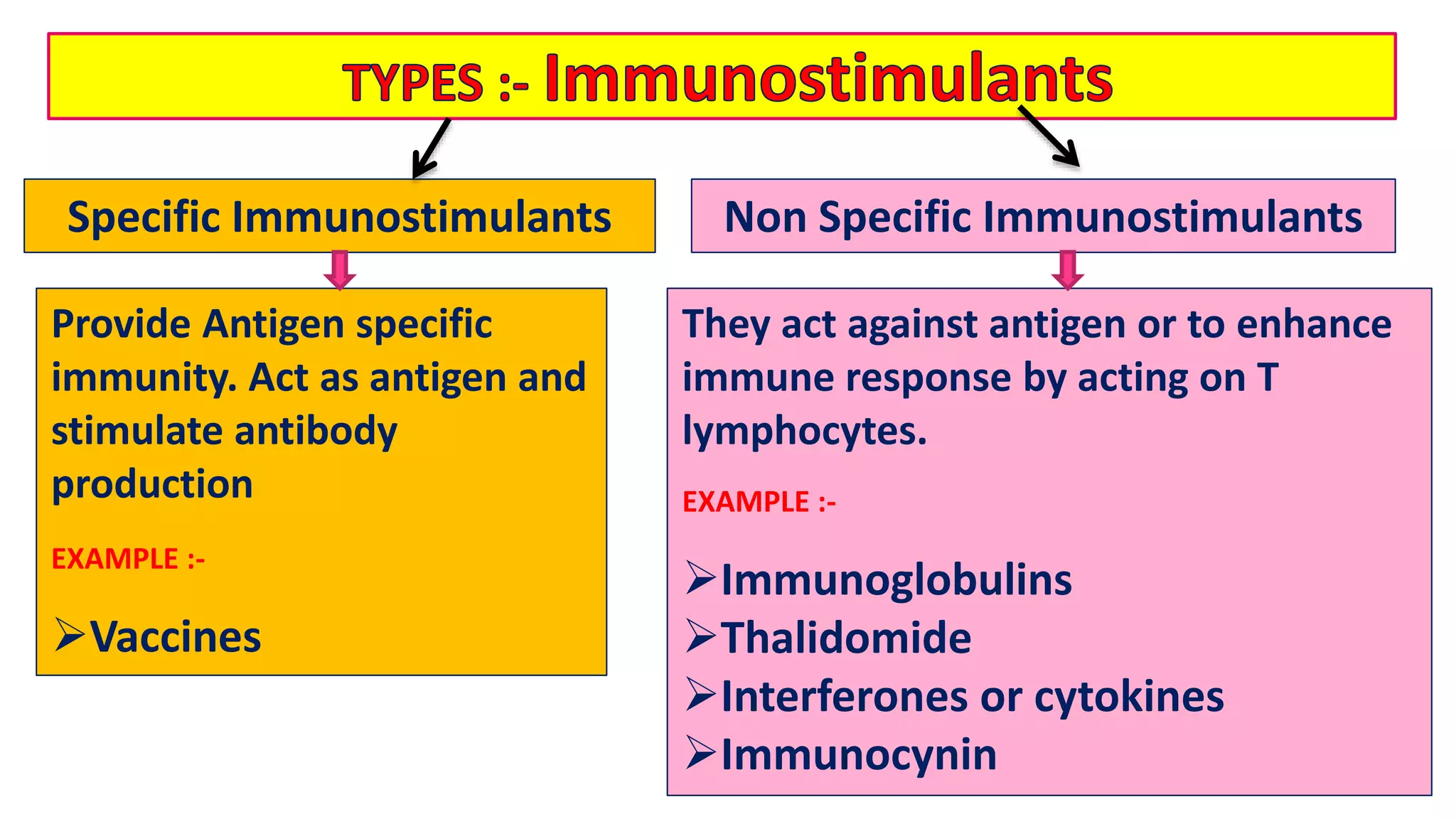
Immunostimulants are substances that stimulate the immune system to fight infections and diseases. They can be specific, providing immunity to particular antigens through vaccines, or non-specific by generally enhancing immune responses through substances like immunoglobulins, thalidomide, interferons, or immunocynin. Immunostimulants are useful for treating infections, cancers, and immunodeficiencies. In contrast, immunosuppressants are drugs that inhibit immune responses and are used to prevent organ transplant rejection and treat autoimmune disorders. Common side effects of immunosuppressants include infection, headaches, stomach upset, and weight gain.