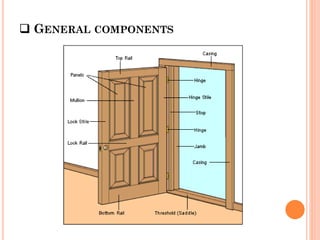
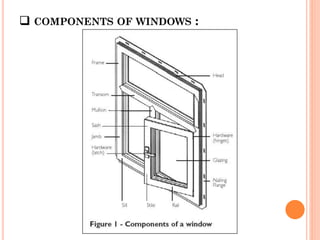
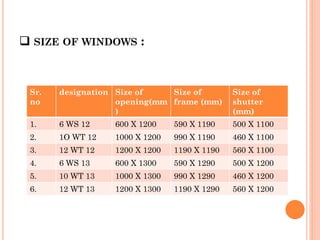
Doors and windows provide access and ventilation for buildings. Doors come in various materials and types for different uses. Common residential door sizes are 0.9x2m for internal and 1x2m for external. Doors should be located 20cm from corners and opposite walls for cross ventilation. Windows also have standard sizes and components like frames, shutters, and mullions. Window type and location depends on room size, use, climate and wind direction. Common window types include casement, steel, bay and dormer windows.