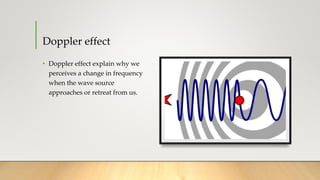
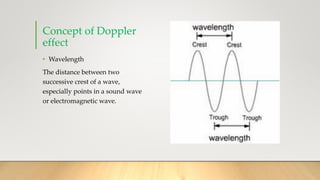
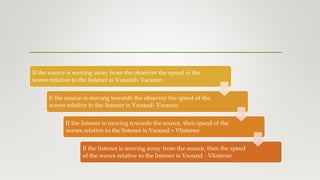
The document discusses the Doppler effect, which is defined as the change in frequency or pitch of a wave when the source of the wave and the observer are in relative motion. It explains that when the source approaches the observer, the observed frequency increases, and when the source moves away, the frequency decreases. An equation is provided to calculate the observed frequency based on the source frequency, speed of sound, and speeds of the source and observer. Examples are given of how the Doppler effect causes changes in the sound of a siren as a police car approaches or recedes from an observer. The summary concludes by noting that the Doppler effect is used in radar to measure the speeds of detected objects.