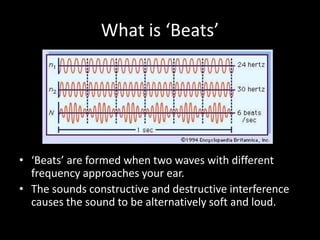
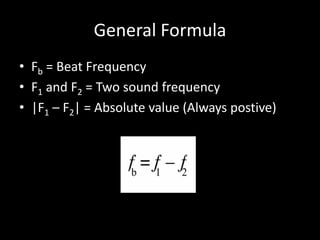
Beats occur when two sounds of different frequencies reach the ear. The interference of the waves causes the overall sound to rise and fall in amplitude at a rate equal to the difference between the frequencies. If two waves have frequencies of 330Hz and 350Hz, the beat frequency will be 20Hz, which is the absolute value of the difference between the frequencies. When tightening a piano string from 448Hz to 450Hz, the beat frequency remained 2Hz, so the original frequency must have been 448Hz. For a tuning fork at 430Hz sounding with a guitar where 10 beats occurred in 3 seconds, the guitar's frequency is either 433.33Hz or 426.67Hz.