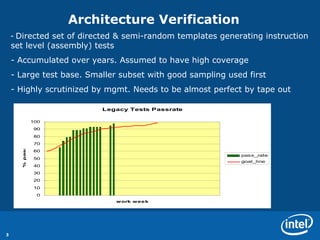
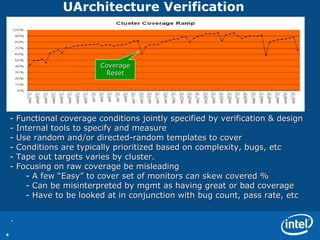
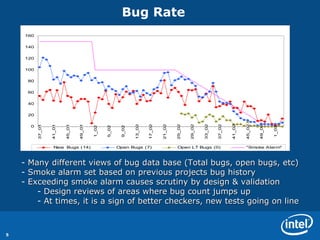
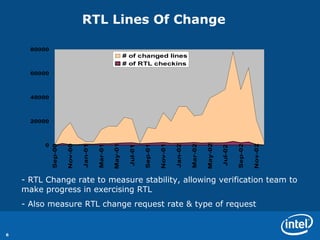
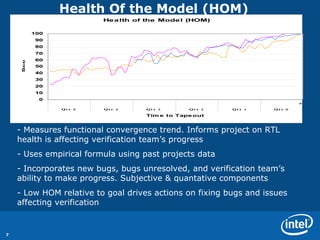
The document discusses various metrics used to measure CPU verification progress including architectural verification, uArchitecture verification, formal verification, and system level verification. It outlines metrics such as functional coverage conditions, bug rates, RTL lines of change, and a health of the model score. Secondary metrics include cycles run, licenses used, and bugs caught at different levels.