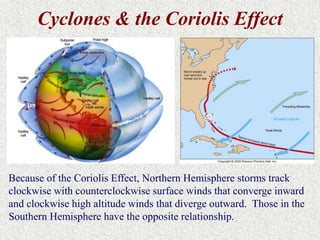
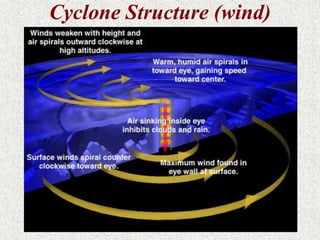
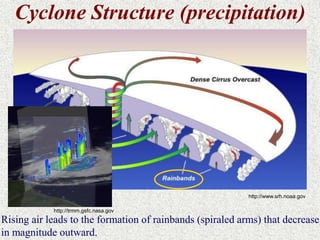
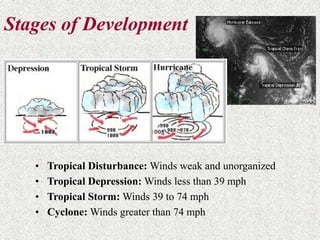
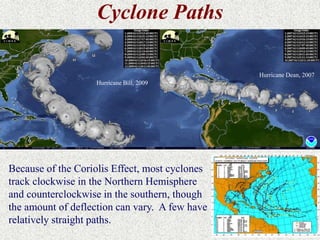
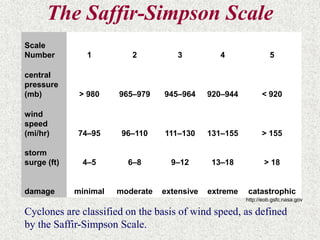
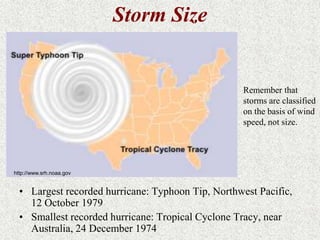
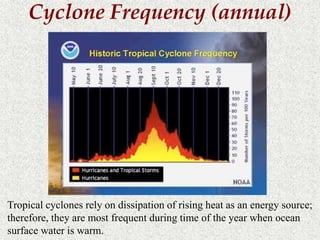
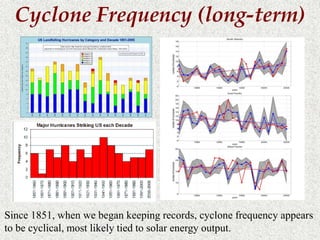
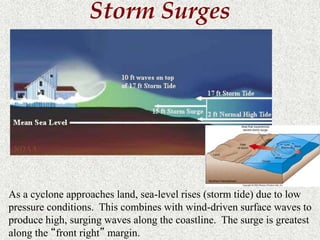
Cyclones are rotating storms characterized by inward spiraling winds surrounding a center of low pressure. They form over warm ocean waters when air rises and condenses. Due to the Coriolis effect, cyclones in the Northern Hemisphere rotate clockwise and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere. Cyclones can have devastating effects through high winds, heavy rain, storm surges, flooding, and tornadoes. They are classified based on wind speed scales like the Saffir-Simpson scale. Regional names like hurricanes and typhoons are used depending on ocean basins.