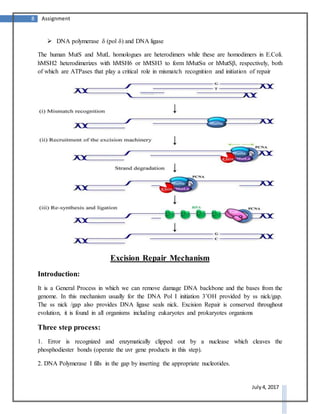
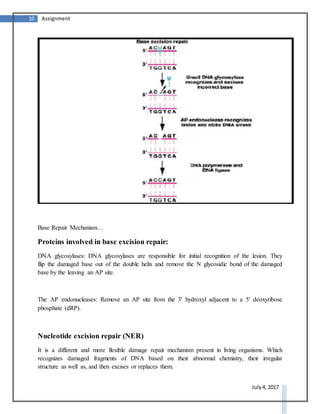
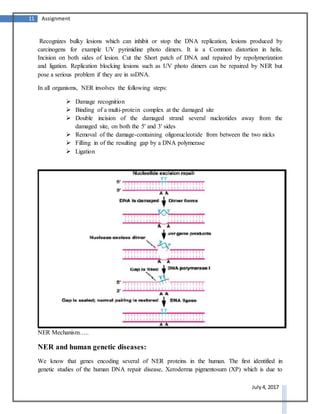
DNA repair systems are critical for correcting damage to DNA that occurs naturally. There are multiple DNA repair mechanisms that have been discovered, including direct reversal of damage, mismatch repair, recombinational repair, and excision repair. Excision repair involves removing damaged sections of DNA. It is a conserved process in prokaryotes and eukaryotes that utilizes DNA glycosylases to recognize and remove damaged bases, AP endonucleases to excise areas around the damaged bases, DNA polymerase to fill in the gaps, and DNA ligase to seal the gaps.