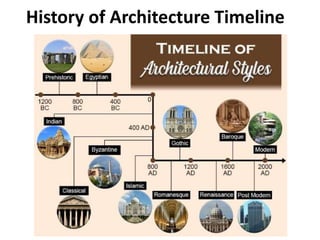
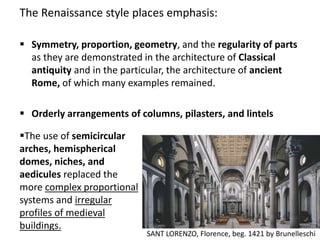
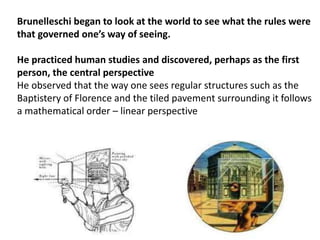
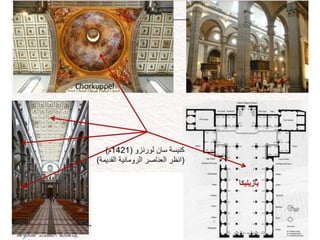
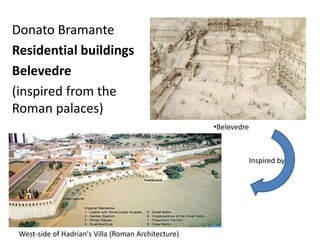
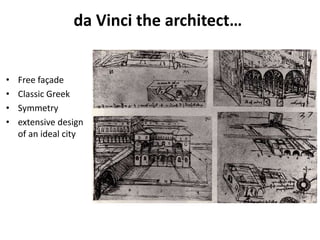
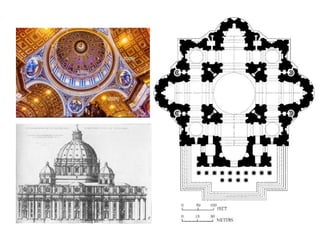
The document provides a timeline overview of architectural history from prehistoric to Renaissance periods. It begins with Prehistoric architecture such as Paleolithic, Mesolithic, and Neolithic structures. Next it discusses Early Mesopotamian, Ancient Egyptian, Classical Greek and Roman, Byzantine, Romanesque, and Gothic architectures. Key characteristics and prominent examples of each style are mentioned. The document then focuses on the Renaissance period, describing its origins, time periods of Early Renaissance, High Renaissance, and Mannerism. It highlights influential Renaissance architects like Brunelleschi, Bramante, Leonardo da Vinci, Raphael, Michelangelo, Palladio and their major works.