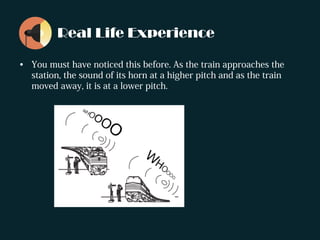
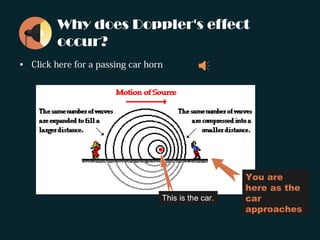
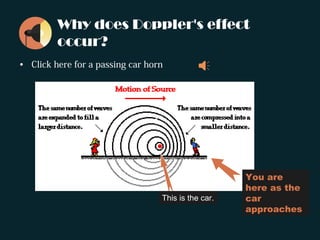
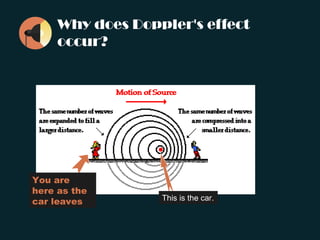
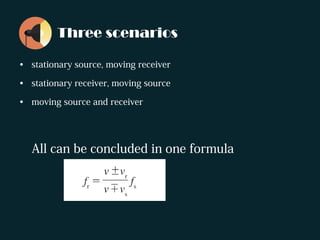
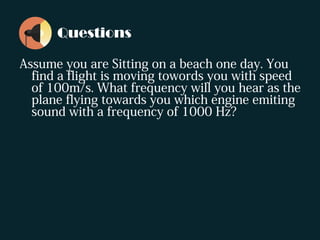
The document discusses the Doppler effect, where the observed frequency of a wave depends on the relative motion between the observer and the source. It notes that a train horn will be higher pitched as a train approaches and lower pitched as it moves away, due to the Doppler effect. It provides examples of this occurring with both trains and cars. The document explains that the Doppler effect is caused by the observer and source moving relative to each other, resulting in a different observed frequency than what is emitted. It also lists the three scenarios that can cause the Doppler effect: a stationary source with a moving receiver, a stationary receiver with a moving source, and both the source and receiver in motion. Finally, it introduces the Doppler effect formula and poses sample