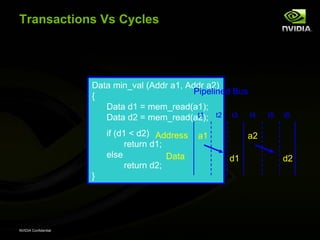
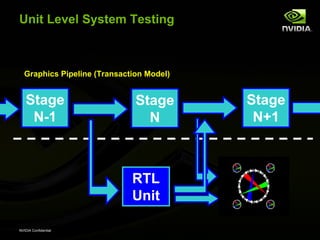
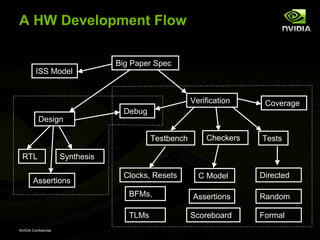
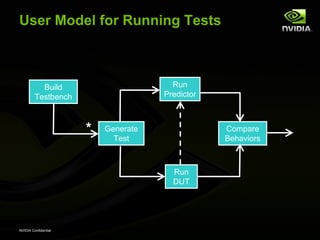
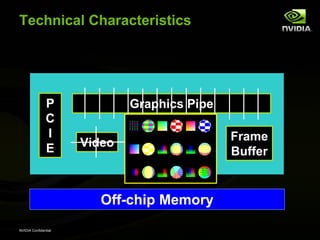
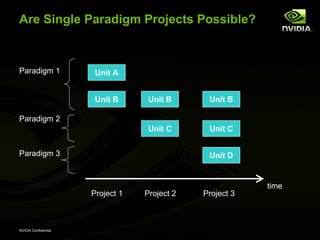
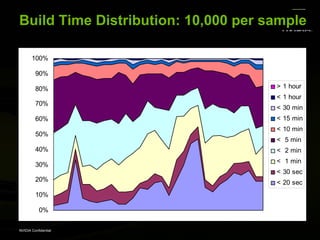
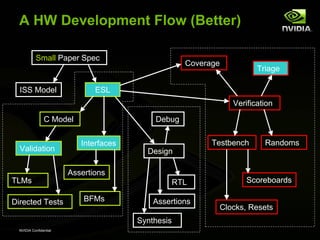
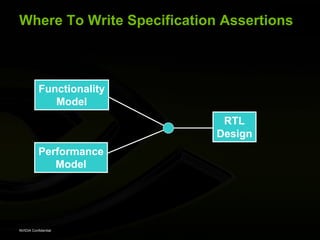
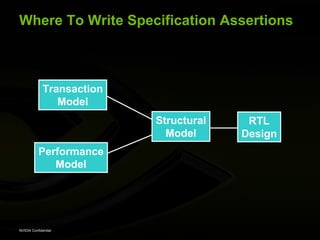
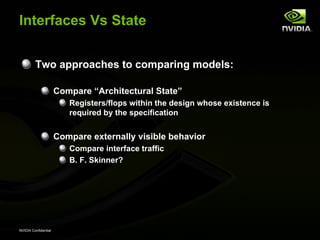
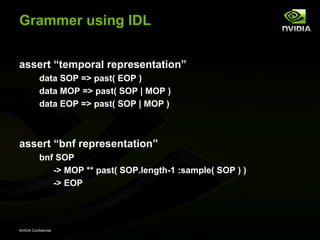
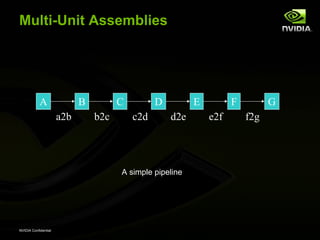
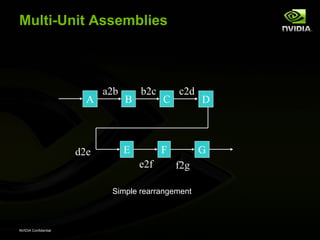
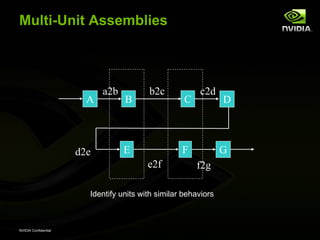
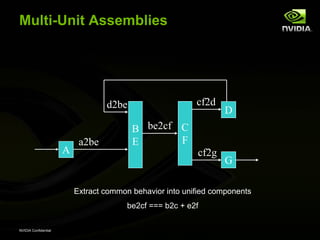
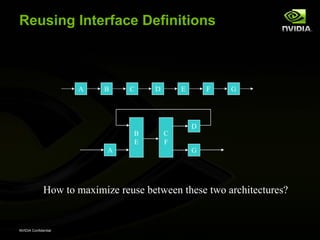
The document discusses efficient verification methodology. It recommends defining a conceptual framework or methodology to standardize some aspects while allowing diversity. The methodology should define interfaces and transactions upfront using an interface definition language to generate verification components and reusable assertions. It also recommends modeling systems at the transaction level using executable specifications to frontload the verification schedule.






















