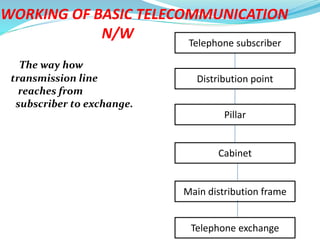
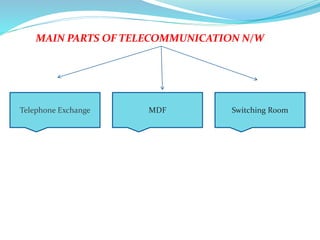
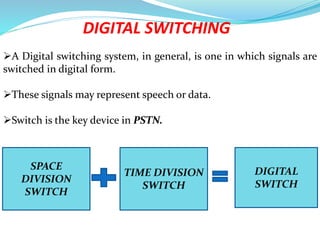
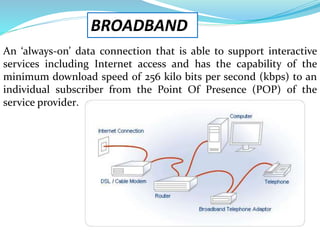
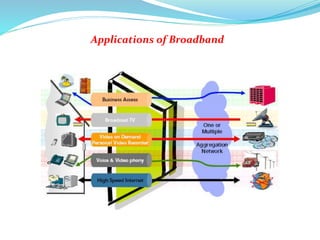
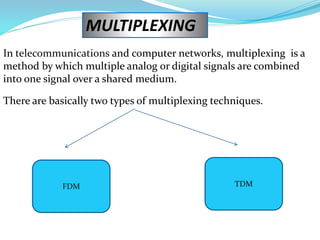
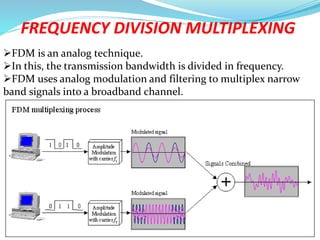
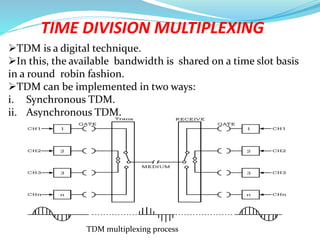
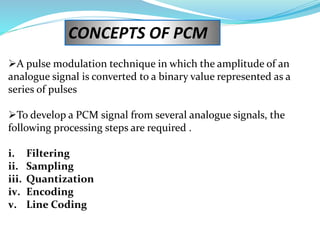
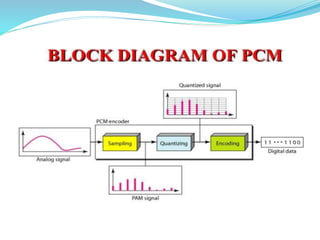
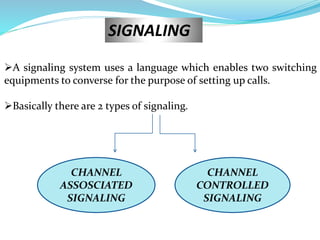
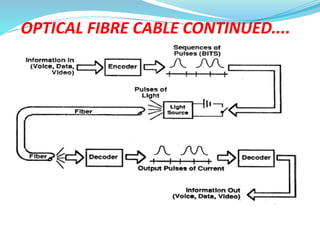
This document provides an overview of telecommunication networks and their evolution. It discusses the main components of basic telecommunication networks including telephone exchanges, distribution points, and switching rooms. The document also covers digital switching techniques, multiplexing methods like FDM and TDM, signaling systems, concepts of PCM, broadband applications, and optical fiber cables.