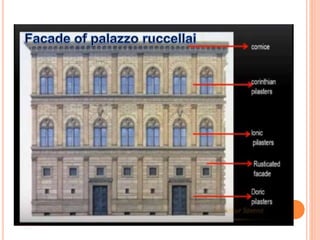
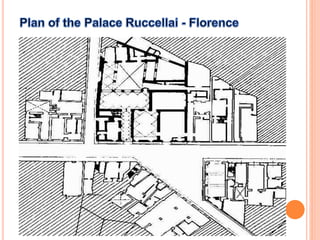
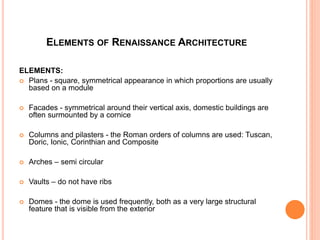
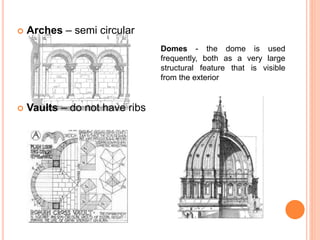
The early Renaissance began in the 15th century in Florence, marked by the contributions of Leon Battista Alberti, a pivotal figure who defined the role of the architect and revived Roman styles in architecture. Alberti's prominent works include 'Della Pittura' and 'De Re Aedificatoria', through which he influenced architectural theory and aesthetic standards. Key architectural elements of this period included the use of classical orders, balanced proportions, and innovative facade designs exemplified by structures like the Palazzo Ruccellai.