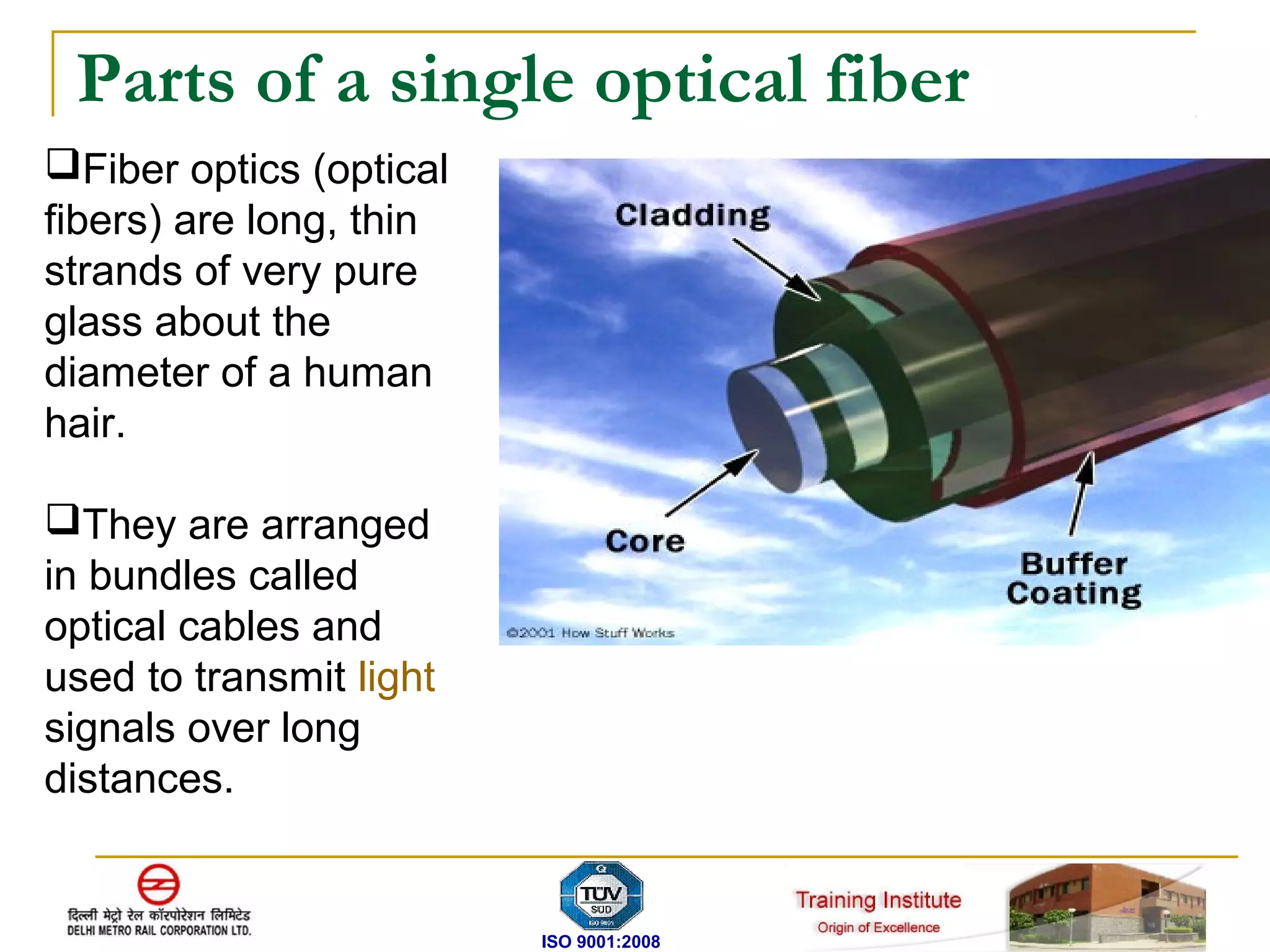
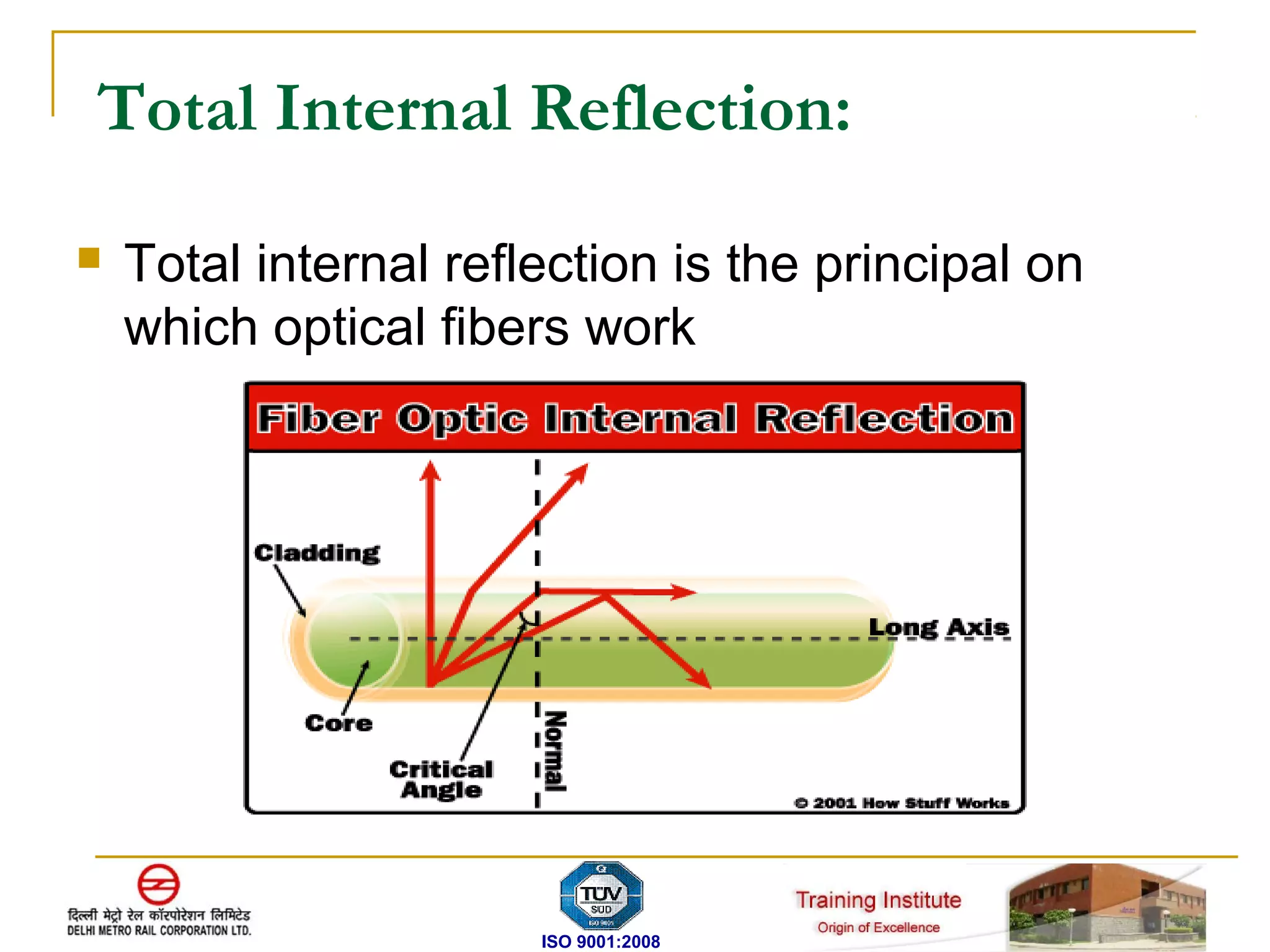
The document discusses fiber optic transmission systems (FOTS). It describes how FOTS uses optical fibers to transmit information over long distances using light signals. It discusses the key components of a FOTS including transmitters, optical fibers, optical receivers, and how total internal reflection allows fibers to transmit signals. The document also covers fiber types, advantages of FOTS over copper wire, components in DMRC's network, and technologies like SDH used for optical communication.