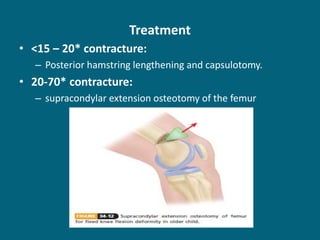
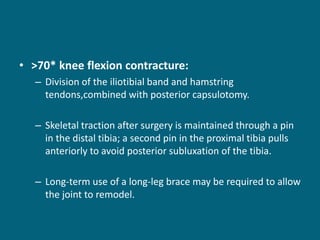
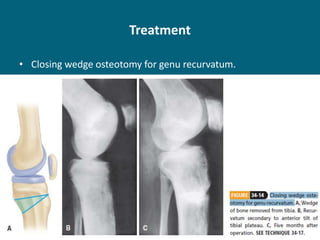
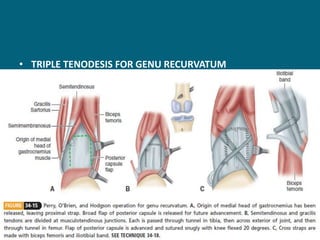
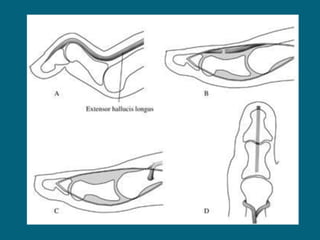
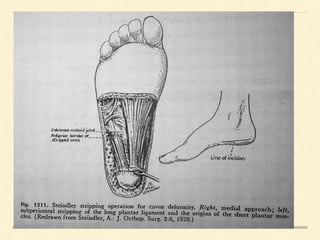
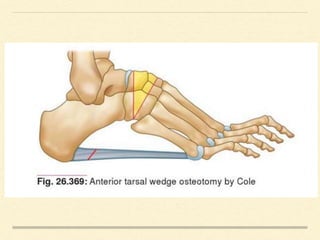
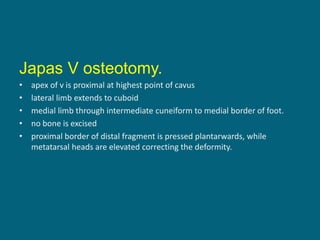
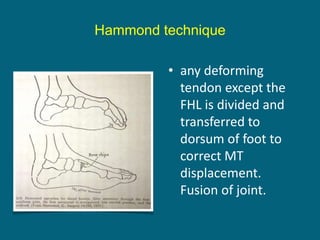
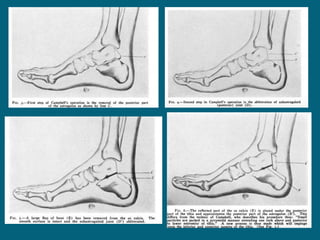
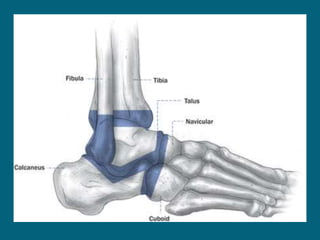
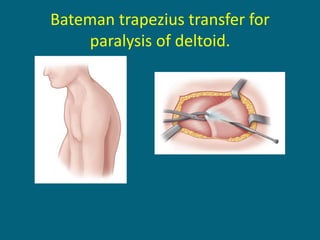
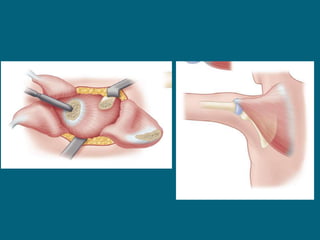
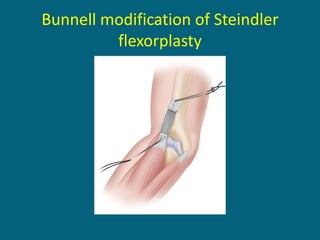
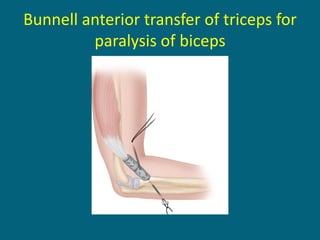
The document discusses post-polio residual paralysis, including:
