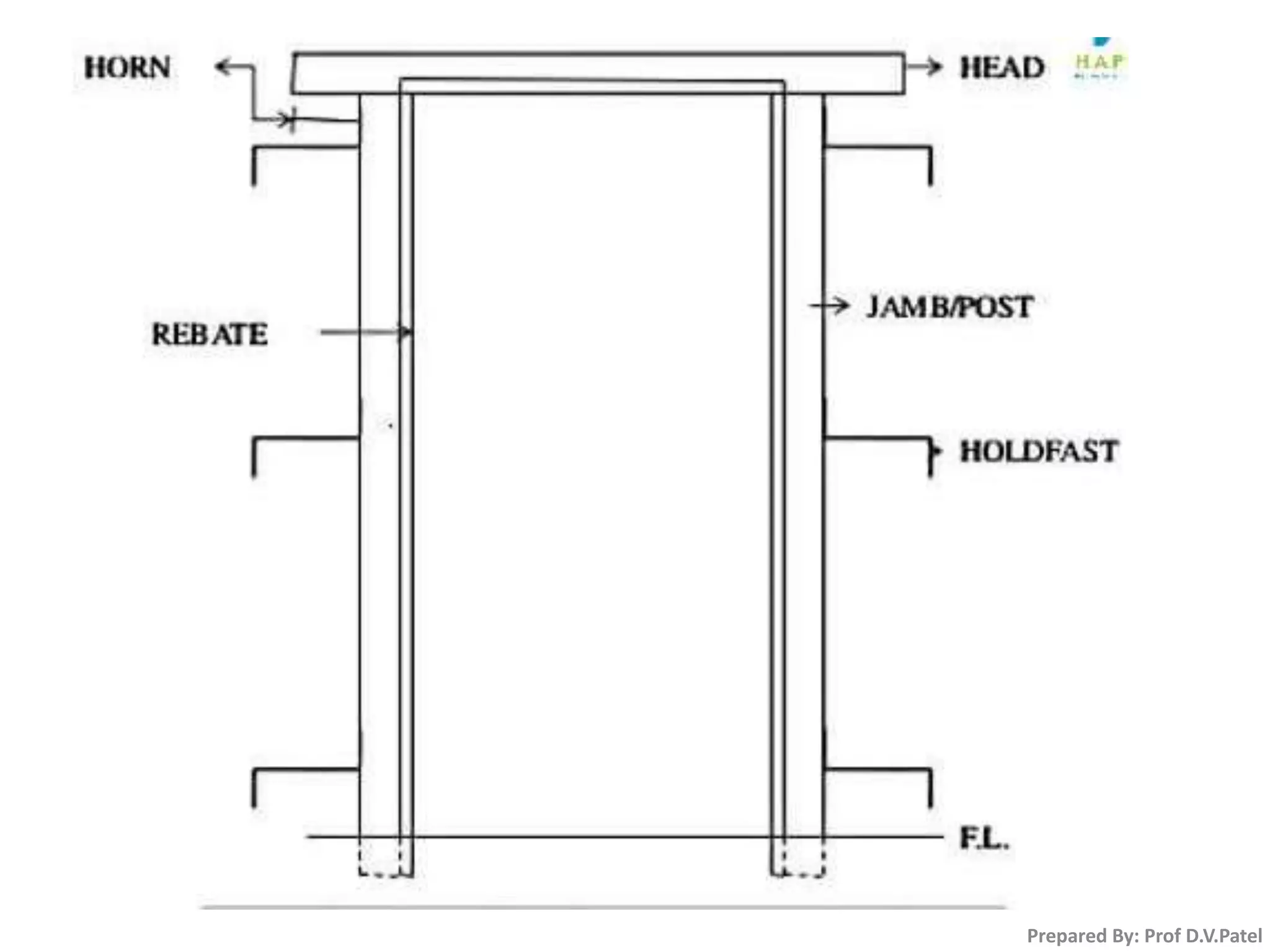
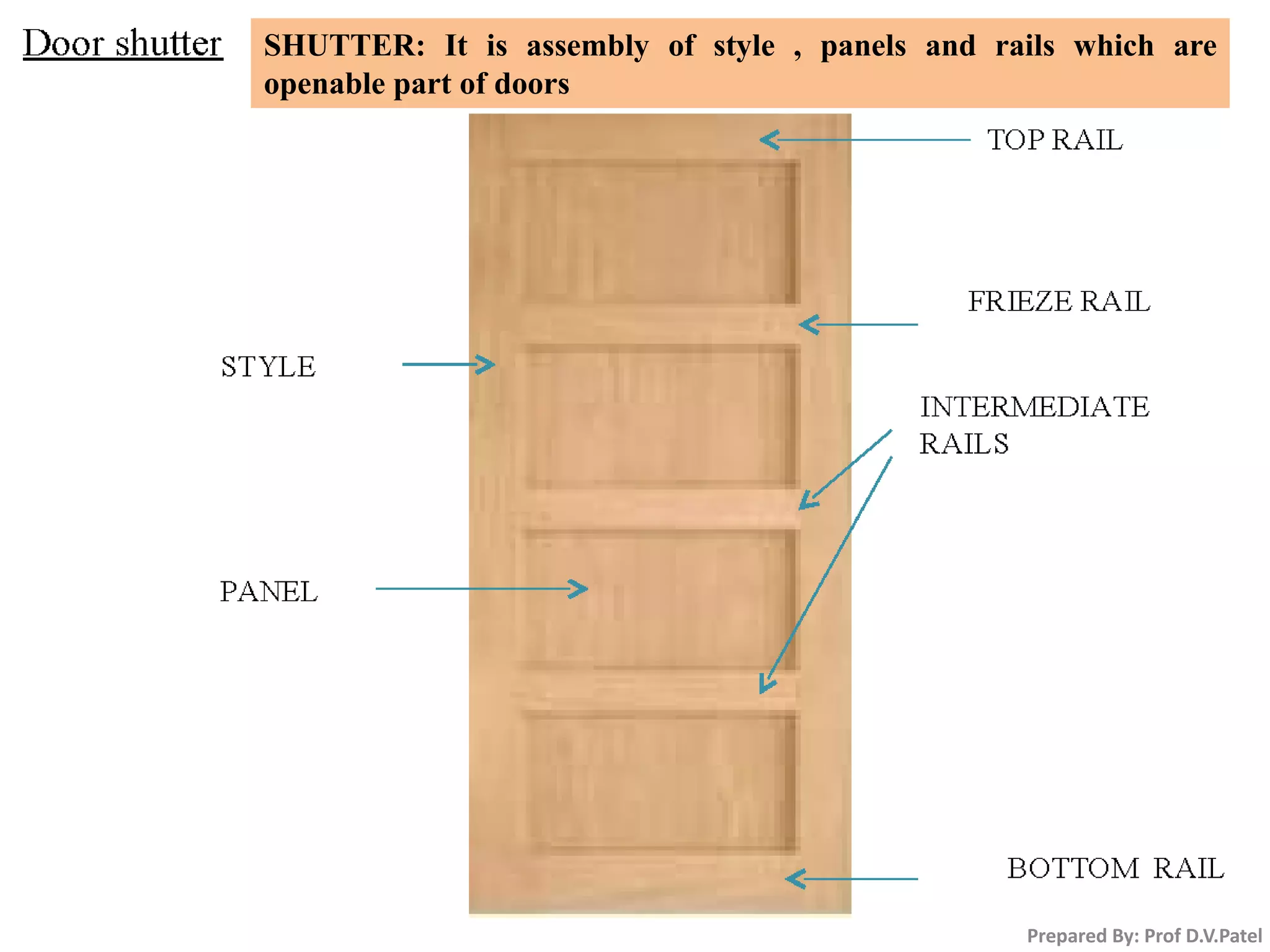
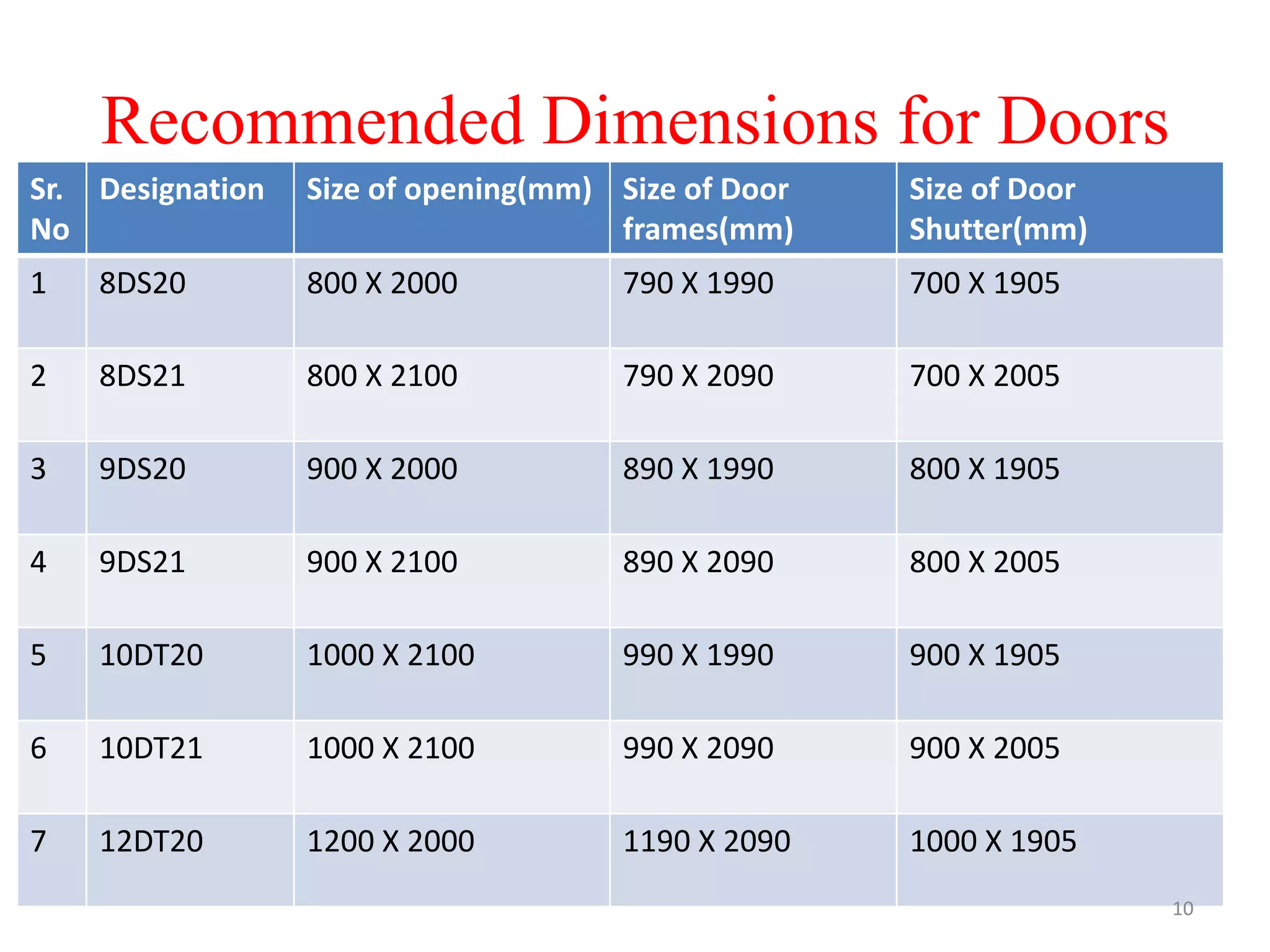
