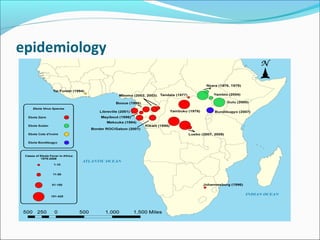
Ebola virus was first isolated in 1976 and is one of the world's most deadly diseases. It has a fatality rate over 90% and outbreaks primarily occur in tropical areas of central and west Africa. There is no approved vaccine or treatment. Transmission occurs via contact with infected animals, fluids, or needles. Health professionals are at risk when treating infected patients without proper protective equipment. Prevention focuses on isolation, protective equipment, hand hygiene, and avoiding contact with infected individuals or animals.