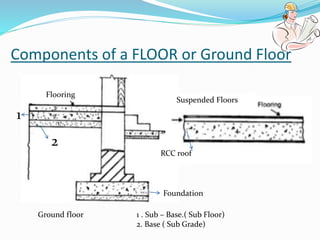
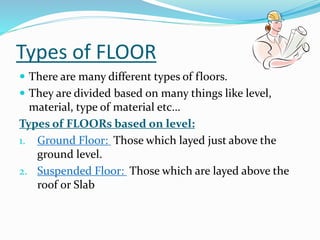
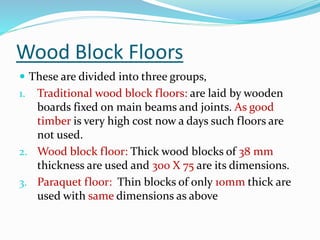
The document discusses the different types of floors used in buildings. It describes floors as horizontal structural elements that divide a building into levels. Floors are categorized based on their level (ground or suspended), material used (cement, stone, tiles, wood, etc.), and other factors. The key components of a floor are identified as the sub-floor, base, and finished floor. Various stone, tile, resilient, terrazzo, and wood floor options are outlined. Economy is noted as a consideration, as finishing costs can exceed initial estimates.