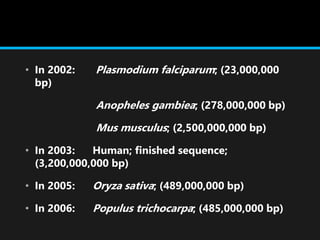
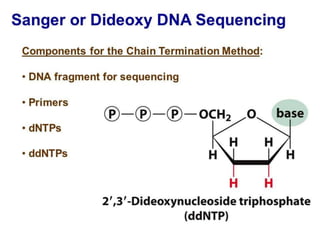
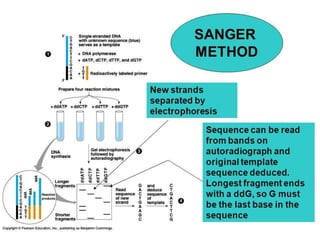
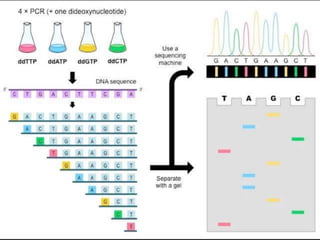
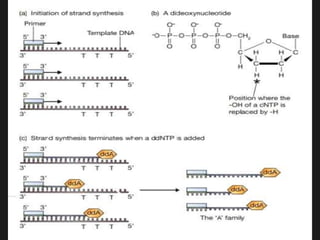
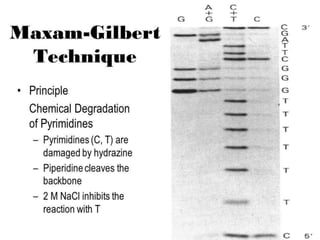
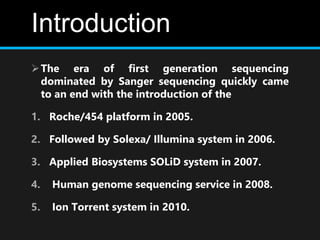
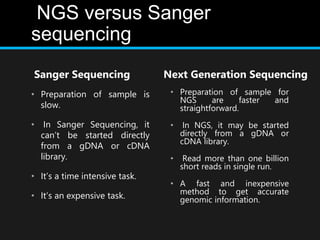
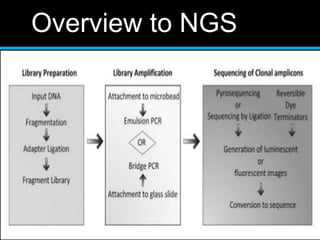
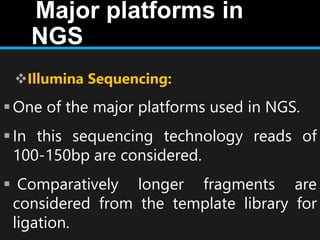
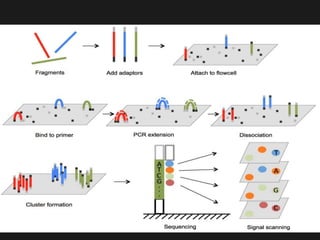
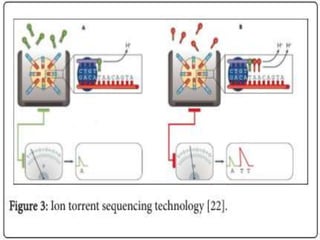
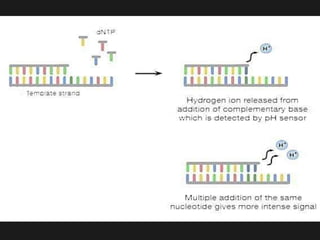
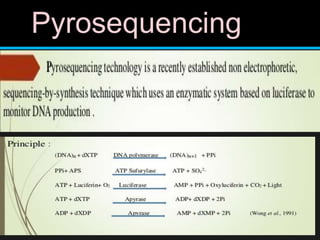
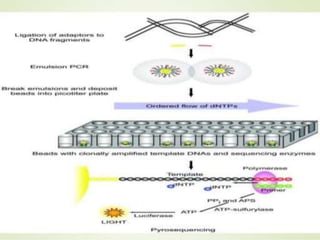
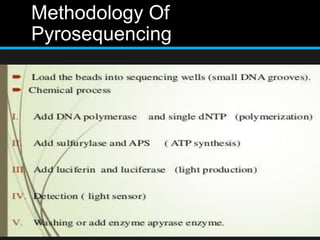
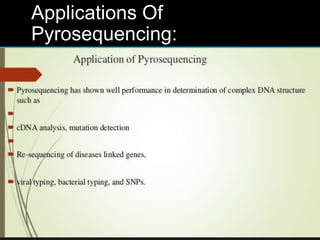
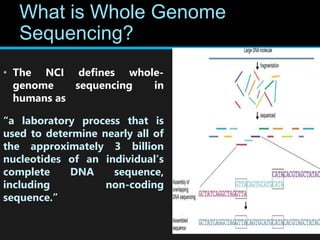
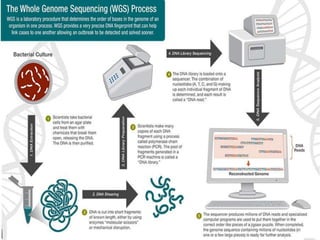
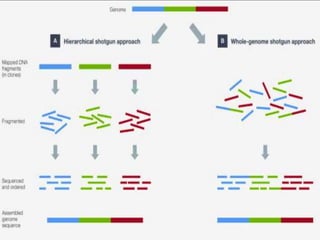
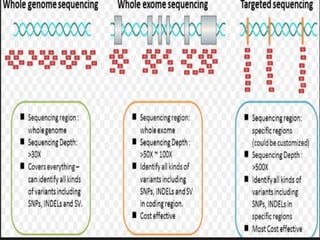
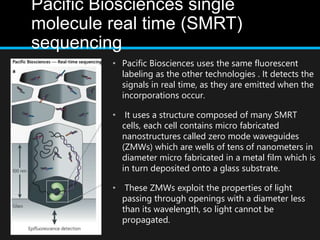
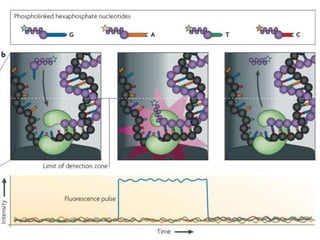