1. It provides historical context on polio and describes the etymology and pathology of the virus.
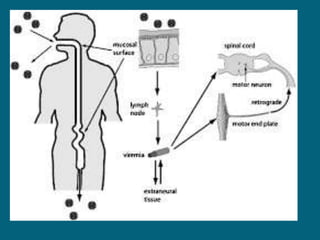
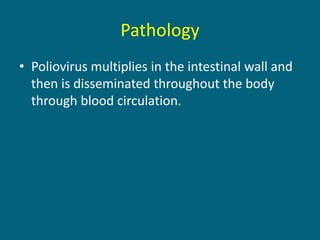
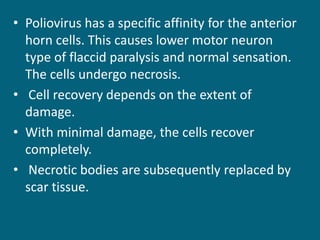
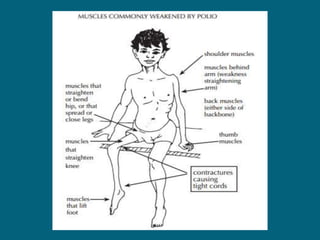
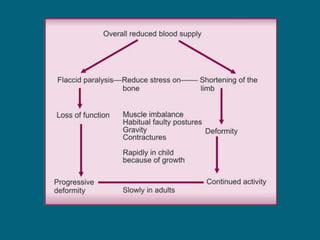
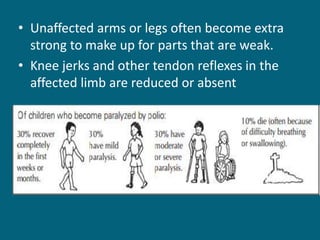
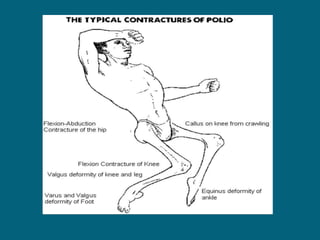
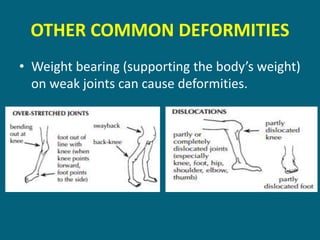
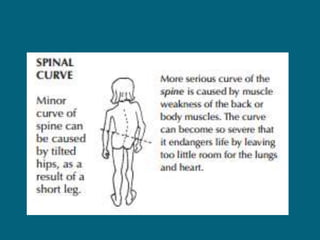
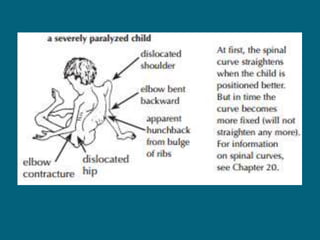
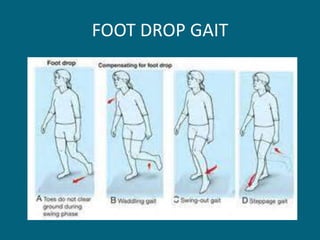
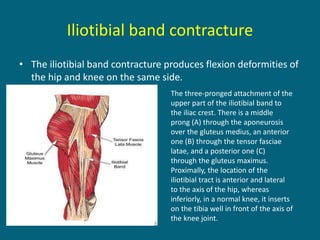
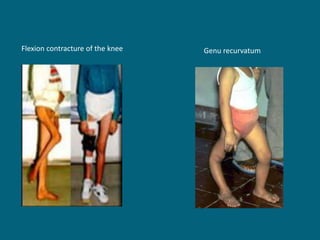
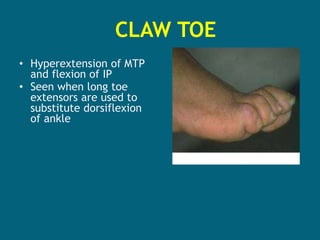
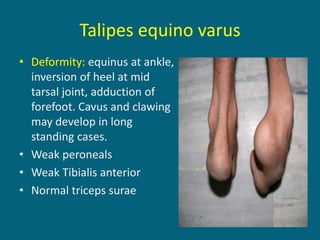
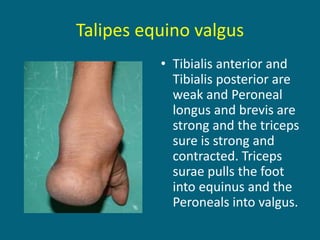
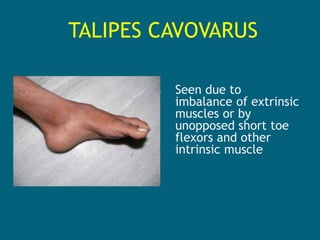
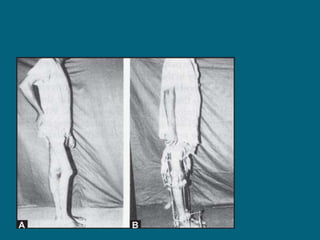
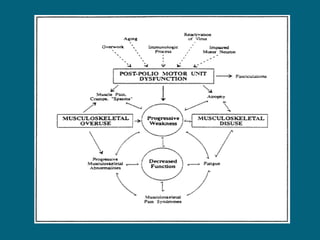
2. Poliovirus attacks the anterior horn cells of the spinal cord, causing flaccid paralysis. This can lead to progressive muscle imbalance and deformities over time if left untreated.
