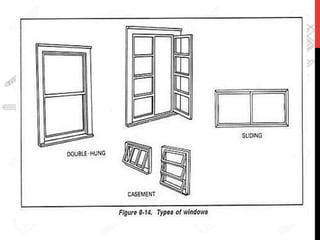
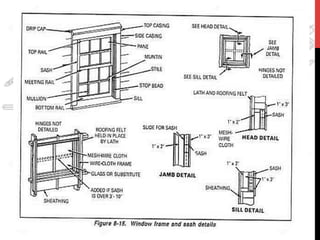
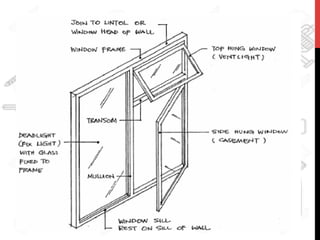
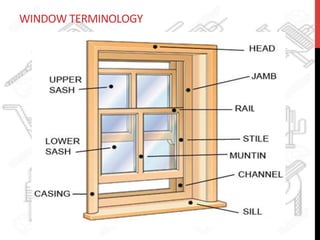
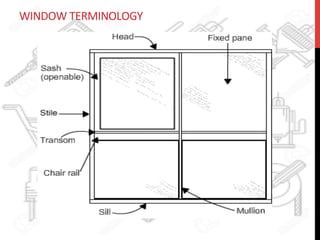
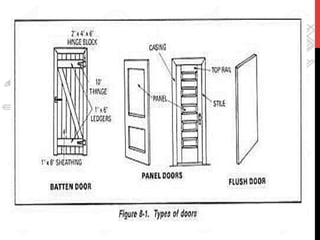
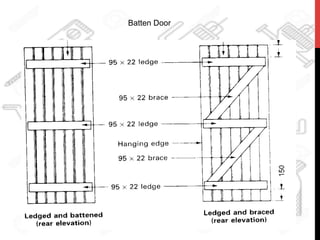
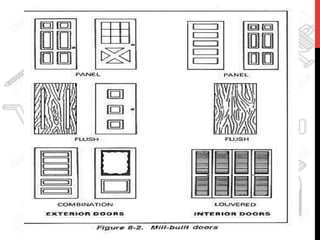
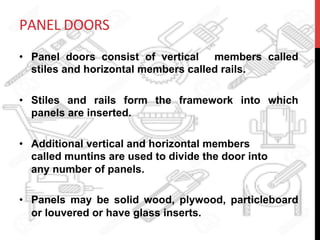
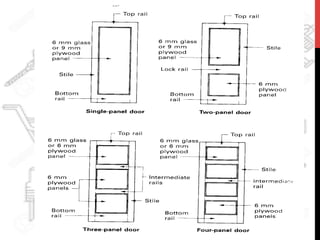
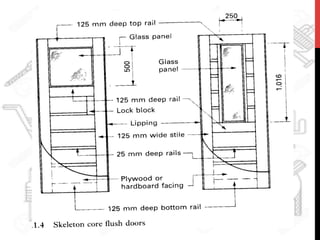
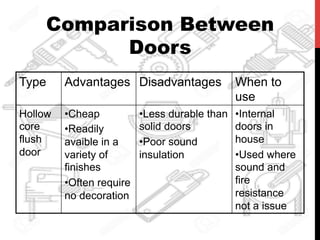
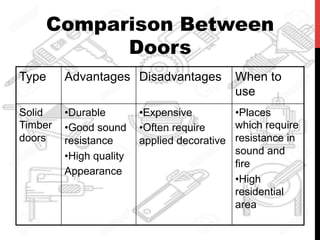
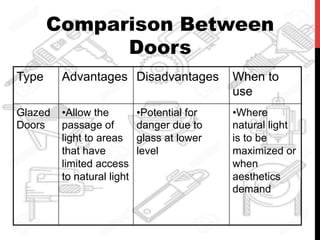
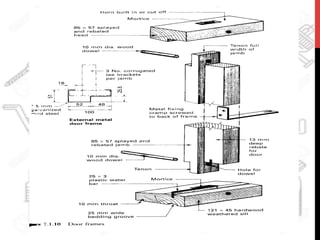
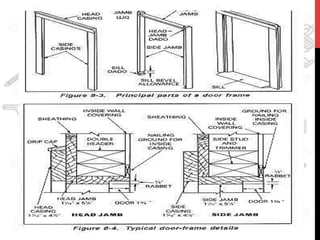
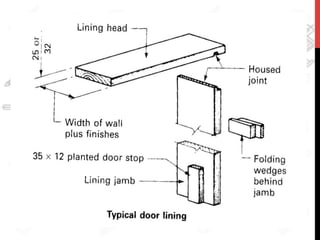
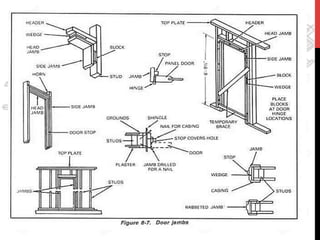
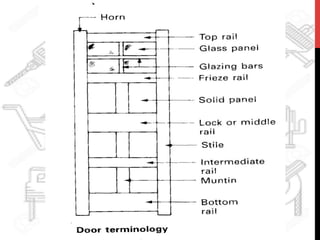
