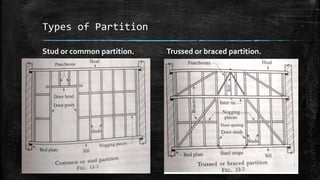
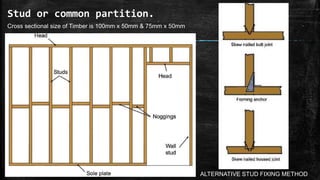
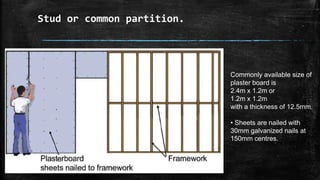
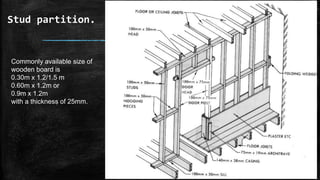
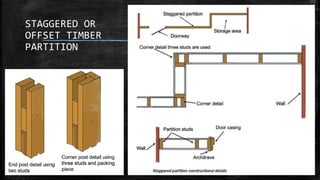
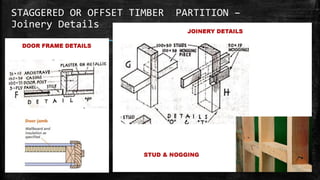
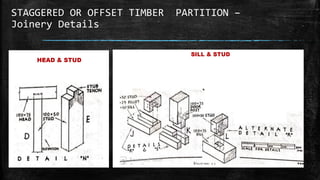
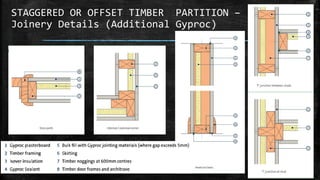
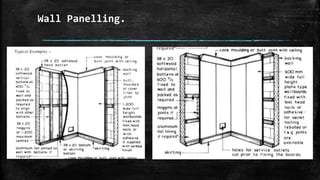
The document discusses wooden partitions and paneling. It describes partitions as interior walls that divide space and lists common types like timber stud, metal stud, and drywall partitions. Partitions are classified based on materials and can be load-bearing or non-load-bearing. Paneling is defined as rigid wall coverings made of interlocking wood or other materials. Details are provided on stud partitions, trussed partitions, and joinery details for staggered timber partitions. Various paneling materials are also listed along with assignments to detail joinery and draft partition and paneling drawings.