![Cycle Level Assertions in SVA
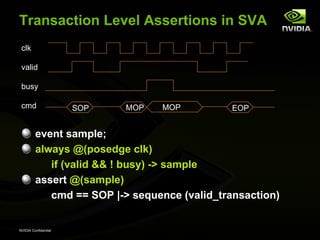
clk
cmd SOP MOP MOP EOP
sequence valid_trans;
(cmd==SOP)
(##1 cmd != SOP && cmd != EOP) [*0:$]
##1 cmd == EOP
endsequence
a_well_formed_transaction: assert @(posedge clk)
cmd == SOP |-> sequence (valid_trans)
NVIDIA Confidential](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whippq32008sv-100716225142-phpapp02/85/Whipp-q3-2008_sv-35-320.jpg)
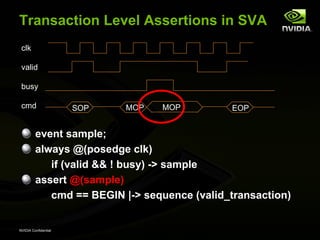
![Transaction Level Assertions in SVA
clk
valid
cmd SOP MOP MOP EOP
sequence valid_transaction;
(cmd==SOP)
(##1 cmd != SOP && cmd != EOP) [*0:$]
##1 cmd == EOP
endsequence
NVIDIA Confidential](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whippq32008sv-100716225142-phpapp02/85/Whipp-q3-2008_sv-36-320.jpg)



![Accumulate Memory State
group mem_write
down U address 16
down U data 1
assign mem[ x = 0 .. 15 ][ y = 0 .. 15 ]
= past( data :sample( address == {x,y} ))
NVIDIA Confidential](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whippq32008sv-100716225142-phpapp02/85/Whipp-q3-2008_sv-49-320.jpg)
![Add Predicates
group_more mem_write
assign is_circle[ r = 0..7 ] = “&&”(
[ x = -8 .. 7 ]
[ y = -8 .. 7 ]
mem[ x+8 ][ y+8 ] == ( x**2 + y**2 <= r**2 )
)
NVIDIA Confidential](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whippq32008sv-100716225142-phpapp02/85/Whipp-q3-2008_sv-50-320.jpg)
![Define the interface
interface render2memory
clock mem_clk
flow valid_busy
packet sync, mem_write
assert “correct sync shape”
sync && sync.shape == CIRCLE
=> past( mem_write.is_circle[ sync.radius ] )
NVIDIA Confidential](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whippq32008sv-100716225142-phpapp02/85/Whipp-q3-2008_sv-51-320.jpg)
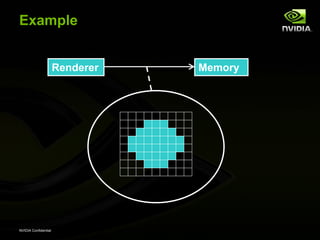
![Example
Renderer Memory
assert “correct sync shape”
sync && sync.shape == CIRCLE
=> past( mem_write.is_circle[ sync.radius ] )
NVIDIA Confidential](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whippq32008sv-100716225142-phpapp02/85/Whipp-q3-2008_sv-52-320.jpg)