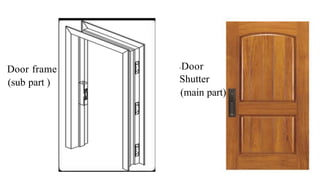
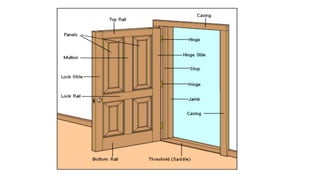
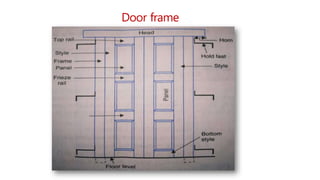
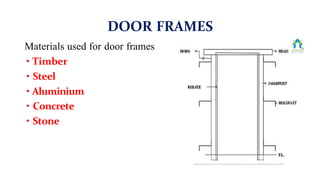
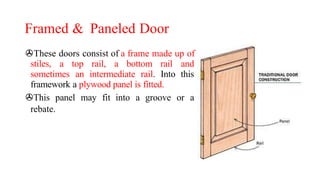
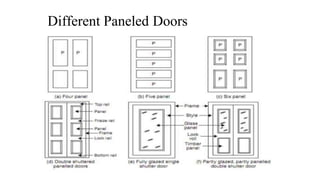
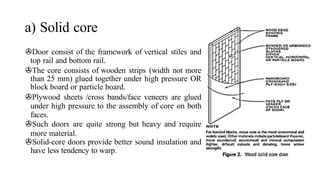
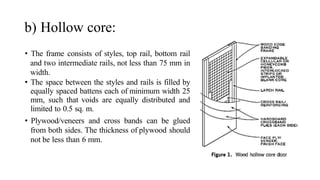
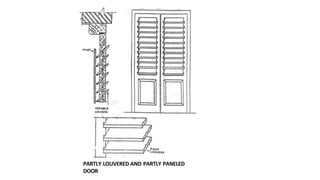
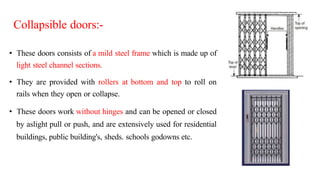
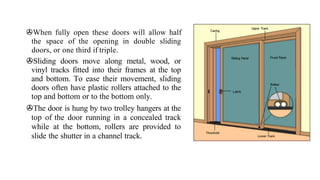
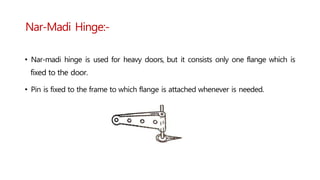
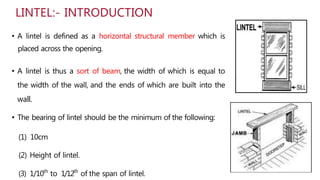
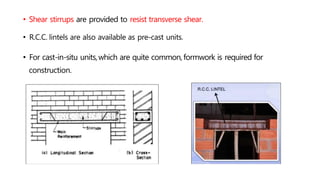
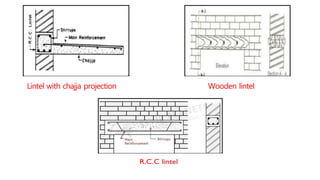
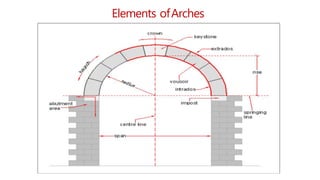
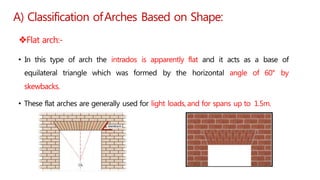
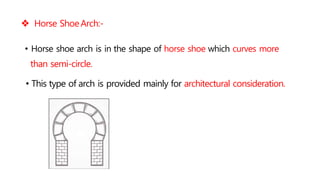
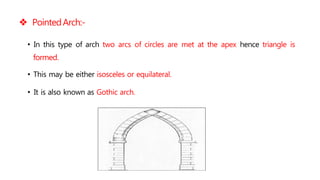
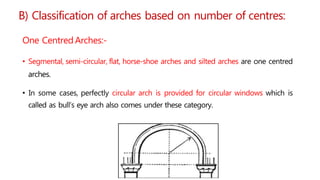
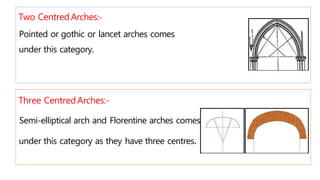
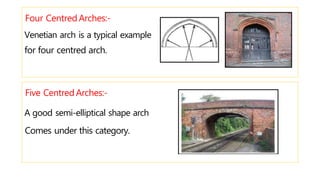
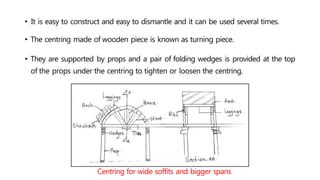
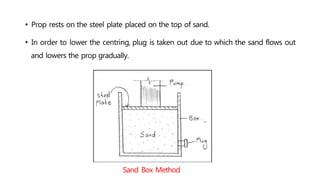
This document provides information about doors and door components. It discusses the definition and purpose of doors, as well as the typical location of doors within buildings. It describes the main parts of a door, including the door frame and shutter. It lists various technical terms used in door construction and gives standard size ranges for internal and external doors. The document also categorizes different types of doors based on their arrangement of components and working operations. Some door types discussed include hinged doors, glazed doors, framed and paneled doors, and sliding doors.