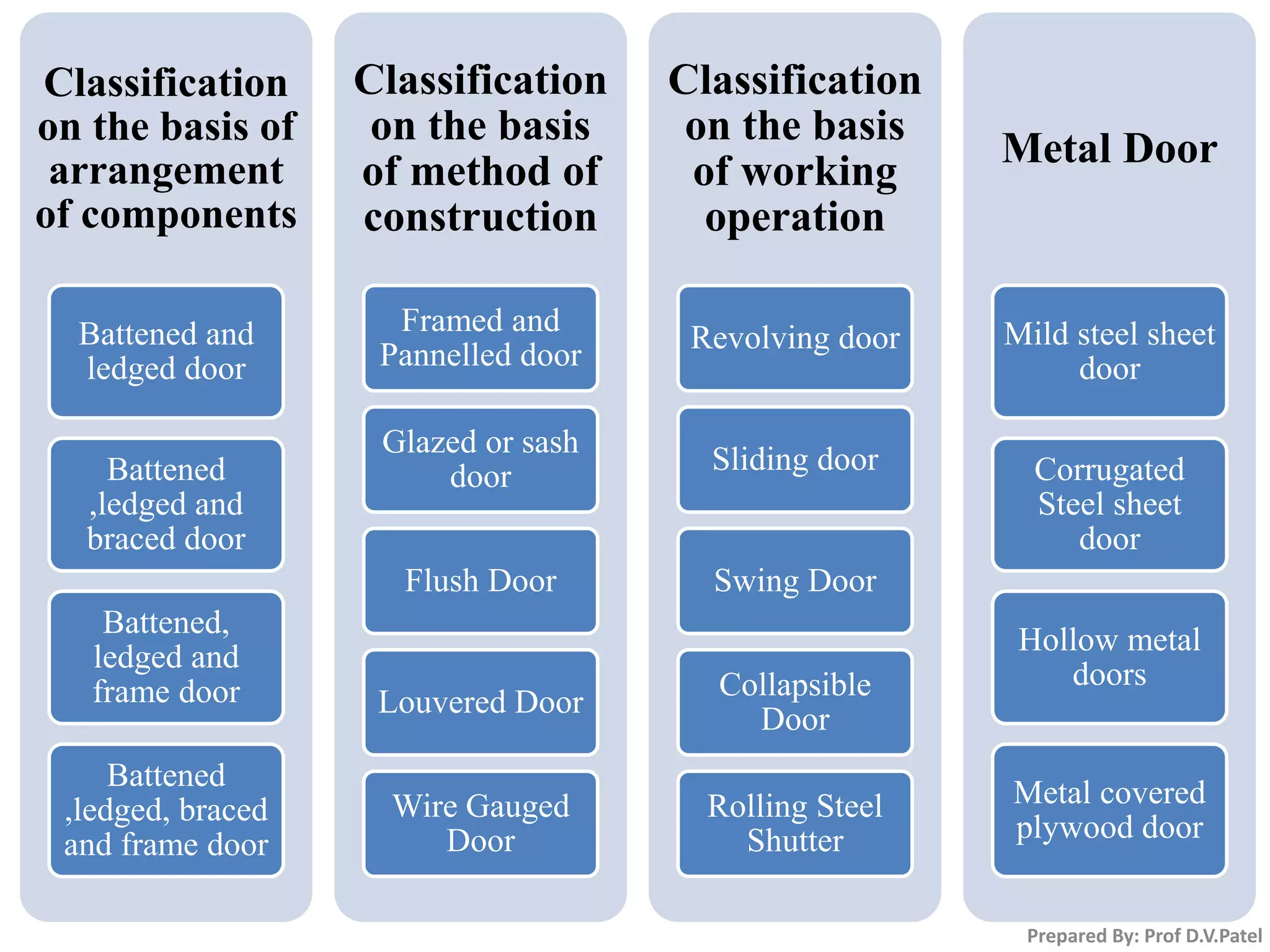
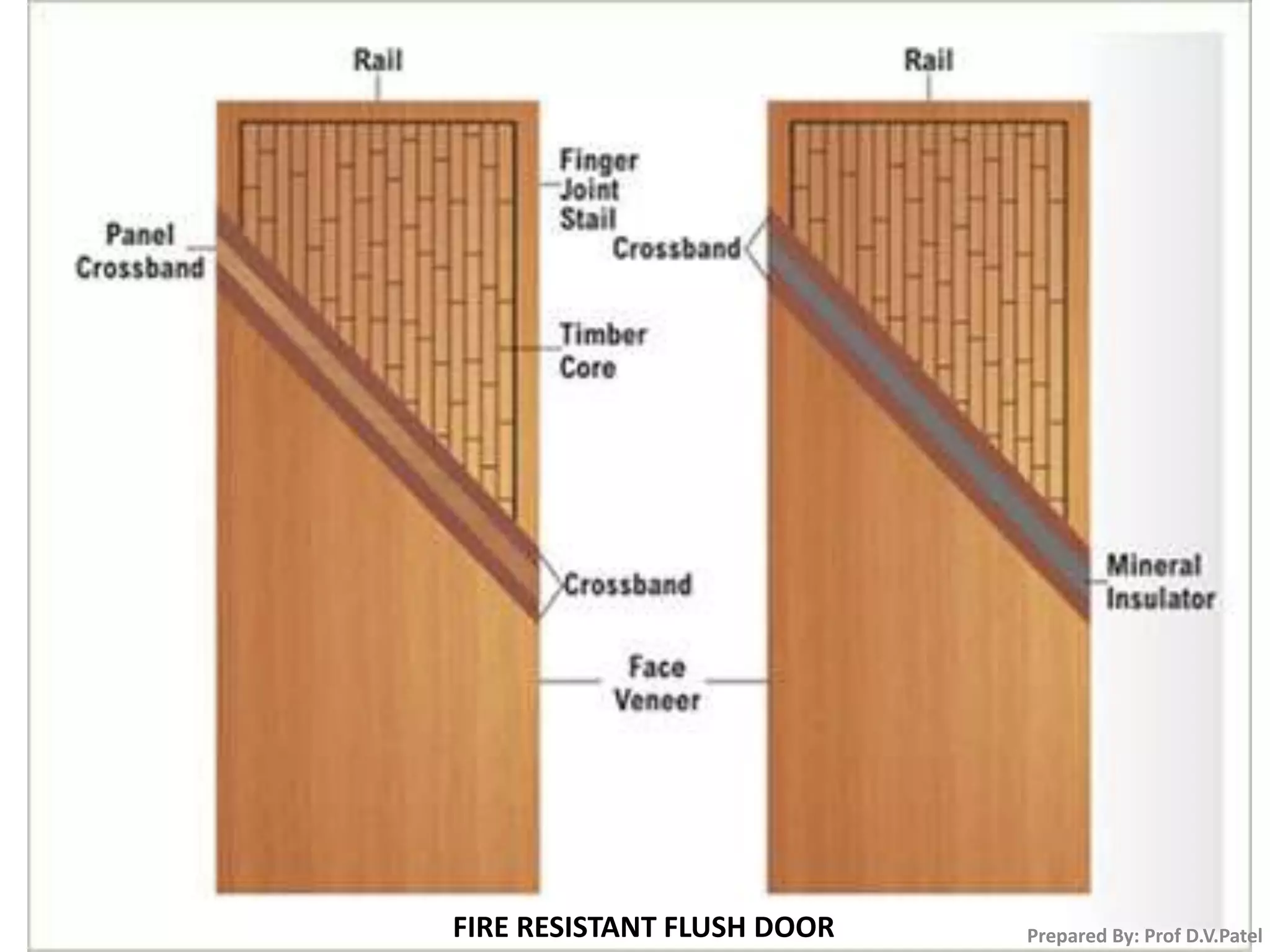
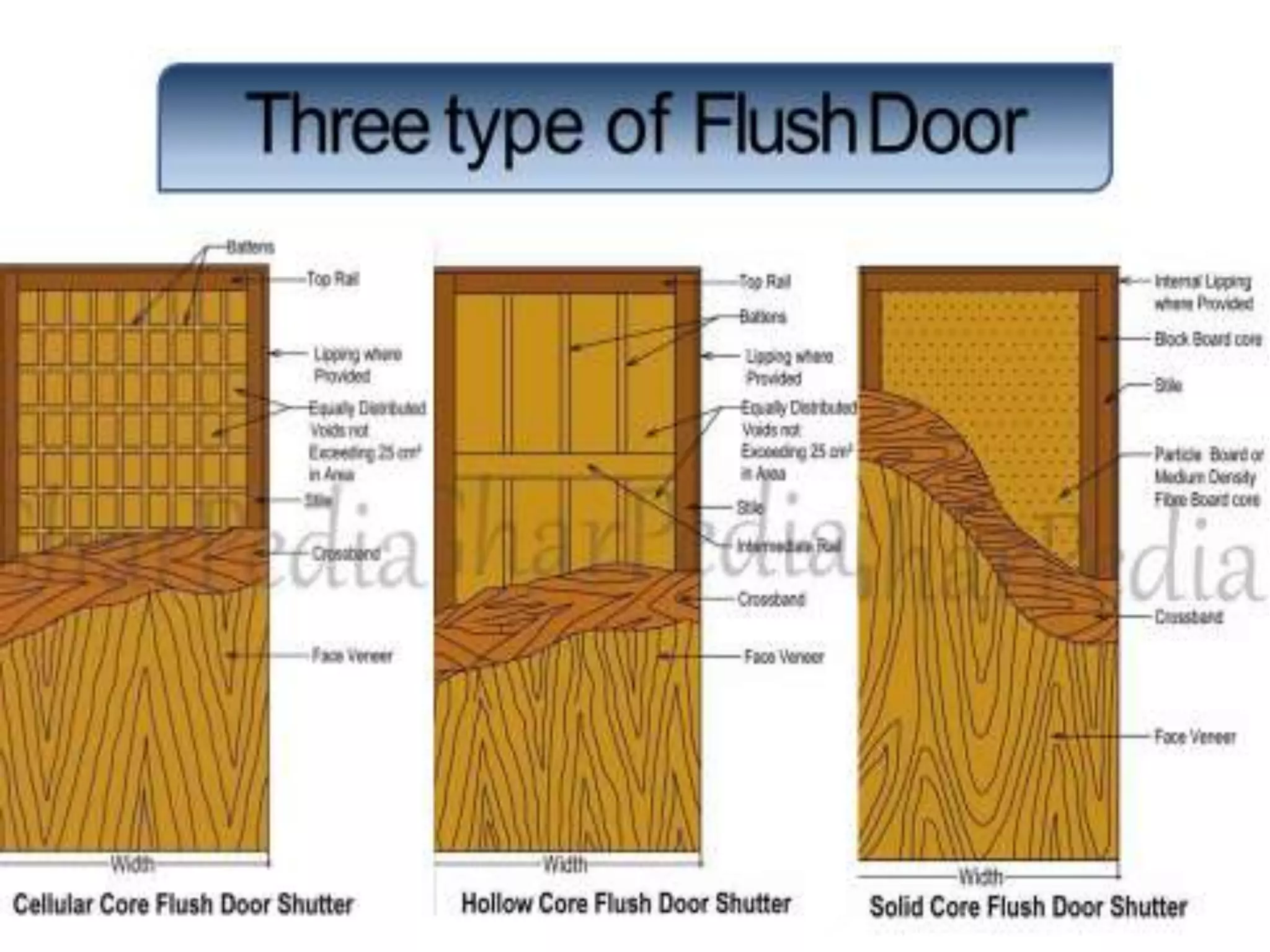
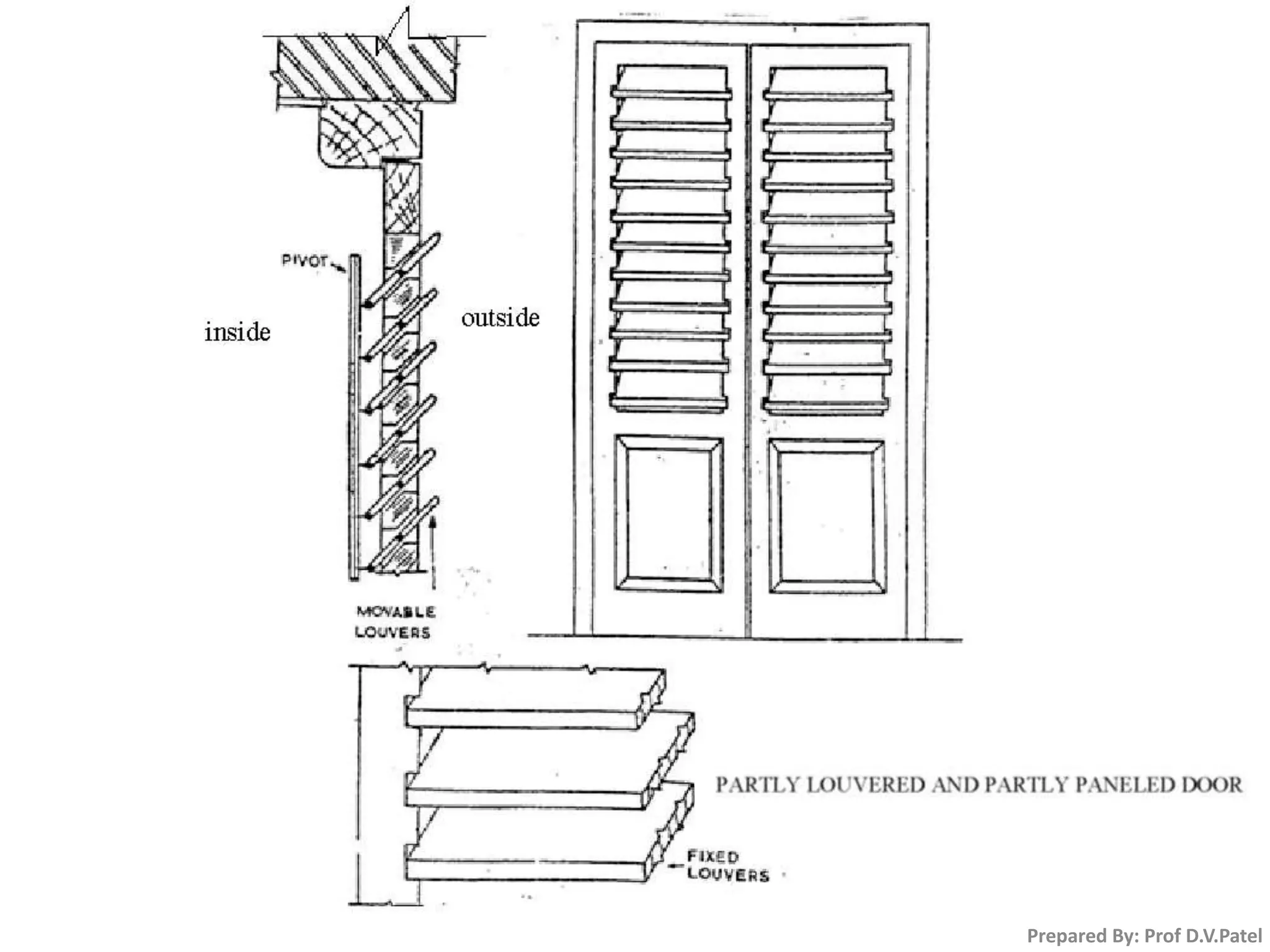
