1) The document discusses various classes of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) including their mechanisms of action, examples, and uses.
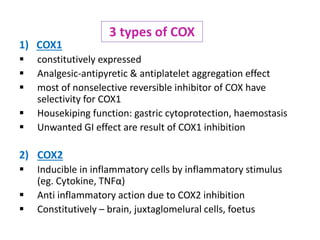
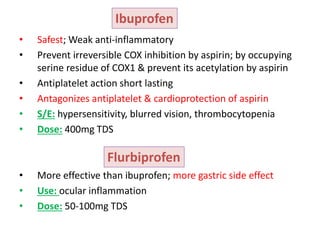
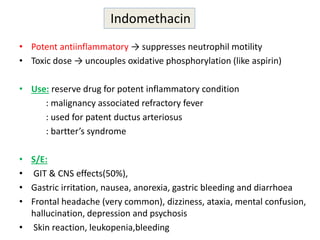
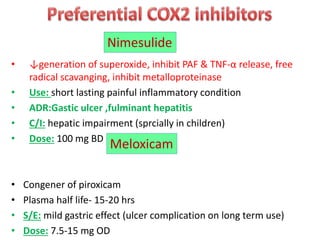
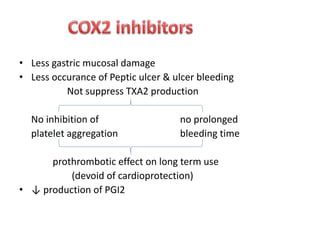
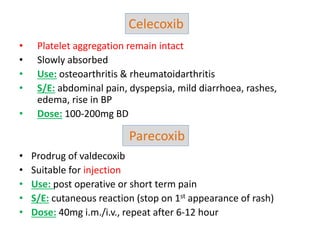
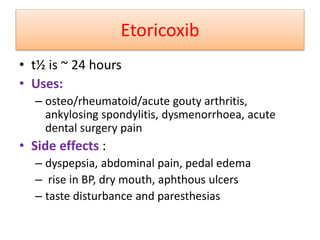
2) It covers traditional non-selective NSAIDs that inhibit both COX1 and COX2 as well as preferential and selective COX2 inhibitors with reduced gastrointestinal side effects.
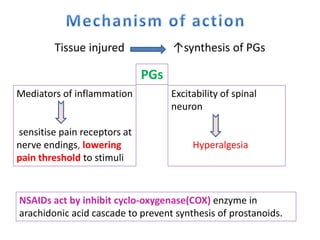
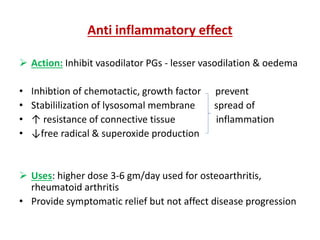
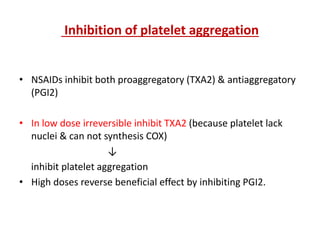
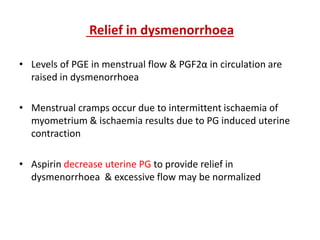
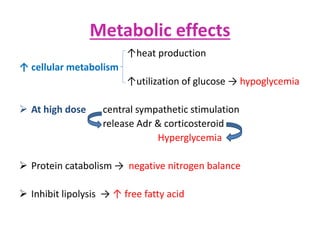
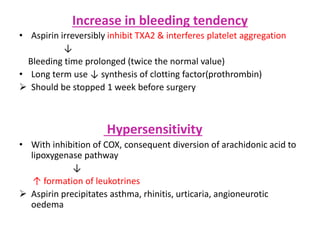
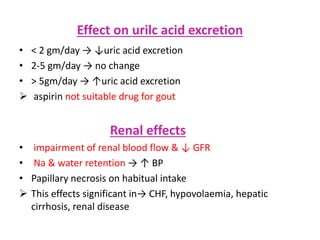
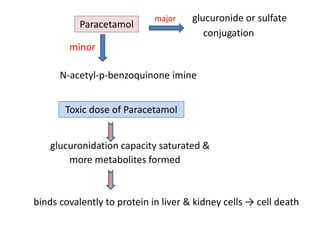
3) The mechanisms of analgesia, antipyresis and anti-inflammation of these drugs are described as inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis through cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibition.