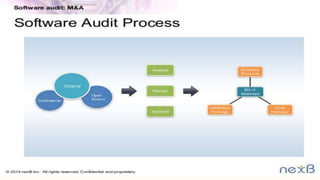
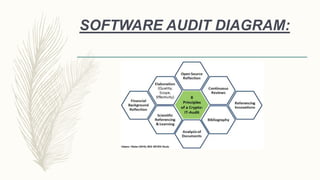
This document discusses software audits, including an overview of the software audit process and its significance. A software audit is an independent examination of a software product, process, or set of processes to assess compliance. It describes the typical participants in an audit, such as the initiator, lead auditor, and audited organization. The document also covers the types of audits, purposes of audits, principles of audits, steps involved, and top audit software products.