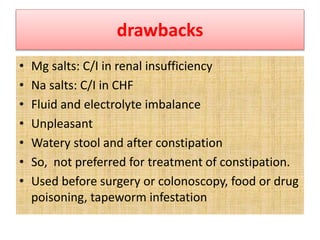
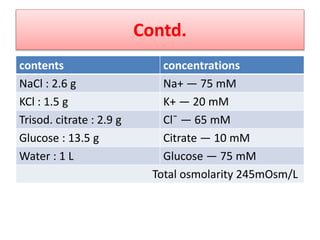
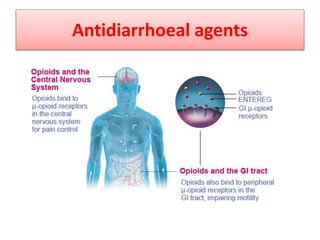
This document discusses the pharmacotherapy of constipation and diarrhea. It describes the pathophysiology, causes, and non-pharmacological approaches for constipation. For pharmacological treatment, it classifies laxatives into bulk forming, stool softeners, osmotic, and stimulant laxatives. Specific drugs are discussed within each class including their mechanisms of action, dosages, and side effects. For diarrhea, it covers rehydration therapy using oral rehydration solution and zinc supplementation in pediatrics. It also discusses when antimicrobial therapy is appropriate for infectious causes of diarrhea.