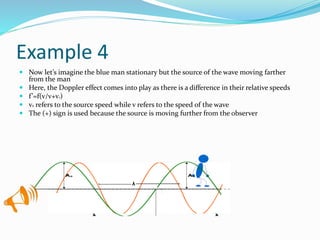
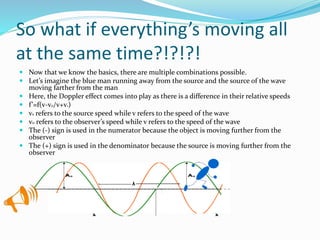
The document discusses the Doppler effect, which occurs when the observer and source of waves are moving relative to each other, causing the observed frequency to differ from the emitted frequency. It provides four examples of different relative motions between observer and source. When the observer moves toward the source, the observed frequency increases, and when they move apart it decreases. The same applies if the source moves toward or away from a stationary observer. Complex scenarios with multiple motions are also considered. Two example problems are worked through to demonstrate applying the Doppler effect concepts.