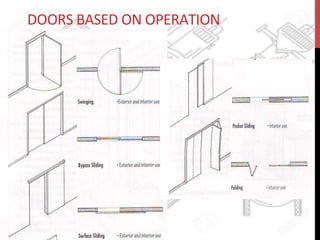
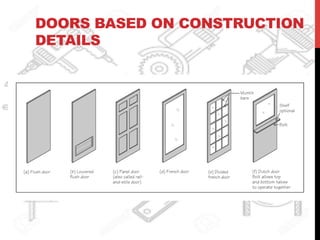
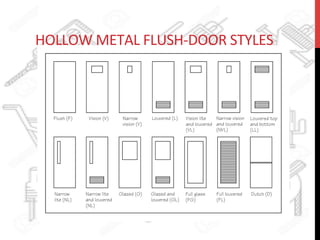
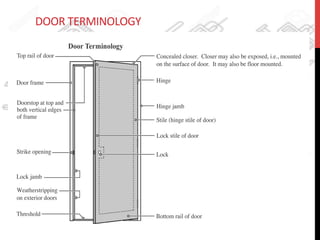
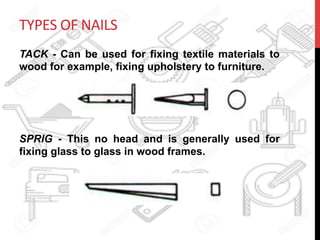
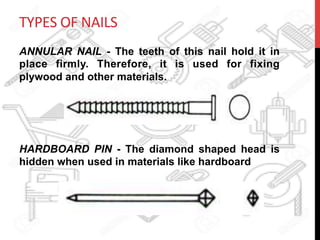
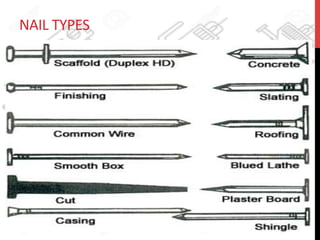
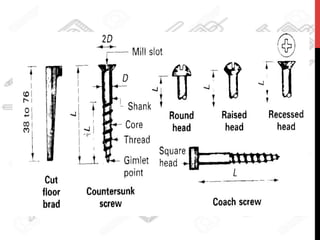
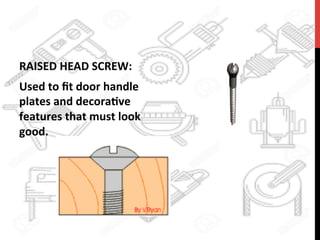
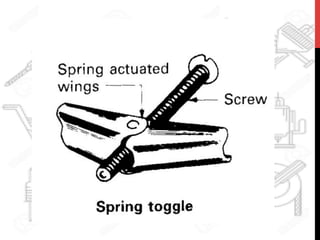
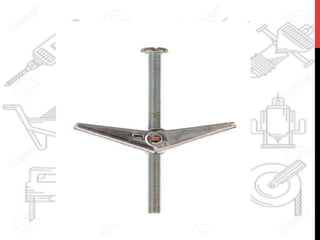
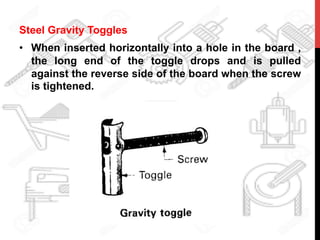
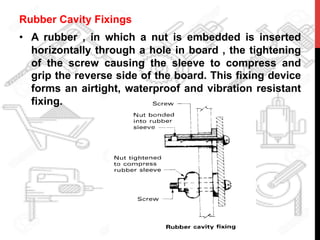
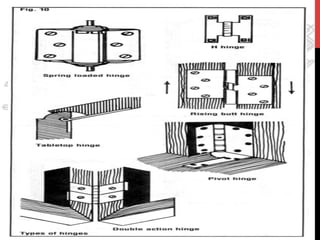
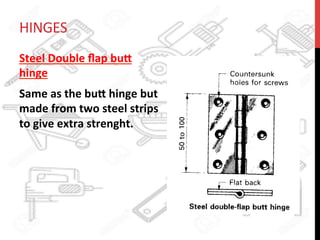
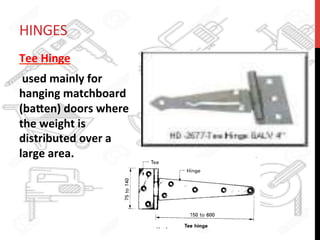
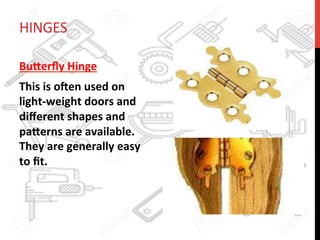
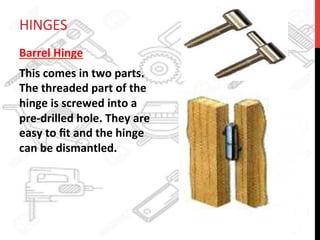
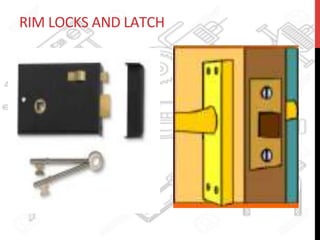
