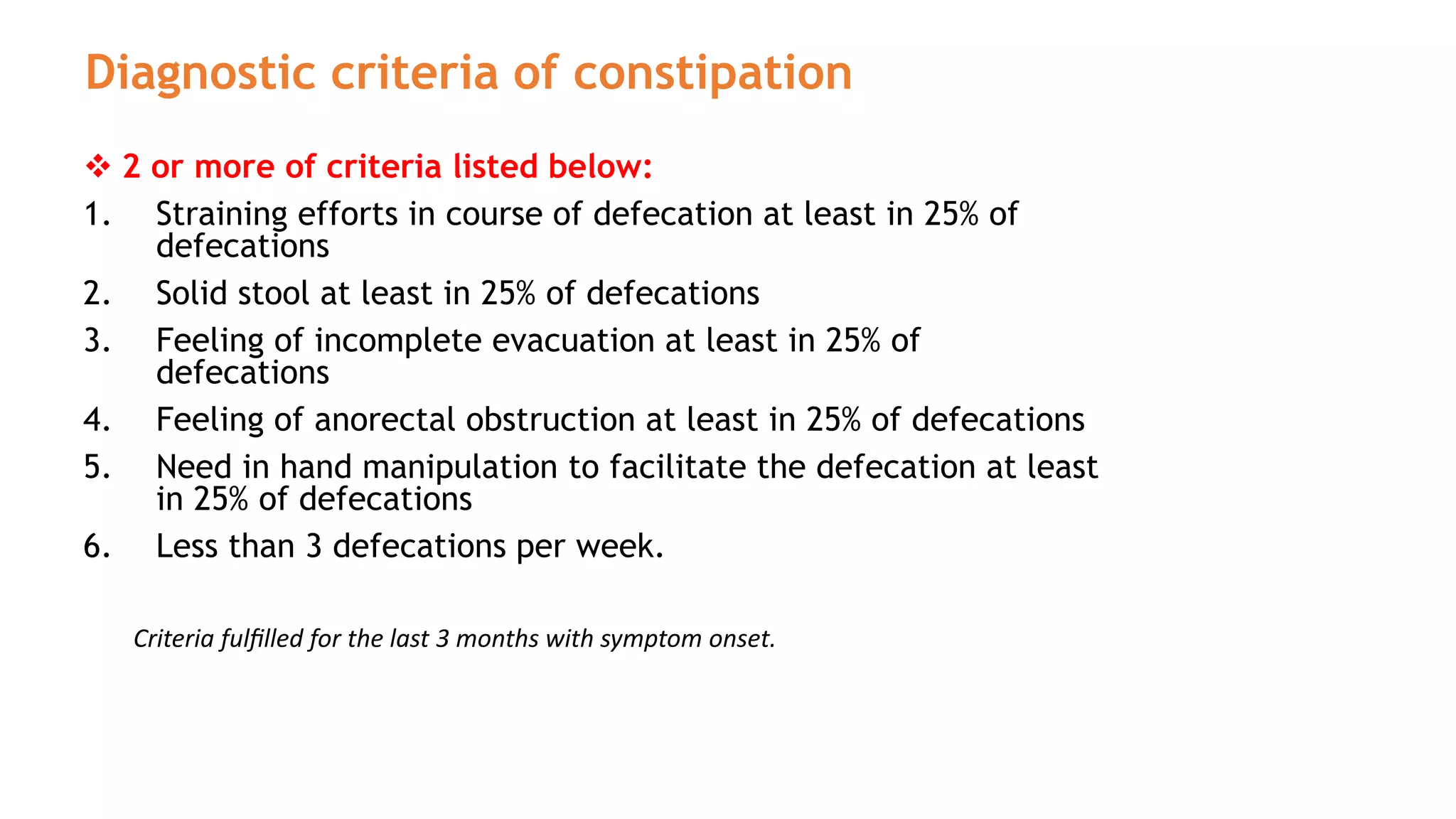
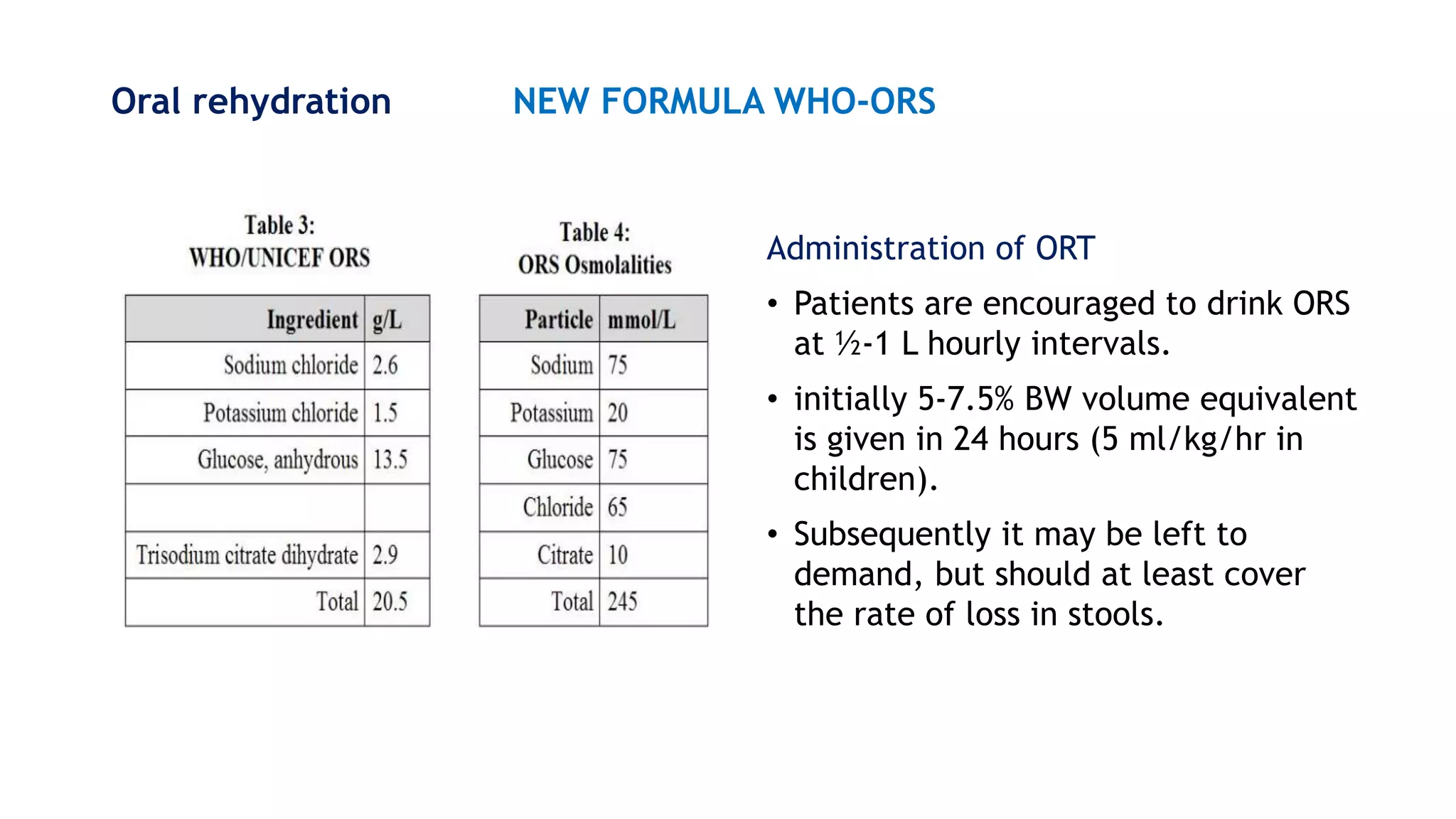
Constipation is a common complaint defined as infrequent bowel movements and difficult bowel movements. The Rome III criteria are used to diagnose chronic constipation. Constipation can be primary/functional with no clear cause or secondary due to causes like immobility, diet, medical conditions, or medications. Management involves lifestyle changes and laxatives. Laxatives are classified as bulk forming, stool softeners, stimulant purgatives, or osmotic purgatives. Bulk forming laxatives like bran and psyllium work by increasing stool bulk while osmotic laxatives like lactulose work by retaining fluid in the intestines. Diarrhea is defined as 3 or more loose stools per day and can