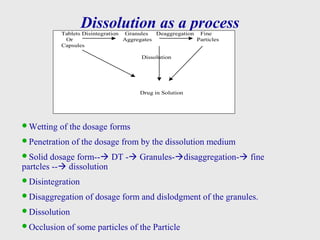
This document discusses dissolution method development. It defines dissolution as a process where a solid substance enters a solvent to form a solution. The key steps in dissolution are wetting, disintegration, disaggregation, and dissolution of particles. Factors that influence dissolution are also discussed, along with the Noyes-Whitney equation. A systematic approach to method development is then outlined, including literature review, solubility studies, sink conditions, apparatus selection, media preparation, method optimization, and sample analysis investigations. The goal is to develop a successful dissolution method and analysis to characterize drug release.