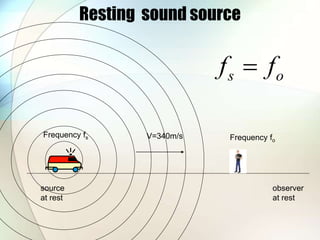
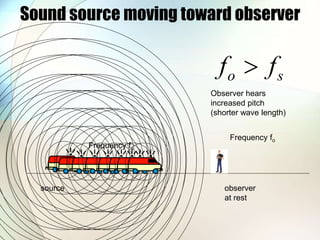
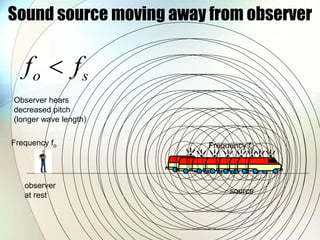
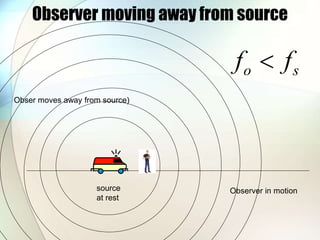
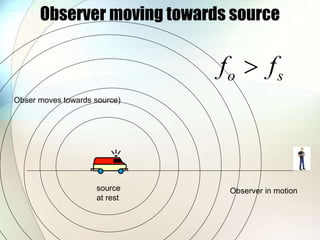
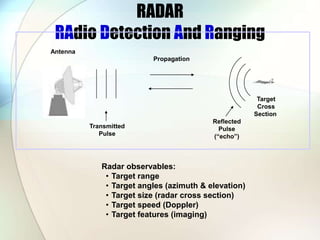
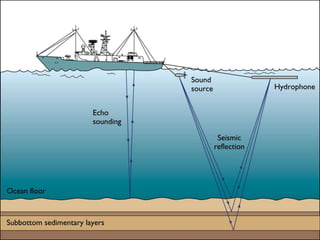
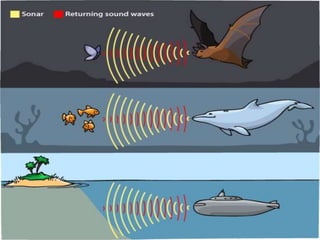
The document discusses the Doppler effect, which is the apparent change in frequency of sound or other waves due to relative motion between the source and observer. It provides examples of how the frequency is higher when the source is moving toward the observer and lower when moving away. Applications of the Doppler effect include radar, which uses changes in radio wave frequency to detect objects' speed and distance, and sonar, which works similarly but uses sound waves underwater for navigation and detection.