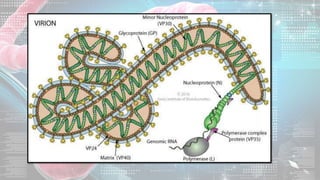
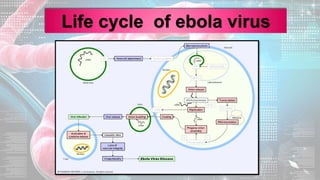
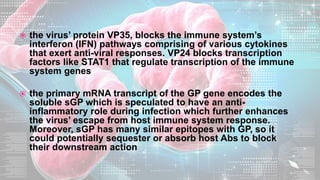
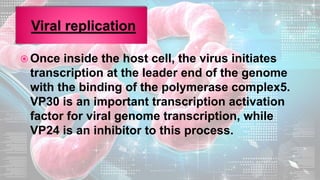
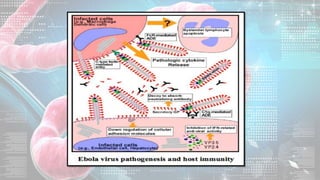
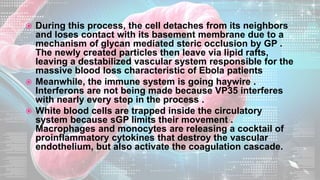
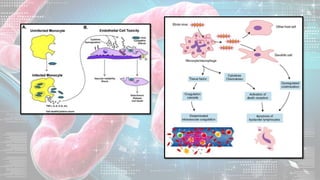
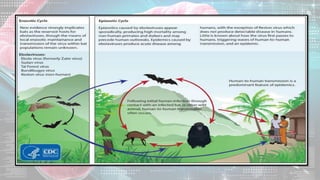
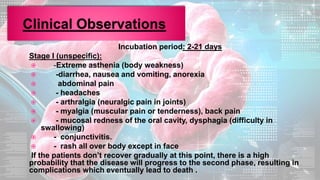
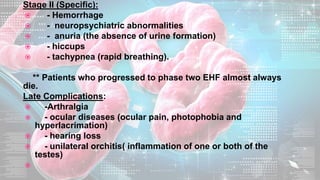
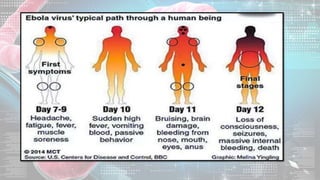
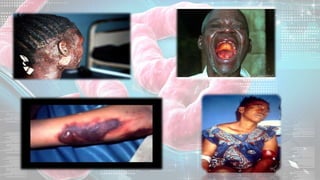
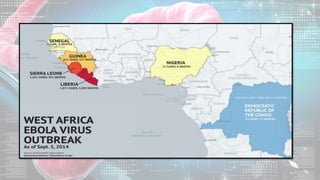
This document summarizes information about the Ebola virus, including its characterization, life cycle, transmission, symptoms, outbreaks, treatment and prevention. It describes Ebola virus as a filamentous, enveloped RNA virus that infects monocytes, macrophages and other immune cells. It evades the host immune system and causes hemorrhagic fever through mechanisms such as blocking interferon response. The largest Ebola outbreak occurred in West Africa from 2013-2016. Treatment involves general medical support and isolation, while prevention focuses on avoiding contact with patients, proper PPE and animal surveillance.