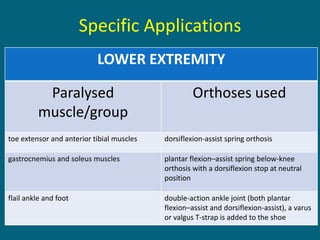
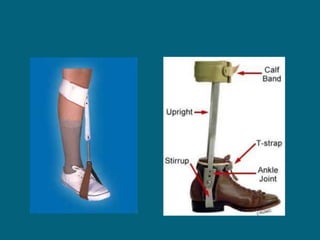
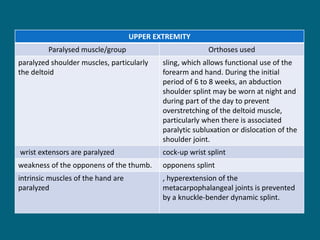
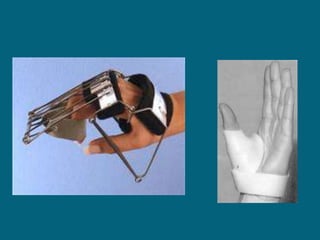
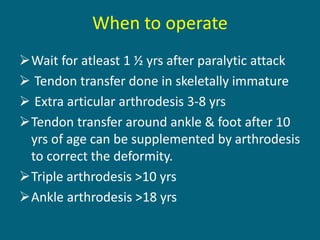
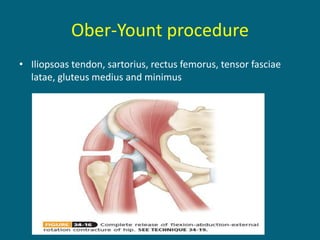
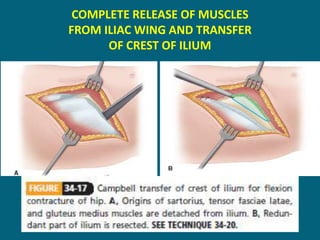
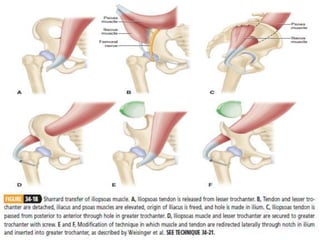
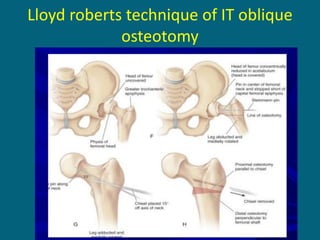
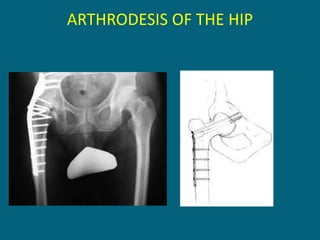
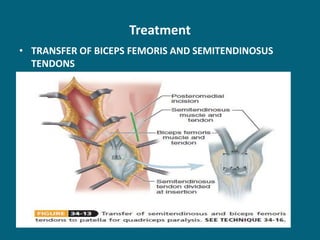
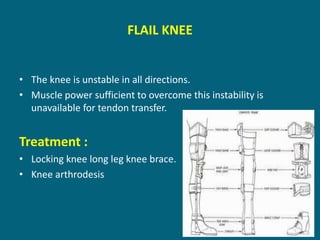
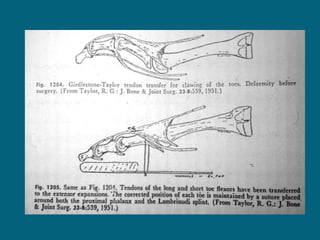
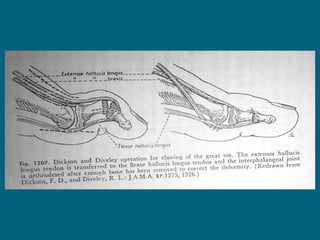
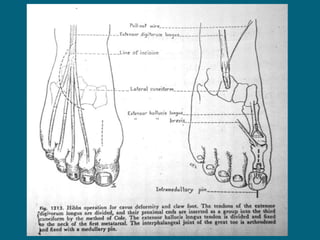
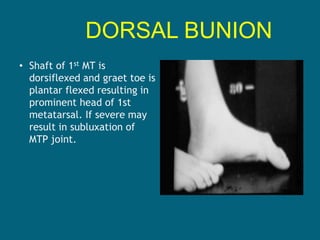
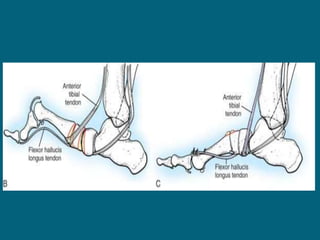
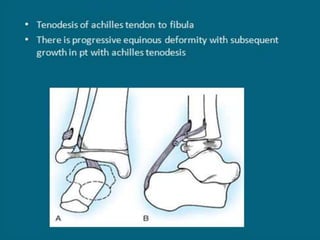
3. Management focuses on strengthening unaffected muscles, stretching shortened muscles, exercises to maintain range of motion, orthotics and bracing, and surgery to correct severe deformities. The goal is maximizing recovery and function.