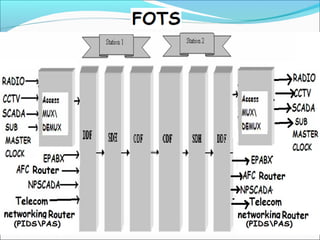
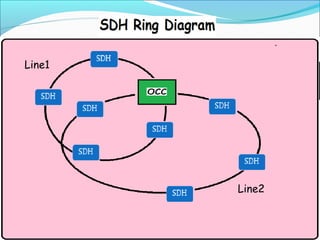
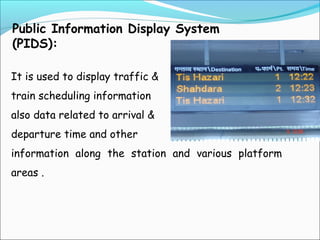
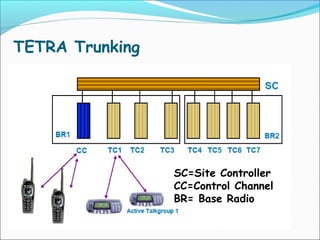
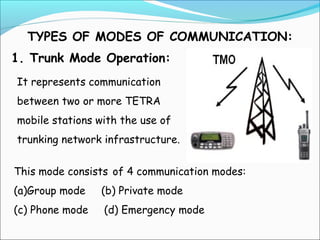
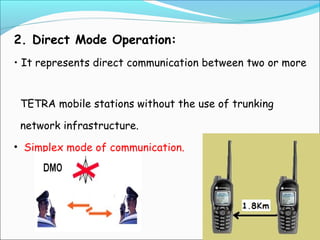
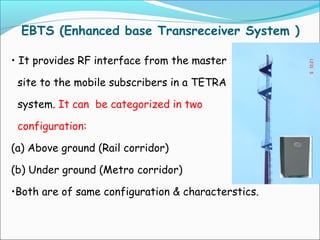
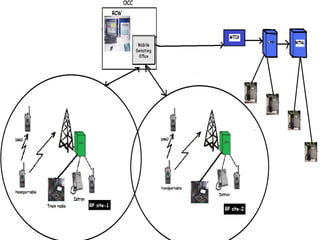
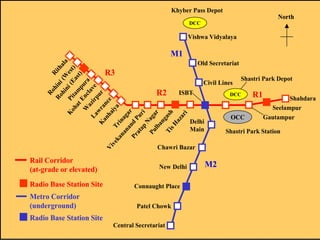
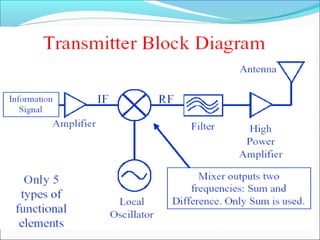
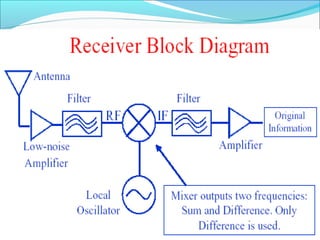
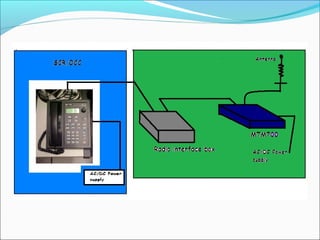
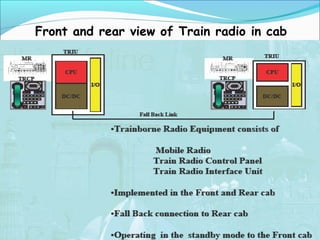
The document discusses the telecommunication systems used by Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC). It describes the key components which include fiber optic transmission, public information displays, public address systems, master clocks, CCTV, radio systems, and telephone exchanges. It focuses on the radio communication system, which uses TETRA technology. The radio system allows voice communication between train operators, station controllers in the Operational Control Center, and other staff via mobile and fixed radios installed across the DMRC network.