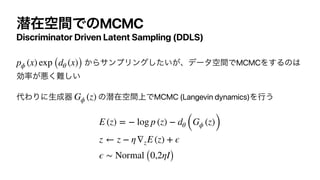
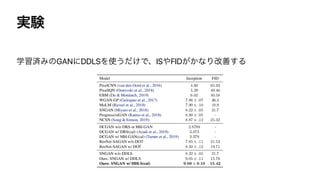
This document discusses the connections between generative adversarial networks (GANs) and energy-based models (EBMs). It shows that GAN training can be interpreted as approximating maximum likelihood training of an EBM by replacing the intractable data distribution with a generator distribution. Specifically:
1. GANs train a discriminator to estimate the energy function of an EBM, with the generator minimizing that energy of its samples.
2. EBM training can be seen as alternatively updating the generator and sampling from it, in a manner similar to contrastive divergence for EBMs.
3. This perspective unifies GANs and EBMs, and suggests ways to combine their training procedures to leverage their respective advantages



![Generative Adversarial Network
[Goodfellow et al.,2014]
ࣝผث ͱੜث ͷϛχϚοΫεήʔϜ
ࣝผث Λ࠷େԽ͠ɺੜث Λ࠷খԽ
Dθ Gϕ
Dθ : ℝdx → [0,1], Gϕ : ℝdz → ℝdx
ℒ (θ, ϕ) =
𝔼
p(x) [log Dθ(x)] +
𝔼
p(z) [log (1 − Dθ (Gϕ (z)))]
ℒ ℒ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlseminar20200828-210519065921/85/DL-GAN-4-320.jpg)

![GANͷҰൠతͳղऍ
ࣝผີʹثൺਪఆث
ࣝผثσʔλ ͱੜαϯϓϧͷ ͷ
ີൺਪఆͯ͠ͱثͷׂΛՌͨ͢
i.e., ࣝผ࠷͕ثదͳͱ͖
p (x) pϕ (x) =
𝔼
p(z) [p (Gϕ (z))]
D*
θ
(x) =
p (x)
p (x) + pϕ (x)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlseminar20200828-210519065921/85/DL-GAN-6-320.jpg)

![Trick
−log D
ΦϦδφϧͷϩεͩͱɺޯফࣦ͕͜ىΓ͍͢ͷͰɺ
ޙΛҎԼͷΑ͏ʹஔ͖͑ΔτϦοΫ͕Α͘ΘΕΔ
ͨͩ͠ɺ͜ͷ߹ີൺਪఆʹͮ͘جղऍΓཱͨͳ͍
ℒ (θ, ϕ) =
𝔼
p(x) [log Dθ(x)] −
𝔼
p(z) [log Dθ (Gϕ (z))]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlseminar20200828-210519065921/85/DL-GAN-8-320.jpg)
![GANͷੜ
σʔλͱͷڑͷࢦඪΛJSҎ֎ʹม͑Δͱɺ༷ʑͳGANͷੜ࡞͕ܥΕΔ
ྫɿWasserstein GAN
1-Ϧϓγοπͳؔʢ ʣ
͜ͷͱ͖ɺੜثͷֶश1-Wasserstein distanceͷ࠷খԽͱͳΔ
ℒ (θ, ϕ) =
𝔼
p(x) [Dθ(x)] −
𝔼
p(z) [Dθ (Gϕ (z))]
Dθ ℝdx → ℝ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlseminar20200828-210519065921/85/DL-GAN-9-320.jpg)
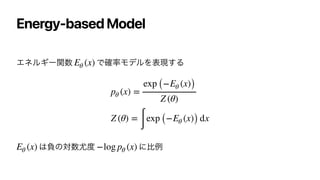
![EBMͷֶश
Contrastive Divergence
EBMͷରͷޯ
܇࿅σʔλͷΤωϧΪʔΛԼ͛ͯɺϞσϧ͔ΒͷαϯϓϧͷΤωϧΪʔΛ্͛Δ
∇θlog pθ (x) = − ∇θEθ (x) + ∇θlog Z (θ)
= − ∇θEθ (x) +
𝔼
x′

∼pθ(x) [∇θEθ (x′

)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlseminar20200828-210519065921/85/DL-GAN-11-320.jpg)
![EBM͔ΒͷαϯϓϦϯά
Langevin dynamics
ޯϕʔεͷMCMC
͜ͷߋ৽ࣜͰ܁Γฦ͠αϯϓϦϯά͢Δͱɺαϯϓϧͷ ʹऩଋ͢Δ
x ← x − η∇xEθ [x] + ϵ
ϵ ∼ Normal (0,2ηI)
pθ (x)
ޯ߱Լ๏ʹϊΠζ͕ͷͬͨܗ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlseminar20200828-210519065921/85/DL-GAN-12-320.jpg)









![EBMͷֶश
Contrastive Divergence
EBMͷରͷޯ
͔ΒͷαϯϓϦϯάΛ ͔ΒͷαϯϓϦϯάͰஔ͖͑Δ
∇θlog pθ (x) = − ∇θEθ (x) +
𝔼
x′

