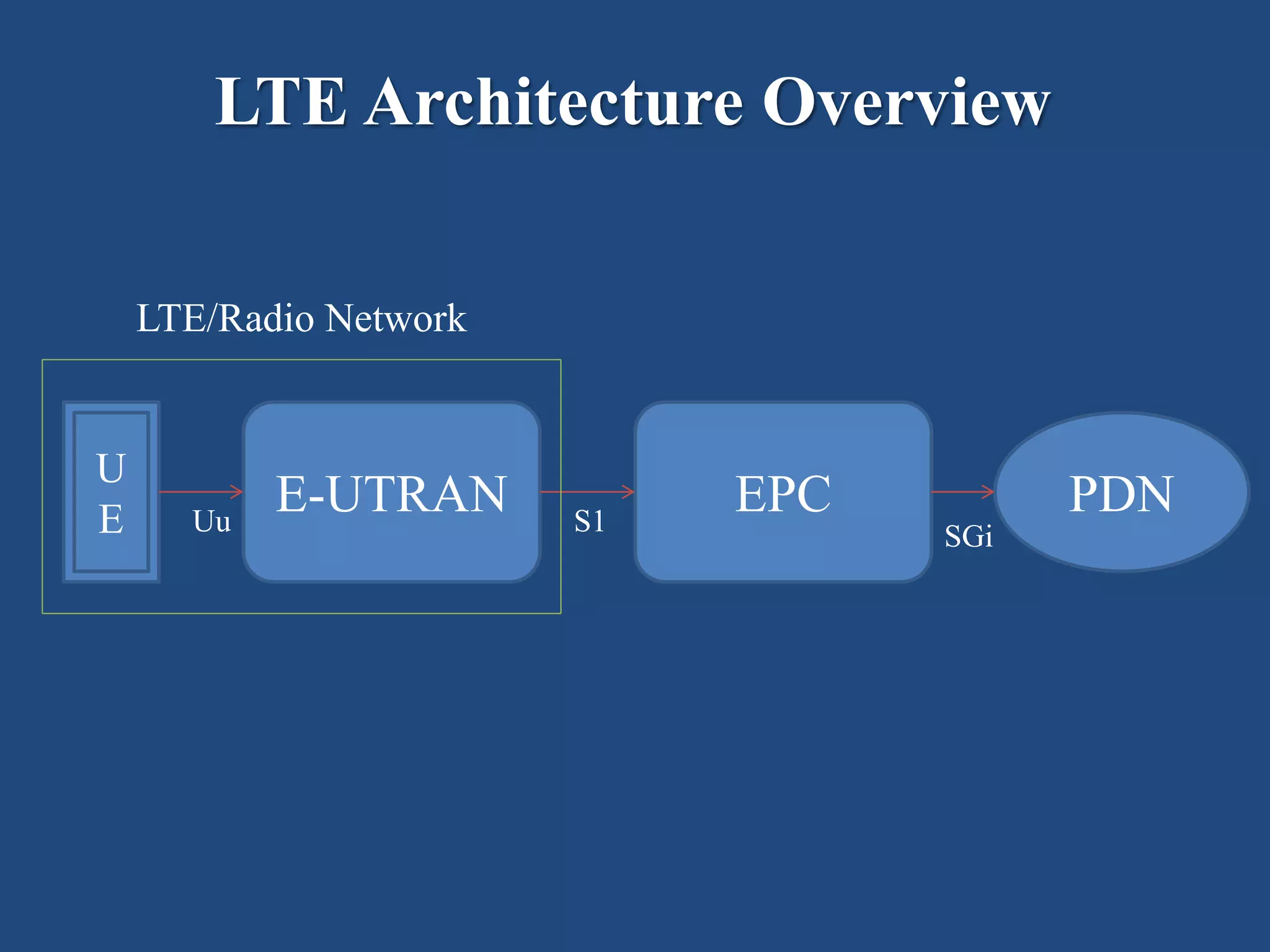
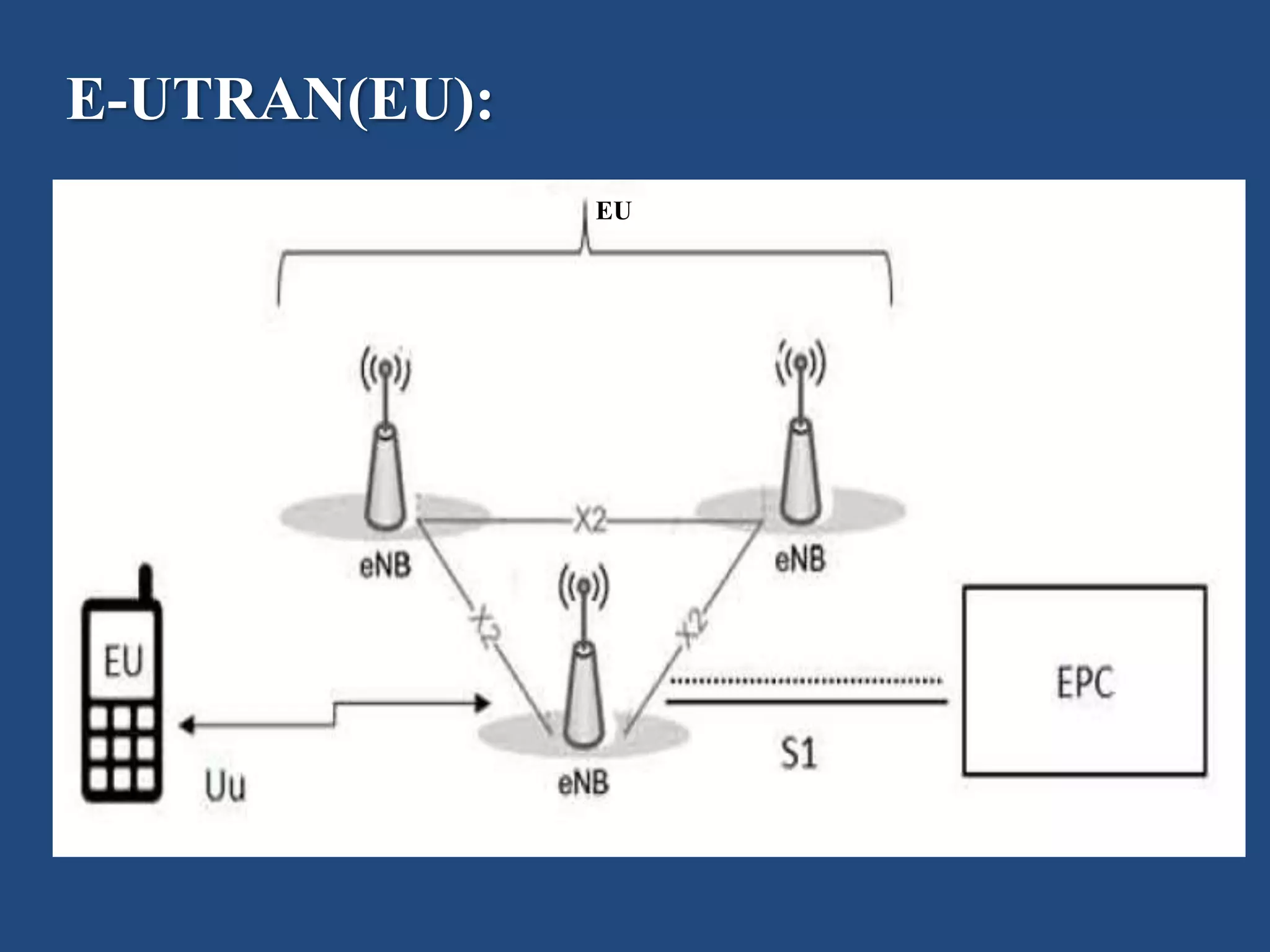
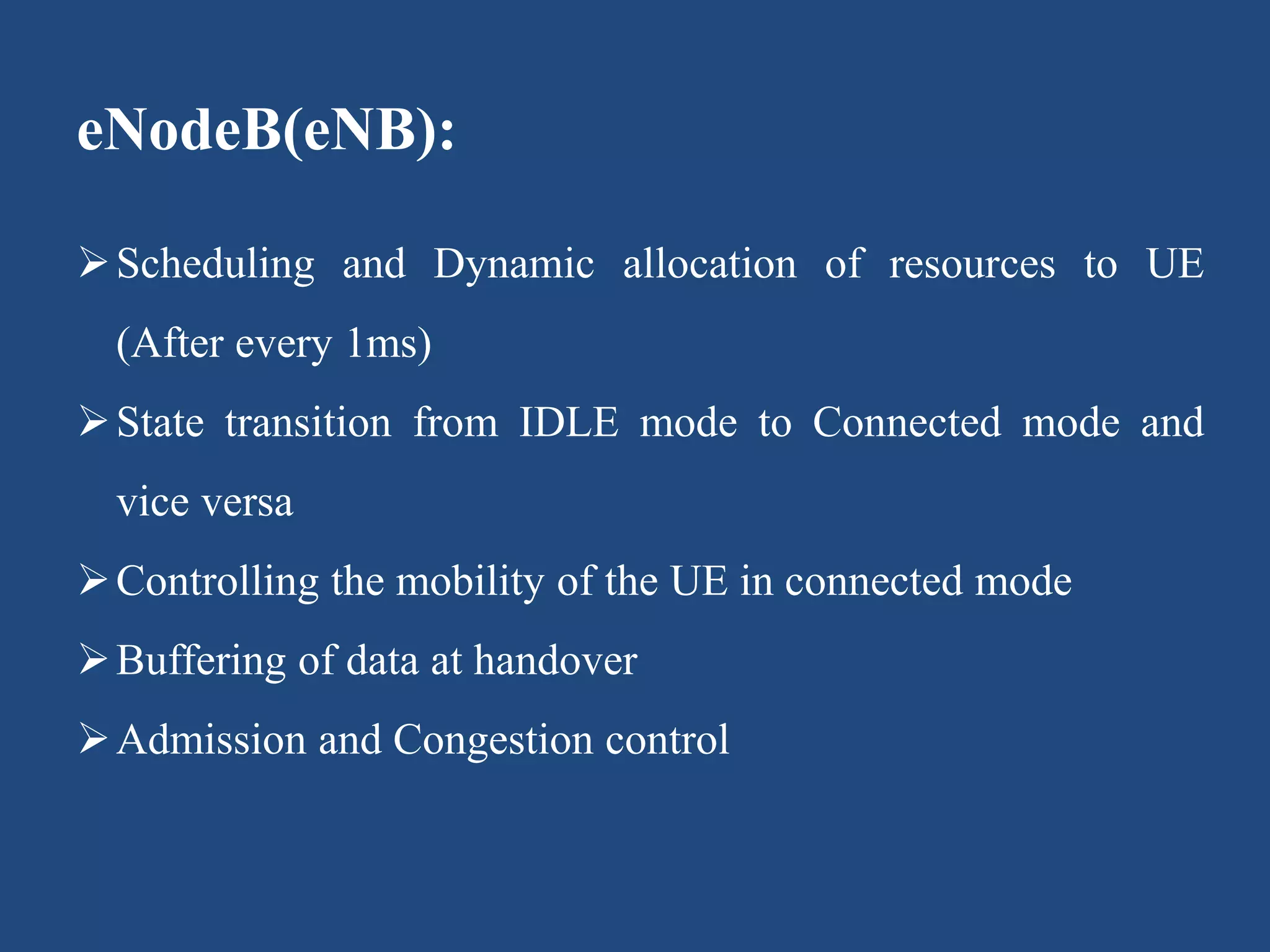
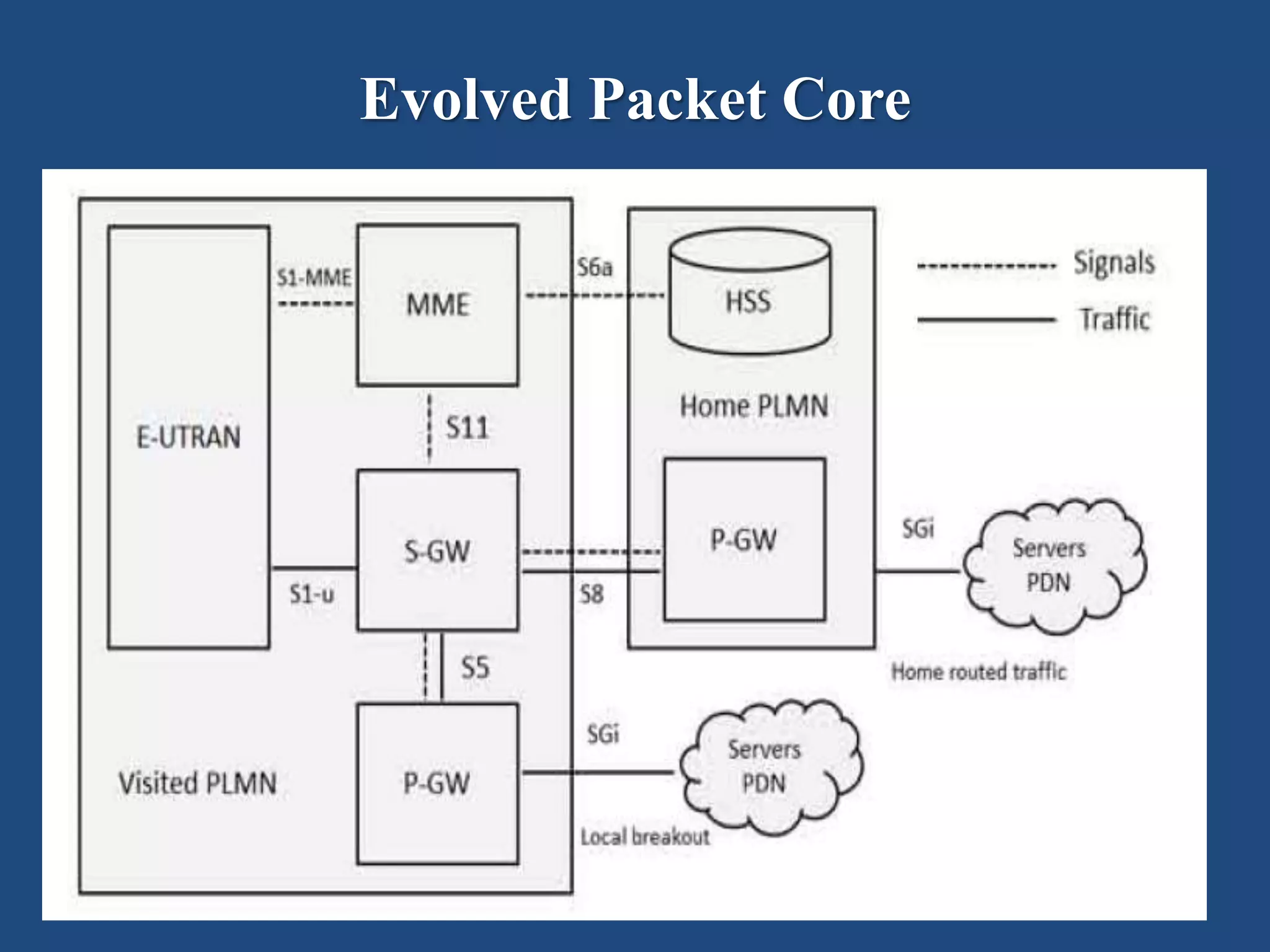
The presentation discusses LTE (Long Term Evolution), the fourth generation mobile network technology, highlighting its architecture, basic parameters, and advantages and disadvantages. Key components include user equipment (UE), evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (e-UTRAN), and the evolved packet core (EPC) with their respective functions. Notably, LTE offers high data rates, low latency, and supports multiple services, but requires specific devices and additional antennas for optimal functioning.