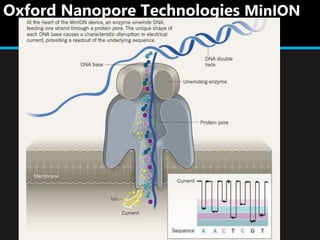
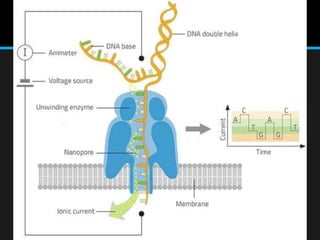
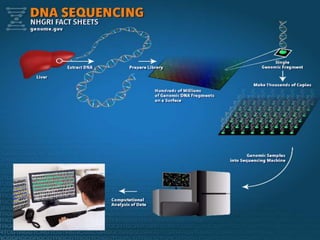
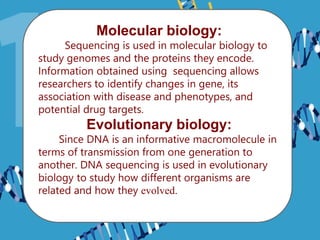
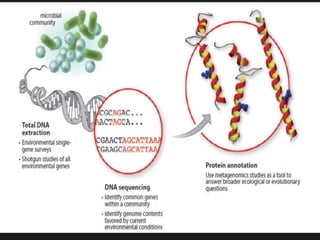
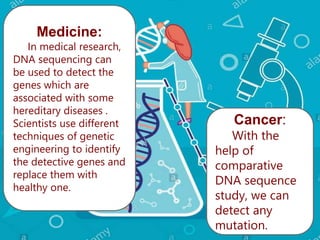
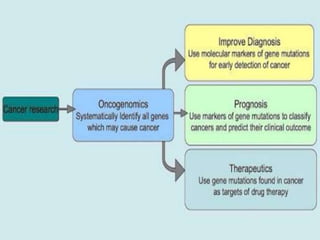
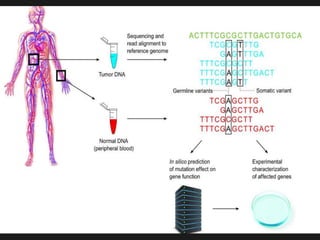
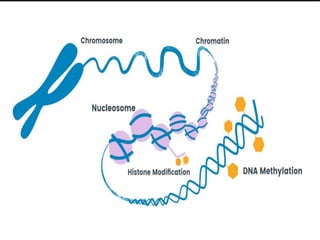
Gene sequencing is the technique that determines the order of nucleotide bases in DNA. It allows researchers to read genetic information and understand genes. The first genome sequenced was a bacteriophage in 1977. Techniques have advanced from Sanger sequencing to second-generation sequencing using platforms like Illumina and third-generation single-molecule techniques. Gene sequencing has various applications in medicine, forensics, agriculture, cancer research and more. It is an important tool for understanding genomes and their relationship to traits and disease.