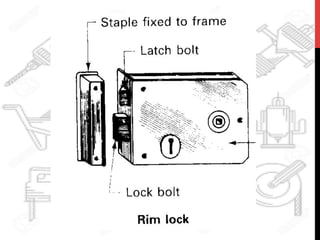
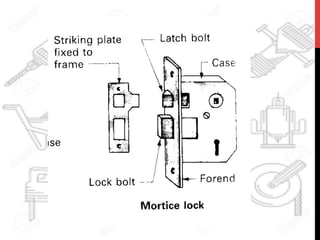
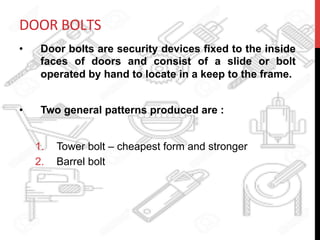
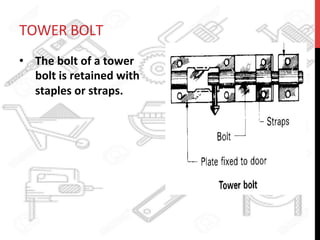
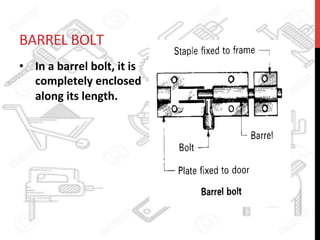
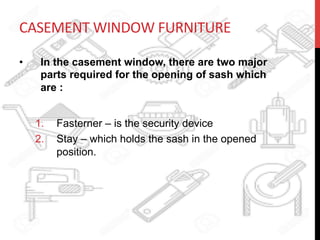
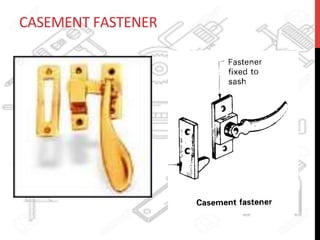
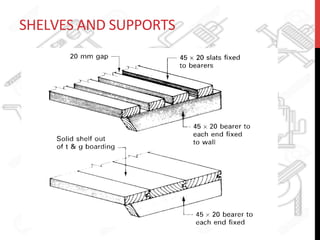
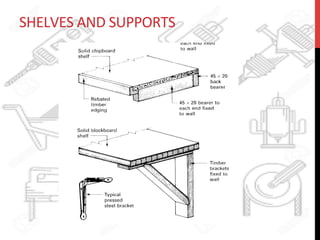
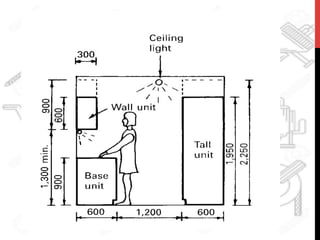
This document provides information about windows, doors, and ironmongeries used in construction. It discusses the most common types of windows, such as double-hung and casement windows. It also describes door types, including panel, flush, and batten doors. Additionally, it covers door and window frames, sashes, terminology, and basic ironmongery items like nails, screws, and hinges.