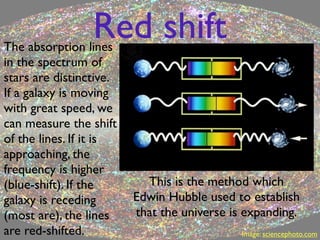
The document discusses the Doppler effect, explaining how it affects the perception of sound and light based on the motion of the source and observer. It details how frequencies change when a source moves towards or away from an observer, with applications in astronomy and ultrasound measurements. Calculations for determining frequency changes and shifts, such as redshift for galaxies, are also included.




![Doppler calculation f’ = frequency detected
f = frequency emitted
v = velocity of sound
uo = velocity of observer
us = velocity of source
When the velocities are in opposite directions, we add them.
A police car siren emits a Speed of sound = 330 m/s
sound of frequency 600 Hz A cyclist approaches at 18
while travelling at 40.0 m/s. m/s a stationary transformer
What does this sound like humming at 50.0 Hz. What
to a stationary observer wavelength of sound does
behind the car? [535 Hz] she measure? [6.26 m]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dopplereffectflip-120314233457-phpapp02/85/IB-Physics-Doppler-effect-flippingphysics-by-Nothingnerdy-6-320.jpg)
![Calculating red shift
∆f = change in frequency
v = relative speed of source and observer
An approximation of c = speed of light (300 000 km/s)
the Doppler formulas f = original frequency
when c >> v
A star emits light at 456 THz which is detected
at the earth as 416 THz. What is the speed of
the star relative to the Earth? [26 300 km/s]
Infra-red radiation from a police radar gun
bounces off a car travelling at 30 m/s. The car
receives a frequency of 200 THz; what will be the
change in frequency? [20 MHz]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dopplereffectflip-120314233457-phpapp02/85/IB-Physics-Doppler-effect-flippingphysics-by-Nothingnerdy-8-320.jpg)