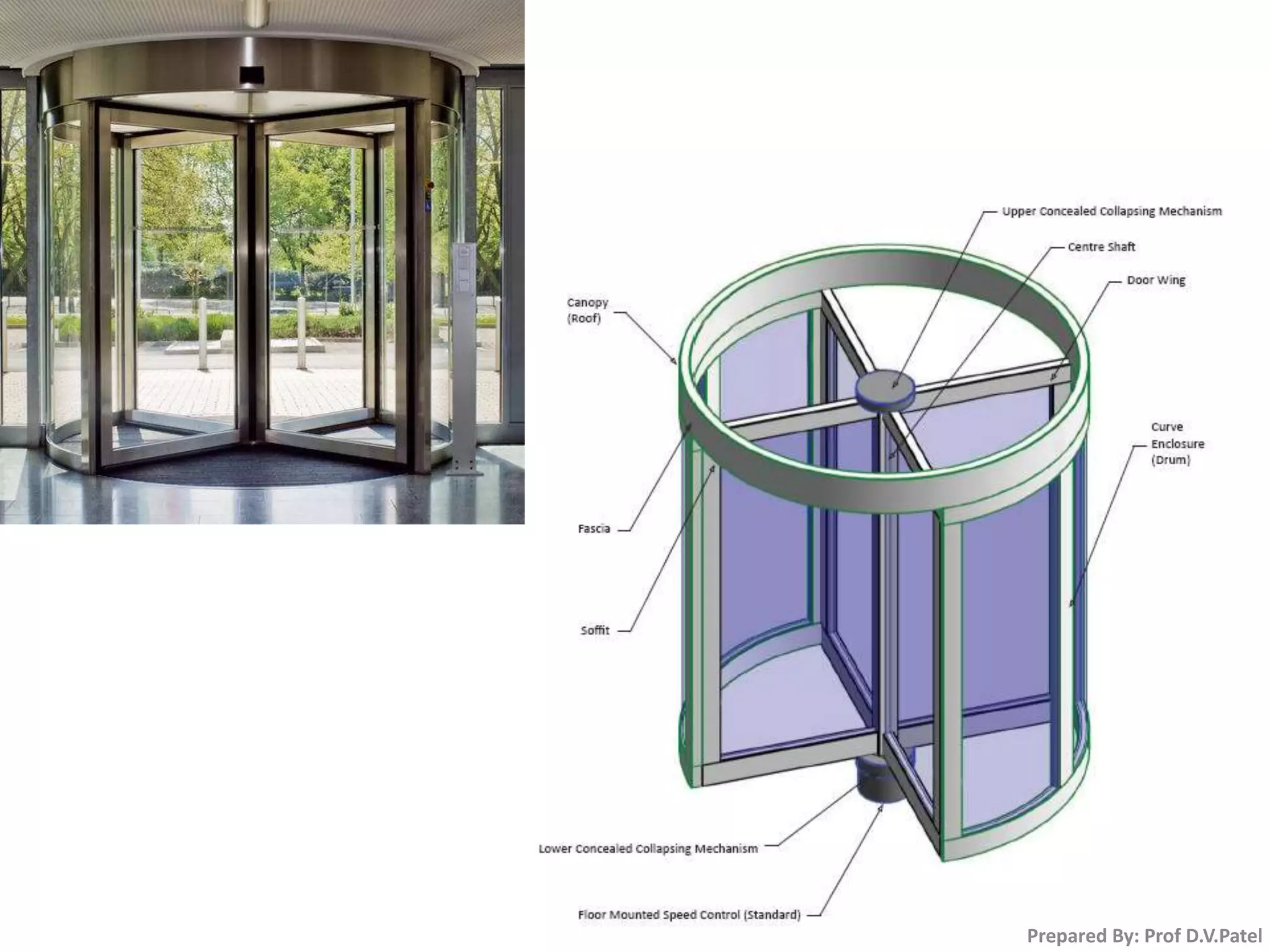
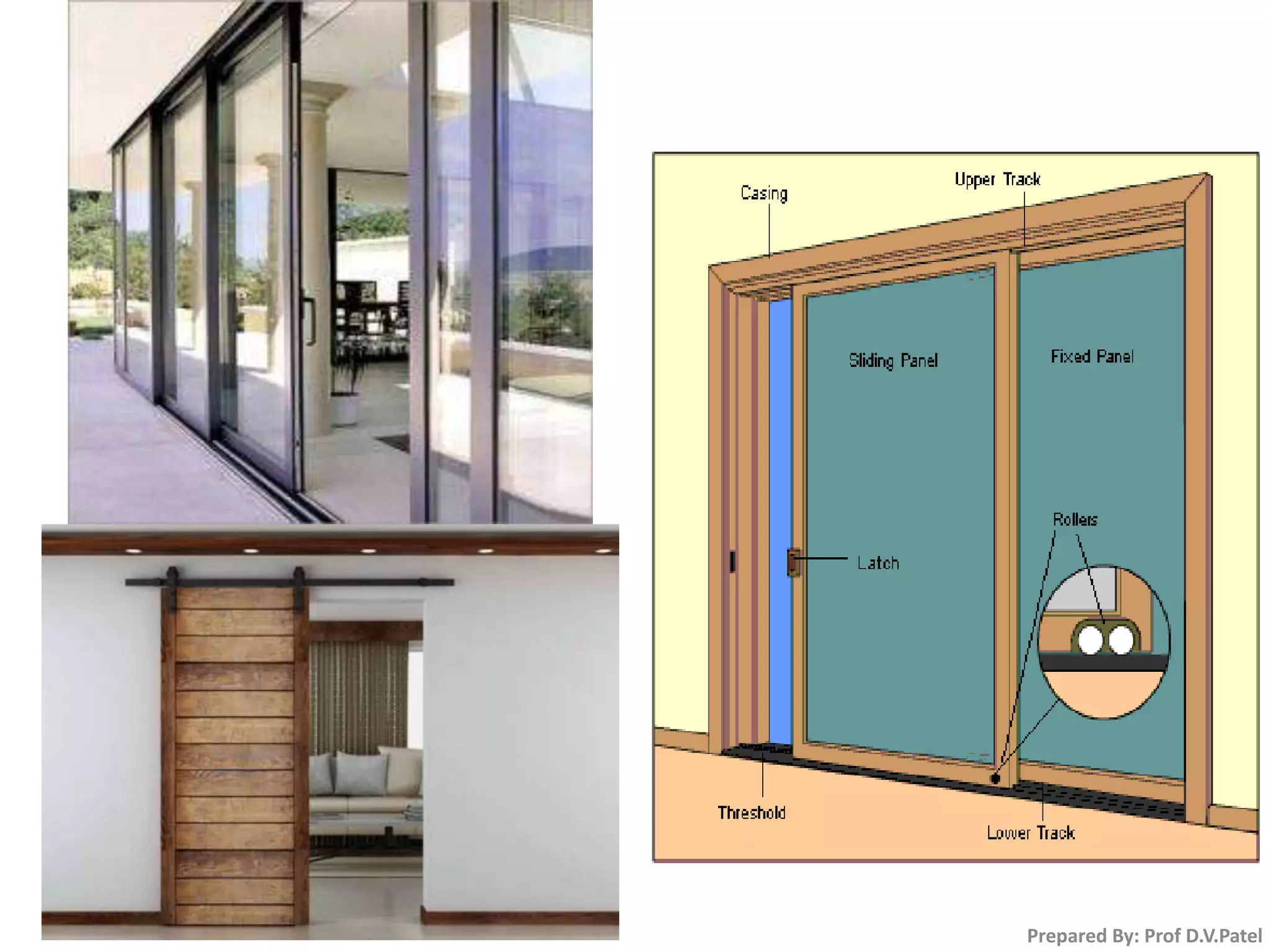
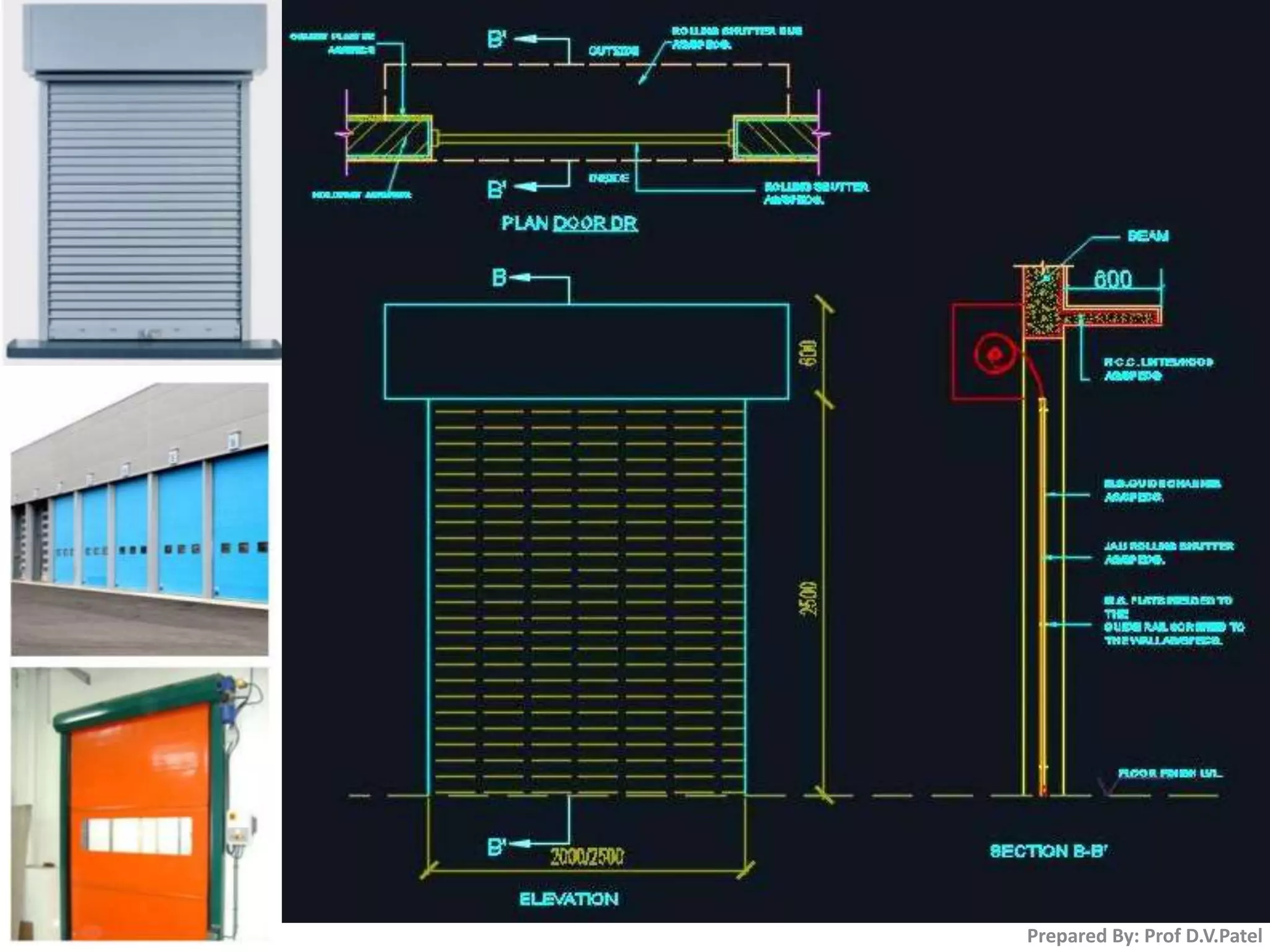
