Embed presentation
Downloaded 58 times
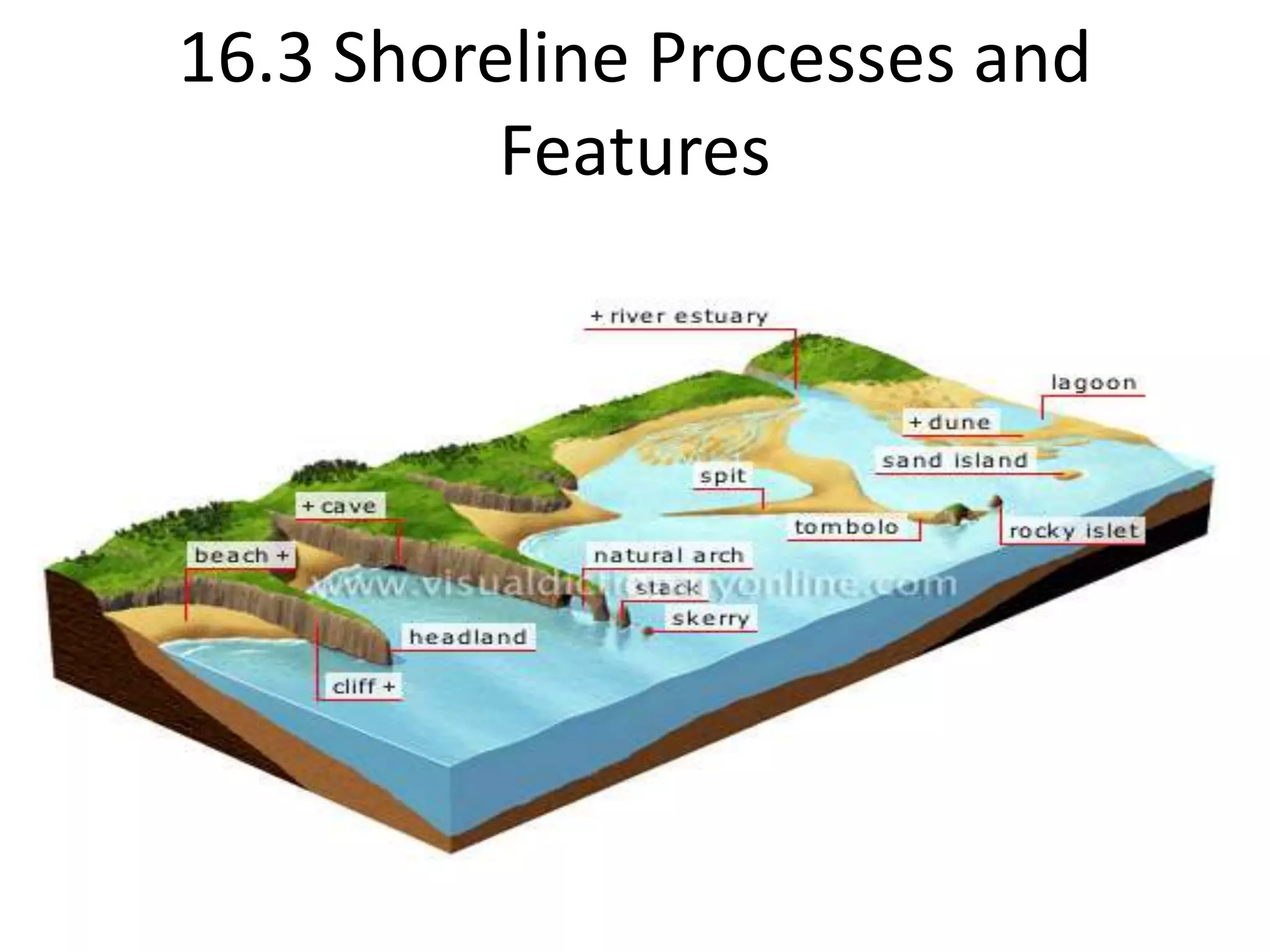

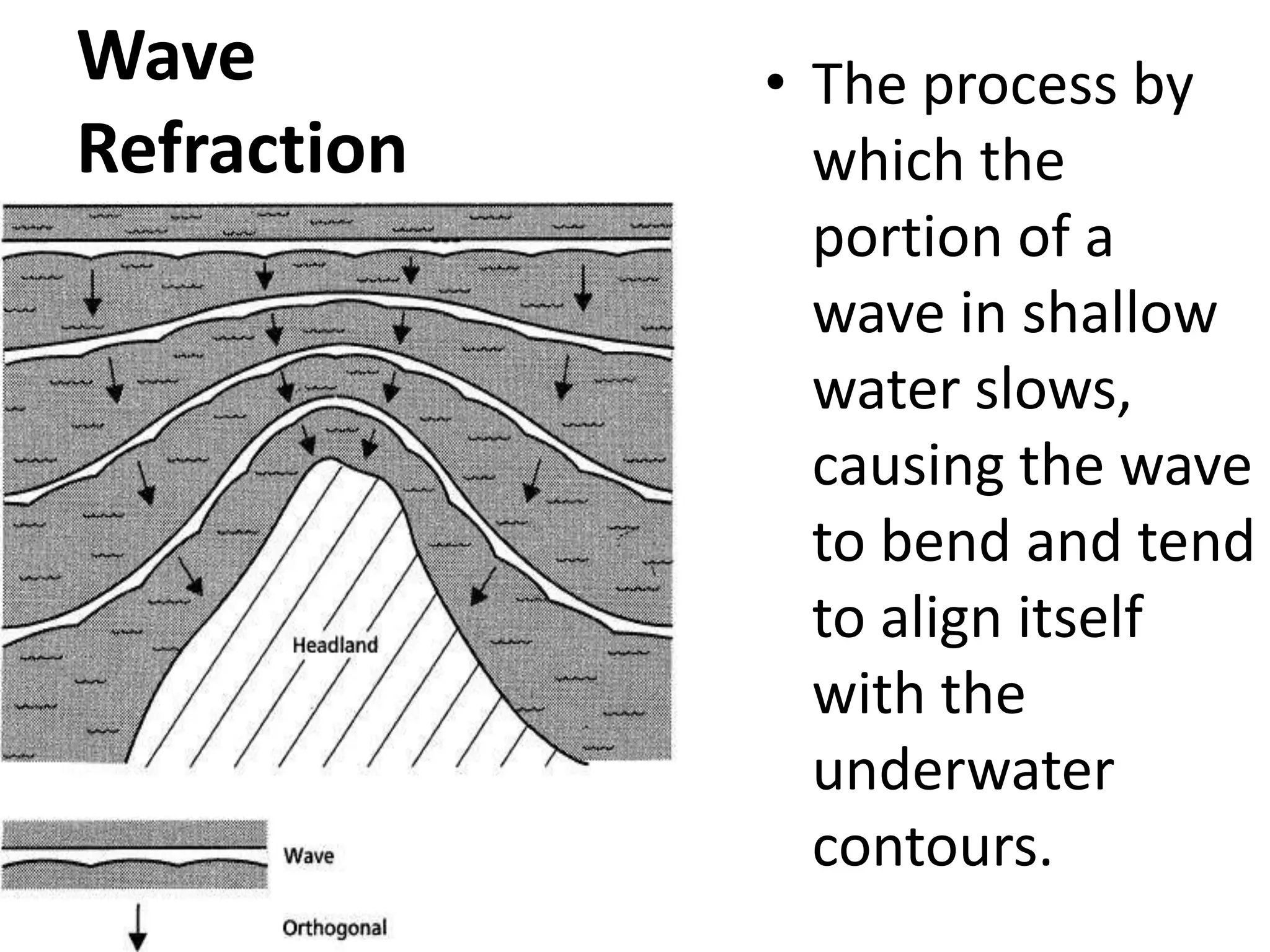
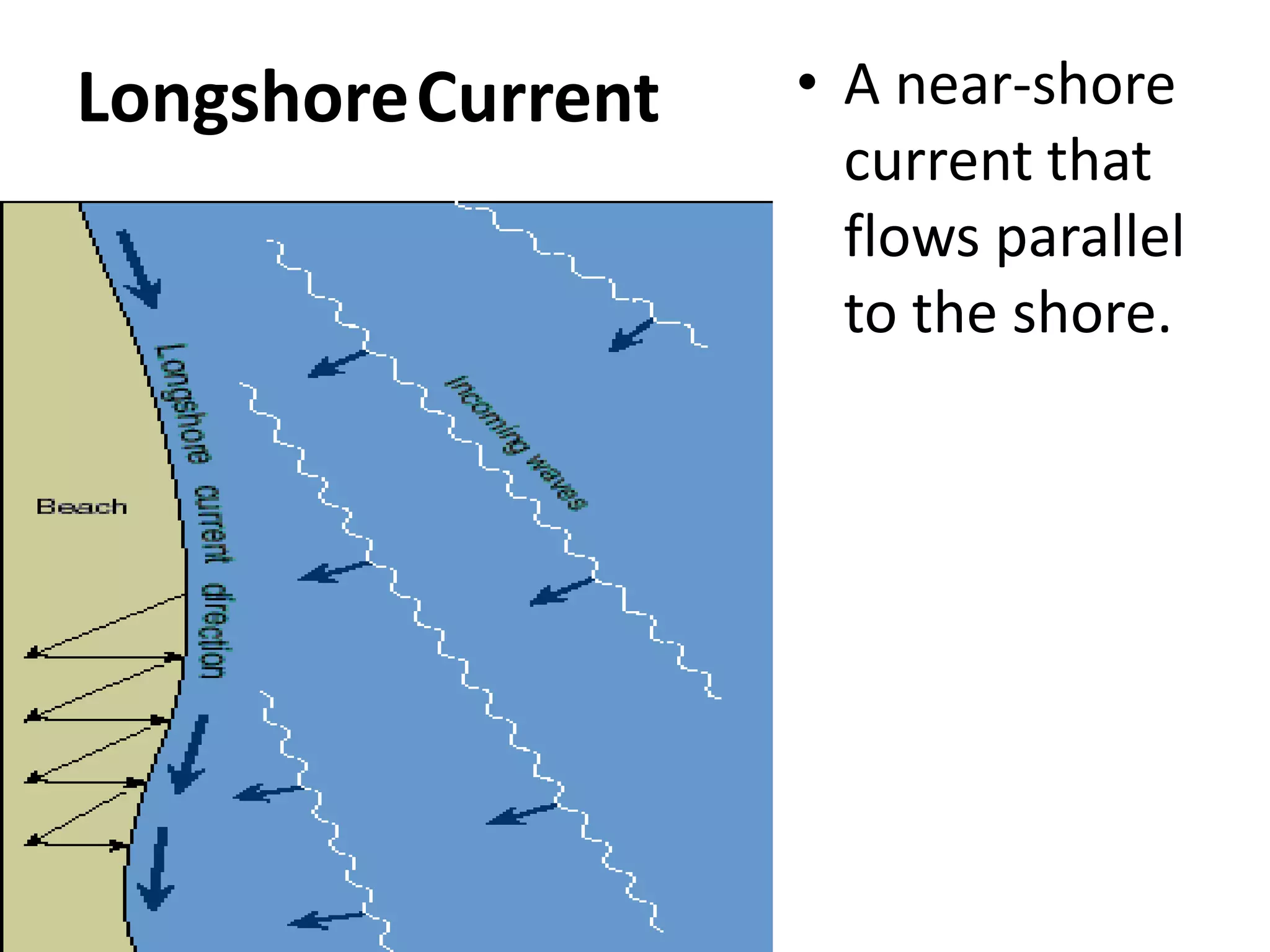
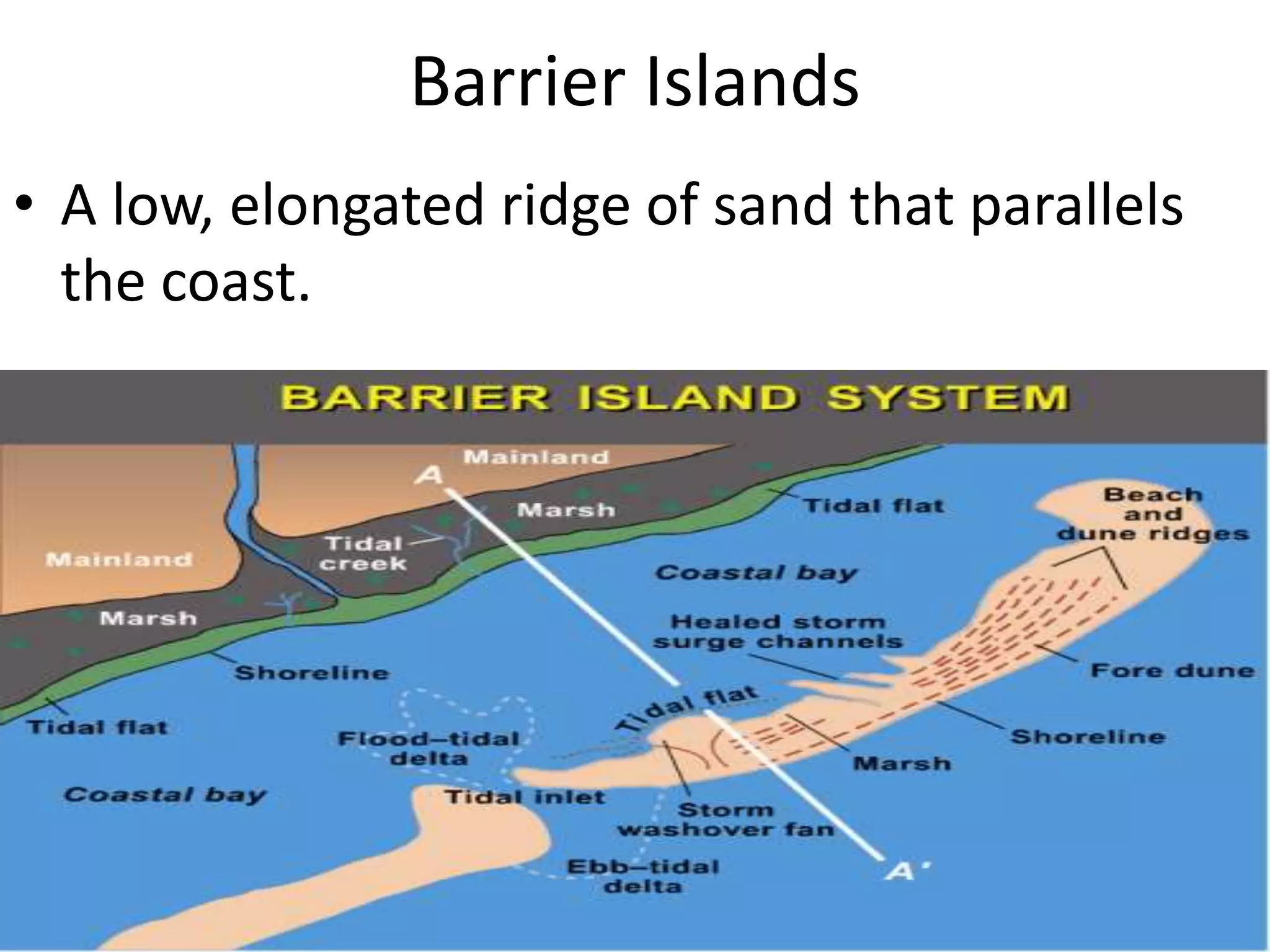






Waves erode, transport, and deposit sediments along shorelines, forming features like beaches and barrier islands. Wave refraction causes waves to bend and concentrate energy against headlands and shores, while weakening in bays. Longshore currents flow parallel to shore and are driven by waves, moving sediments such as sand and gravel along the coast. Shoreline features are either erosional, formed by erosion, or depositional, formed by sediment deposition in low-energy areas. Structures like groins, breakwaters, and seawalls can protect shorelines from erosion. Beach nourishment involves adding large amounts of sand to beaches.










