Embed presentation
Downloaded 10 times

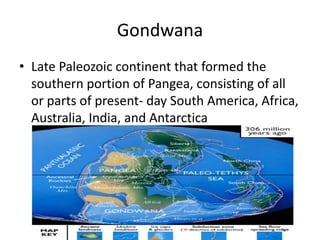







The Paleozoic Era saw an explosion of life, as the continents of Gondwana and Laurasia formed most of the southern and northern portions of the supercontinent Pangea. During the Cambrian, Ordovician, and Silurian periods, life was restricted to the seas surrounding Gondwana, which contained the continents of present-day South America, Africa, Australia, Antarctica, and parts of Asia. By the end of the Paleozoic Era, around 400 million years ago, all continents had fused into the single landmass of Pangea, and plants first began moving from waterside habitats onto land.








