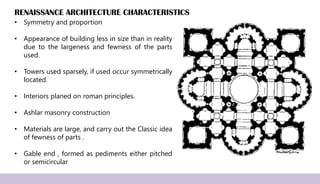
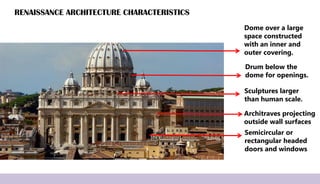
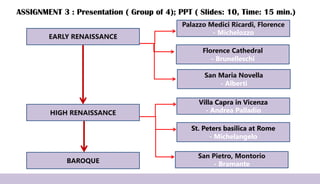
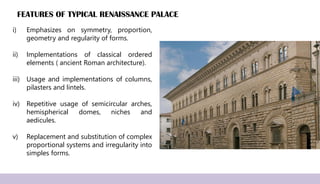
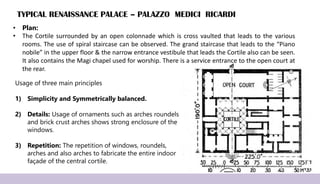
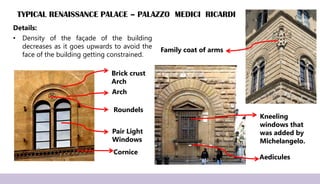
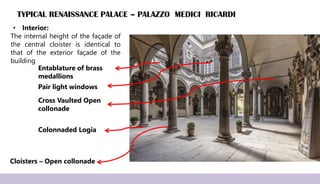
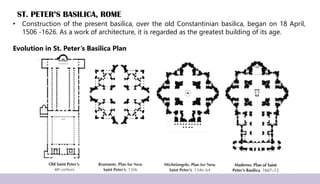
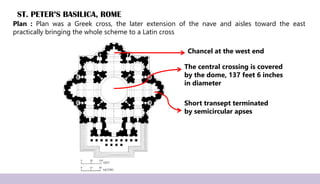
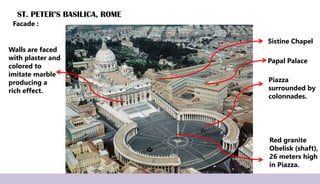
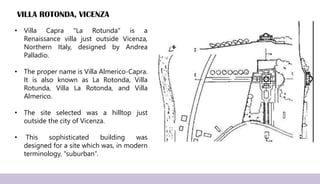
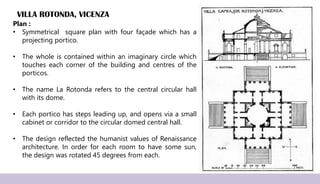
Renaissance architecture, spanning the 14th to 17th centuries, signifies a revival of classical Greek and Roman artistic achievements, initiated in Italy and supported by wealthy patrons. Key features include symmetry, proportion, and the integration of structure and decoration, characterized by iconic buildings such as St. Peter's Basilica and the Villa Rotonda. The movement evolved through phases, including the Early Renaissance, High Renaissance, and Baroque, each contributing to advancements in architectural style and technique.