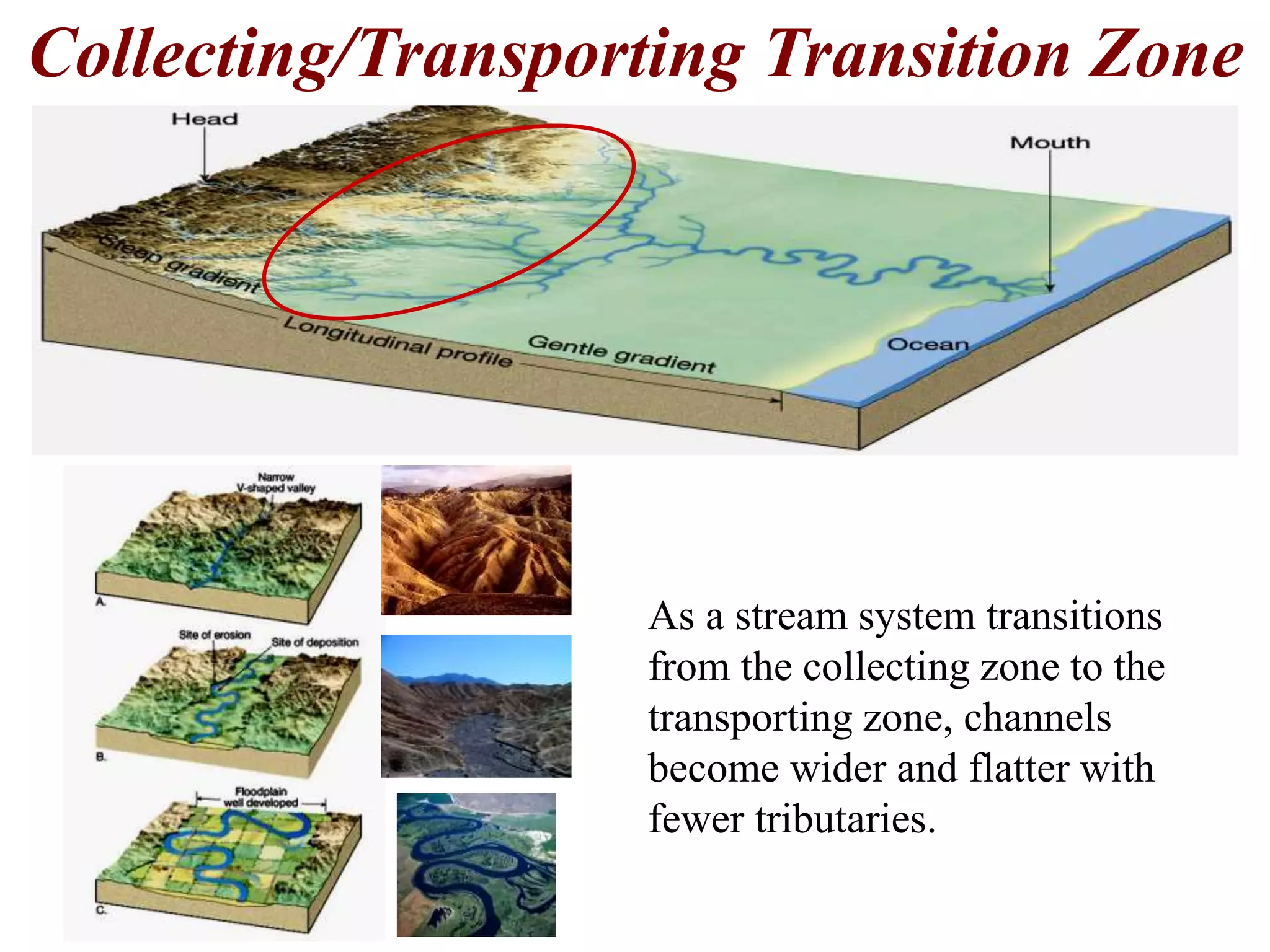
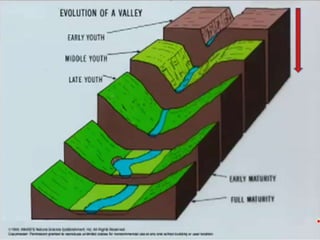
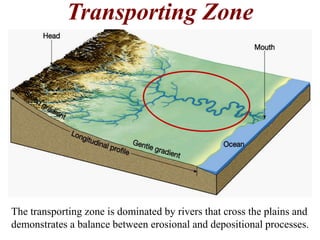
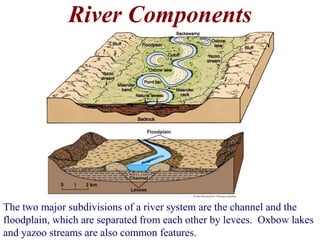
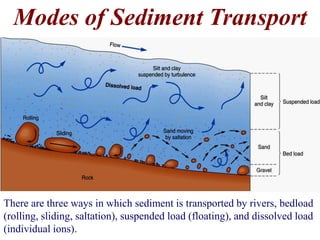
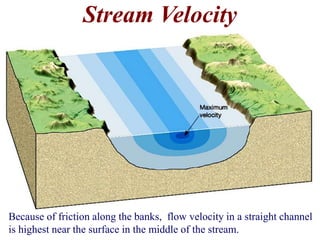
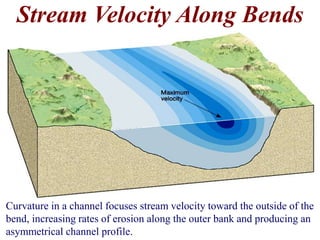
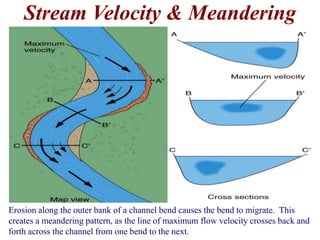
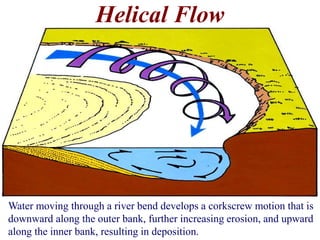
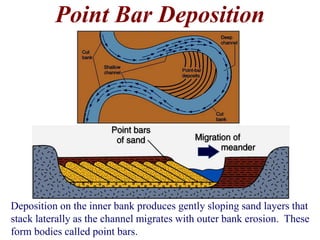
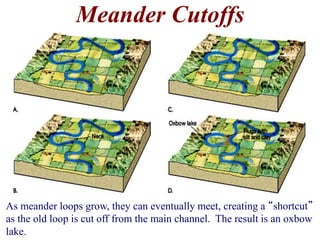
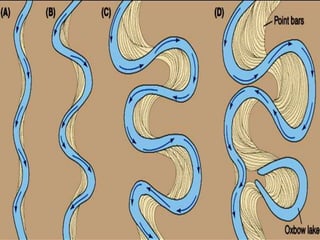
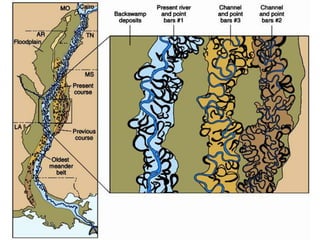
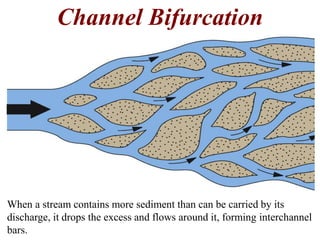
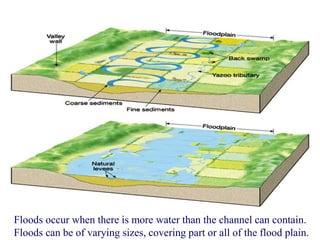
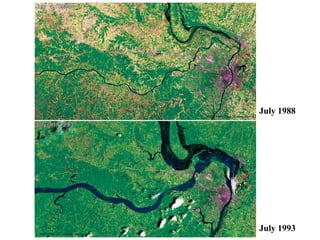
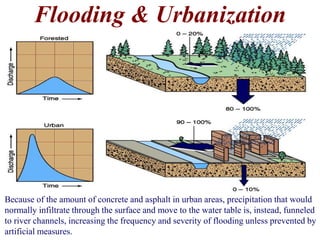
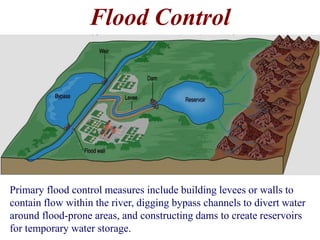