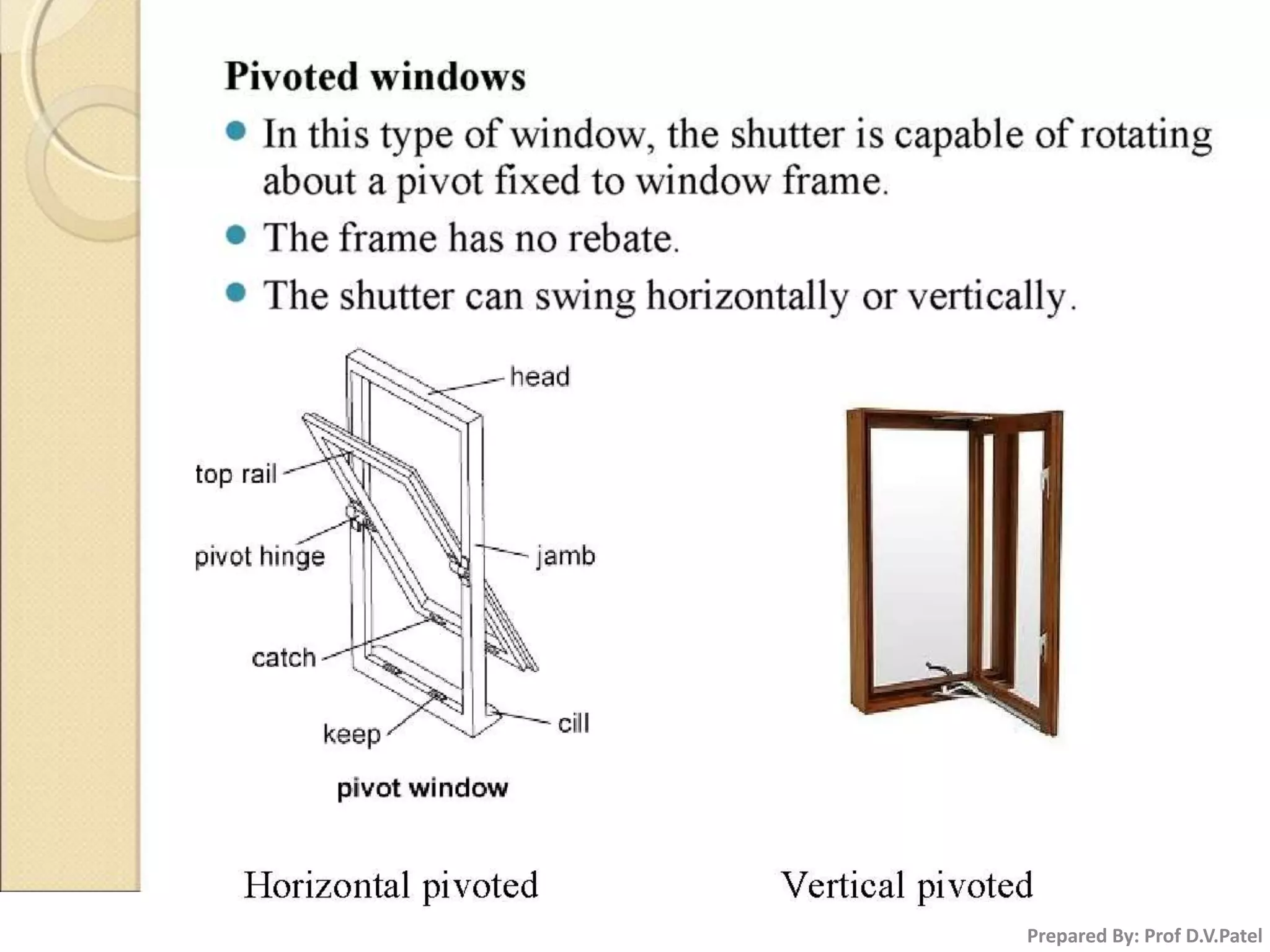
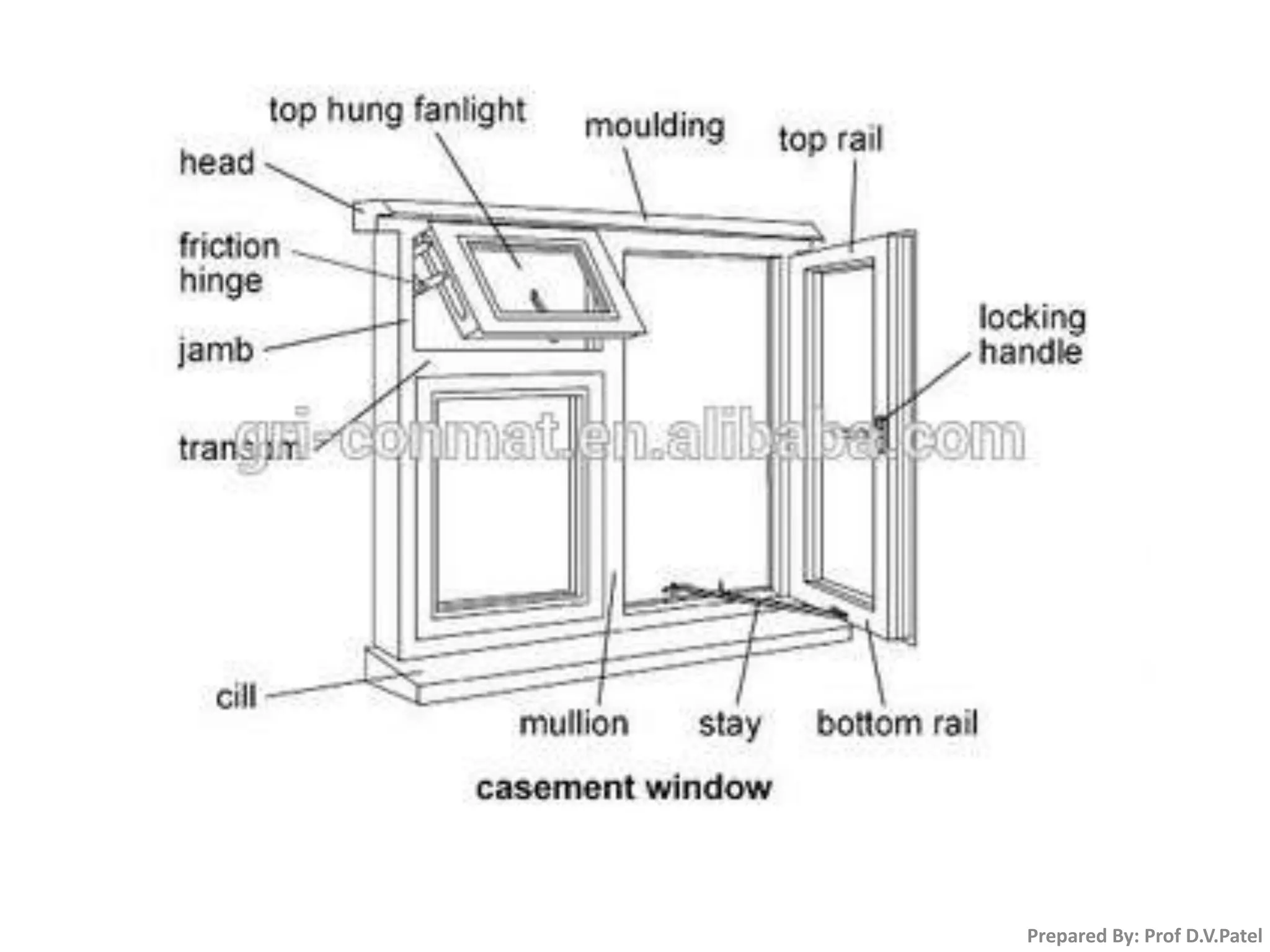
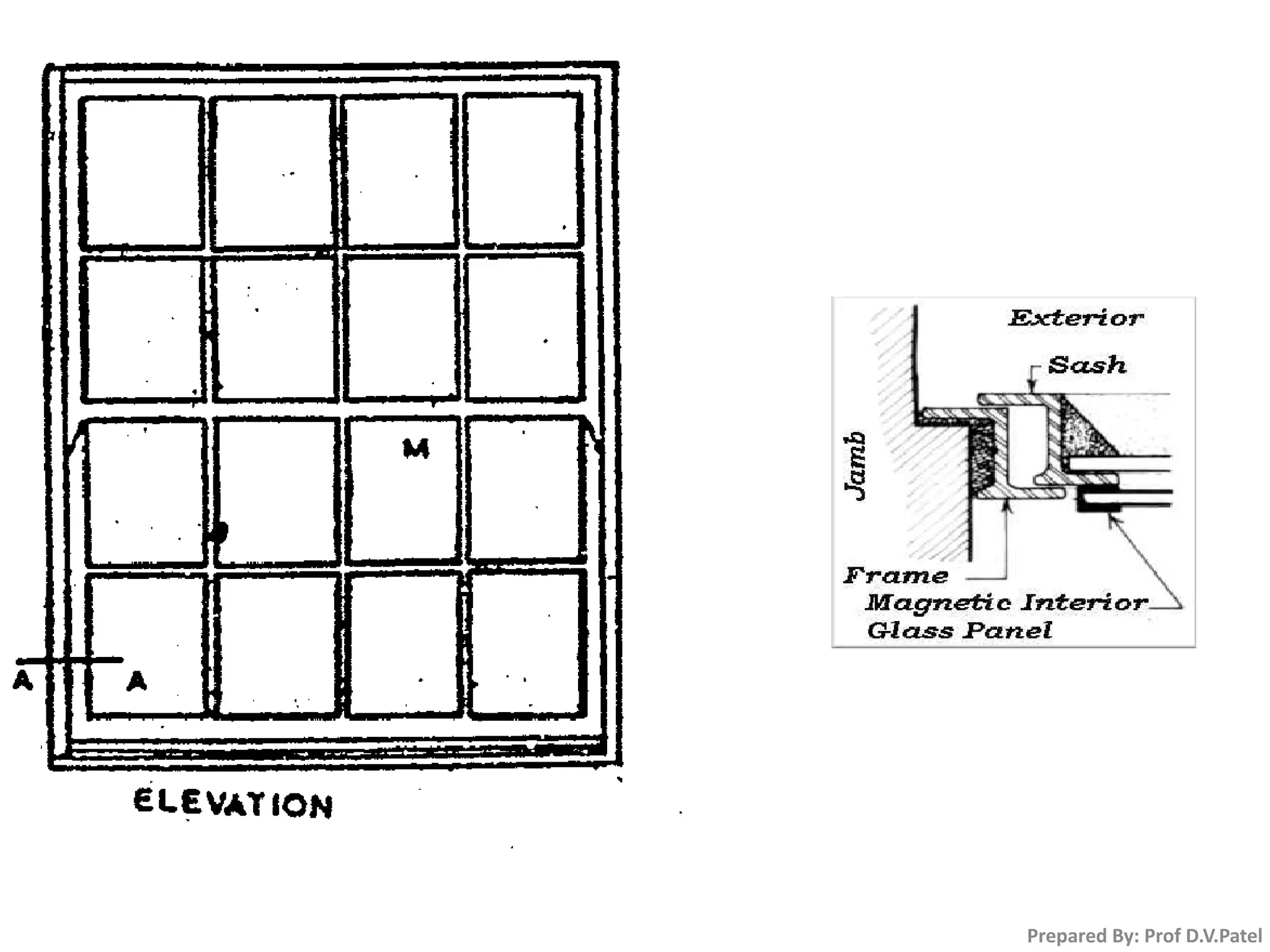
