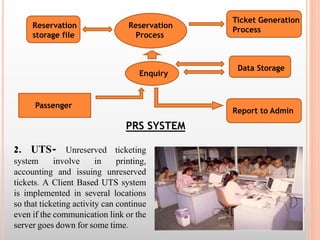
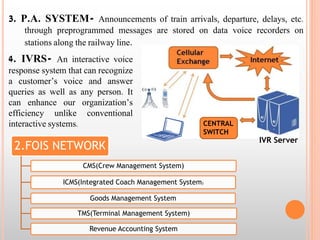
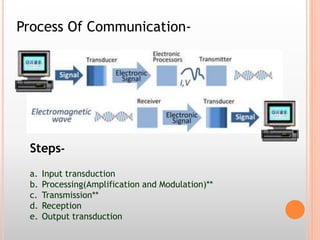
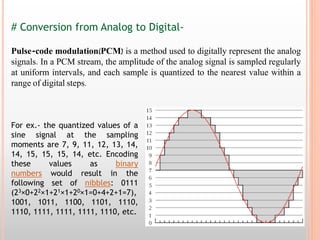
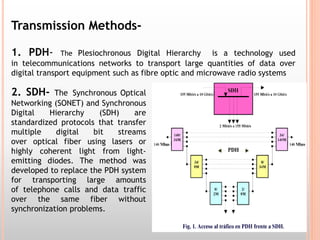
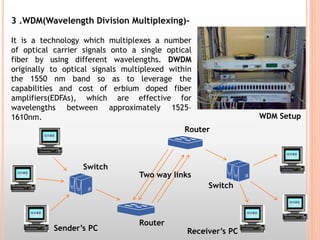
The document discusses the railway communication system in India, including Railnet which allows passengers to access information online, as well as FOIS which manages various railway operations. It describes the methods of communication used in railways like optical fiber, microwave, radio, and telephone, as well as the transmission methods of PDH, SDH, and WDM. The network components that support railway communication are also outlined, including routers, switches, firewalls, and network interface cards.