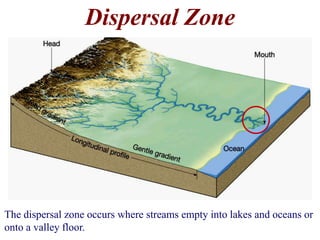
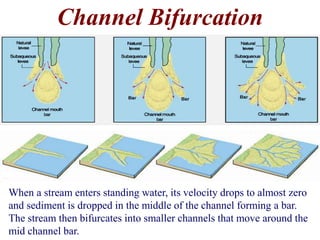
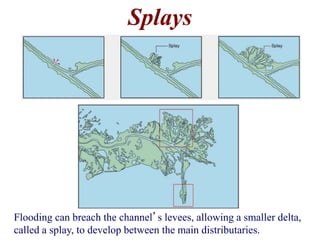
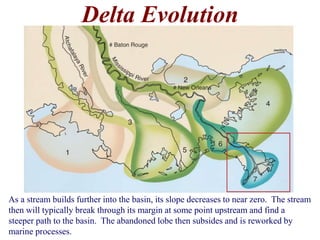
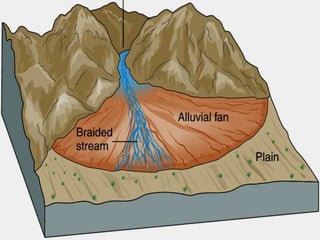
The document summarizes key aspects of river systems and their transport of sediment. It describes how rivers transition from steep mountain headwaters to flatter plains, carrying sediment in various modes of transport. It also discusses characteristics of meandering and braided rivers, and how river channels migrate and deposit sediment in point bars and during floods. The document concludes by outlining features that form as rivers enter standing bodies of water, such as deltas, alluvial fans, and fan-deltas.