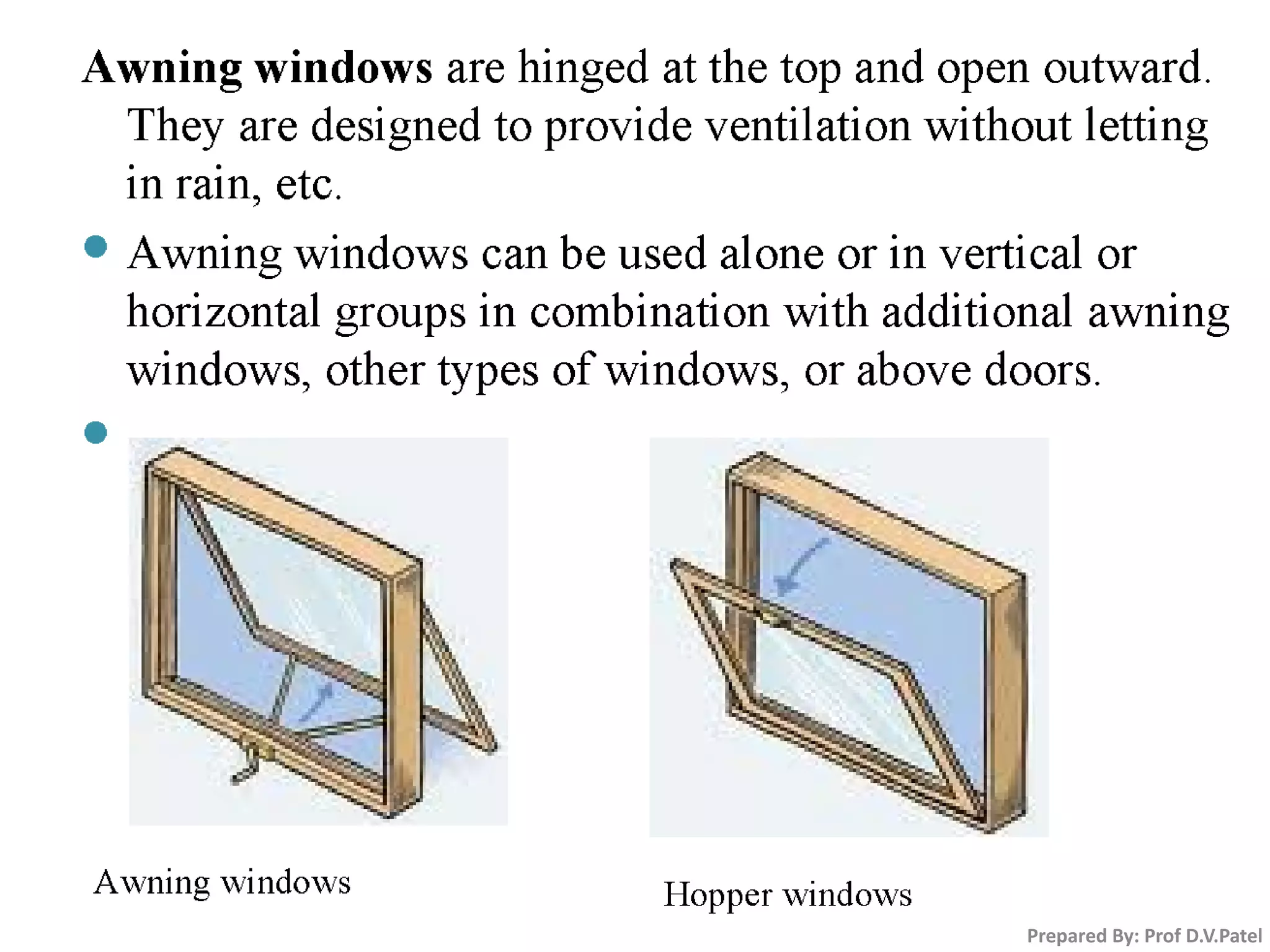
The document discusses doors and windows. It provides details on door frames, types of doors, dimensions of doors, types of door shutters, and factors to consider for window design. It recommends the size of windows should be 10-20% of the floor area and the minimum window area for a room is 1 square meter per 30-40 cubic meters. Dormer and gable windows are described as ways to introduce natural light into sloped roof areas. Fanlights are semicircular or elliptical windows placed above other windows or doors.