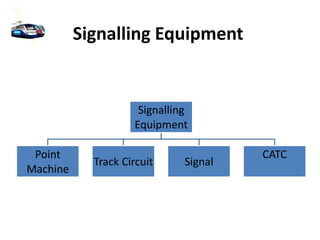
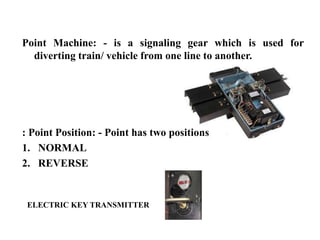
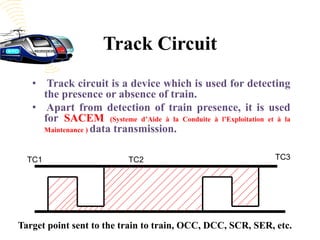
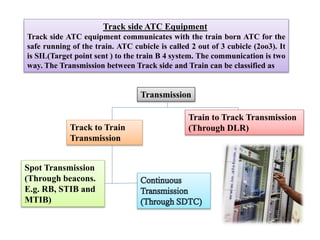
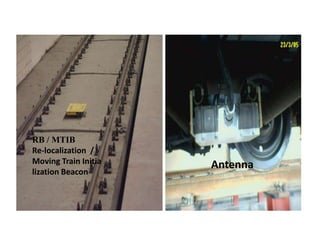
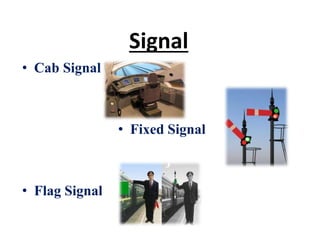
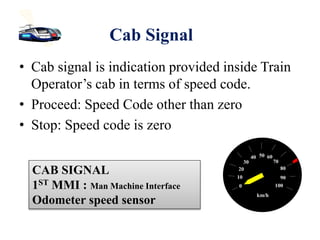
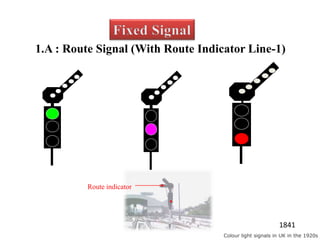
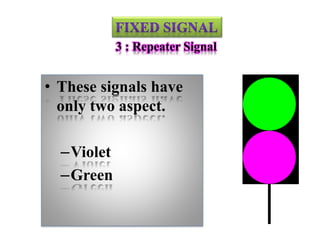
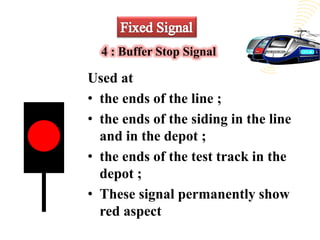
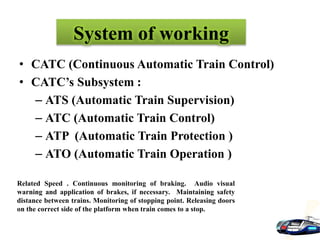
The document discusses various aspects of signalling systems used in Indian metro rail networks such as Kolkata Metro, Delhi Metro, and Bangalore Metro. It describes signalling equipment like point machines, track circuits, and different types of signals including cab signals, fixed signals, and flag signals. The document also provides information on interlocking, train control systems, and operation control centres used for train movement and safety.