∼pθ(x) [∇θEθ (x′

)]
≈ − ∇θEθ (x)+
𝔼
z∼p(z) [∇θEθ (Gϕ (z))]
pθ (x) Gϕ (z)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlseminar20200828-210519065921/85/DL-GAN-22-320.jpg)
![ੜثͷֶश
ͱ͢Δͱɺ ͱͳΕྑ͍ͷͰ
͜ͷ2ͭͷͷKL divergenceΛ࠷খԽ͢Δ͜ͱͰֶश͢Δ
pϕ (x) =
𝔼
p(z) [δ (Gϕ (z))] pθ (x) = pϕ (x)
KL (pϕ∥ pθ) =
𝔼
pϕ [−log pθ (x)] − H (pϕ)
αϯϓϧͷΤωϧΪʔΛ
Լ͛Δ
αϯϓϧͷΤϯτϩϐʔΛ
্͛Δ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlseminar20200828-210519065921/85/DL-GAN-23-320.jpg)
![ੜثͷֶश
ͳͥΤϯτϩϐʔ߲͕ඞཁ͔
͠Τϯτϩϐʔ߲͕ͳ͍ͱɺੜثΤωϧΪʔ͕࠷খʢʹີ͕࠷େʣͷ
αϯϓϧͷΈΛੜ͢ΔΑ͏ʹֶशͯ͠͠·͏
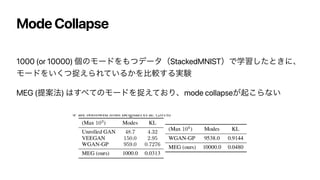
‣ GANͷmode collapseͱࣅͨΑ͏ͳݱ
͜ΕΛ͙ͨΊʹΤϯτϩϐʔ߲͕ඞཁ
KL (pϕ∥ pθ) =
𝔼
pϕ [−log pθ (x)] − H (pϕ)
αϯϓϧͷΤωϧΪʔΛ
Լ͛Δ
αϯϓϧͷΤϯτϩϐʔΛ
্͛Δ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlseminar20200828-210519065921/85/DL-GAN-24-320.jpg)
![ੜثͷֶश
ୈ1߲ͷޯɺҎԼͷΑ͏ʹ؆୯ʹࢉܭՄೳ
∇ϕ
𝔼
pϕ [−log pθ (x)] =
𝔼
z∼p(z) [∇ϕEθ (Gϕ (z))]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlseminar20200828-210519065921/85/DL-GAN-25-320.jpg)




![Τϯτϩϐʔͷࢉܭ
จ1ͰΤϯτϩϐʔ ͷࢉܭΛόονਖ਼نԽͷεέʔϧύϥϝʔλͰ
ߦ͍͕ͬͯͨɺώϡʔϦεςΟοΫͰཧతͳଥੑͳ͍
KL (pϕ∥ pθ) =
𝔼
pϕ [−log pθ (x)] − H (pϕ)
H (pϕ)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlseminar20200828-210519065921/85/DL-GAN-30-320.jpg)
![Τϯτϩϐʔͷࢉܭ
જࡏม ͱੜثͷग़ྗ ͷ૬ޓใྔΛߟ͑Δͱ
z x = Gϕ (z)
I(x, z) = H (x) − H (x ∣ z) =
𝔼
p(z) [H (Gϕ (z)) − H (Gϕ (z) ∣ z)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlseminar20200828-210519065921/85/DL-GAN-31-320.jpg)
![Τϯτϩϐʔͷࢉܭ
͕ܾఆతͳؔͷͱ͖ɺ ͳͷͰ
ͭ·ΓɺΤϯτϩϐʔͷΘΓʹɺ૬ޓใྔΛ࠷େԽ͢Εྑ͍
Gϕ H (Gϕ (z) ∣ z) = 0
H (pϕ) =
𝔼
p(z) [H (Gϕ (z))] = I (x, z)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlseminar20200828-210519065921/85/DL-GAN-32-320.jpg)
![૬ޓใྔͷਪఆ
૬ޓใྔͷਪఆํ๏ɺ͍ۙΖ͍ΖఏҊ͞Ε͍ͯΔ͕ɺ
͜͜ͰɺDeep InfoMaxͰఏҊ͞ΕͨJS divergenceʹͮ͘جਪఆ๏Λ༻͍Δ
͔Βͷαϯϓϧͱ ͔ΒͷαϯϓϧΛݟ͚ΔࣝผͰث
ಉ࣌ʹֶश͢Δ
IJSD (x, z) = sup
T∈
𝒯
𝔼
p(x, z) [−sp (−T (x, z))] −
𝔼
p(x)p(z) [sp (T (x, z))]
T p (x, z) p (x) p (z)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlseminar20200828-210519065921/85/DL-GAN-33-320.jpg)
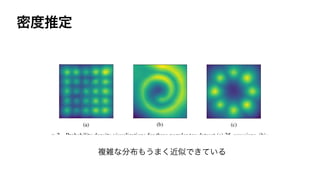


![GANͷҰൠతͳղऍ
ࣝผີʹثൺਪఆث
ࣝผثσʔλ ͱੜαϯϓϧͷ ͷ
ີൺਪఆͯ͠ͱثͷׂΛՌͨ͢
i.e., ࣝผ࠷͕ثదͳͱ͖
p (x) pϕ (x) =
𝔼
p(z) [p (Gϕ (z))]
D*
θ
(x) =
p (x)
p (x) + pϕ (x)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlseminar20200828-210519065921/85/DL-GAN-38-320.jpg)