ecological communities. The main biomes include tundra, taiga, temperate rainforest, temperate deciduous forest, grasslands, deserts, and tropical rainforests.
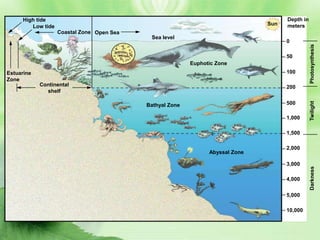
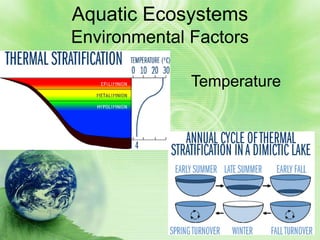
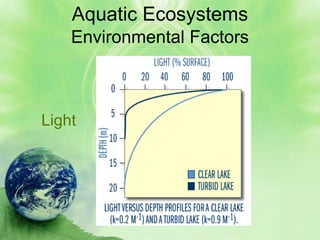
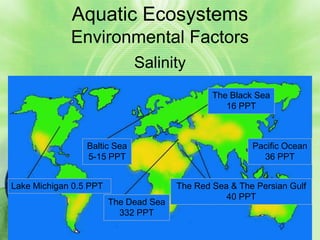
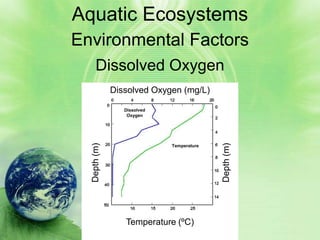
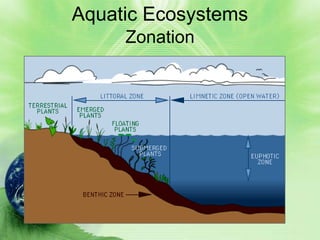
2. Aquatic ecosystems are influenced by environmental factors like temperature, light, salinity, currents, dissolved oxygen, and depth. They can be divided into zones based on these factors.
3. Human impacts on aquatic ecosystems include contamination from pharmaceuticals and agricultural runoff carrying fertilizers and traces of antibiotics into waterways.