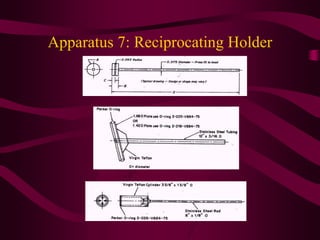
This document discusses dissolution testing, which is used to evaluate how quickly an active pharmaceutical ingredient is released from its solid dosage form after administration. Key points include:
- Dissolution is the process by which a solid enters solution and is controlled by the affinity between the solid and solvent.
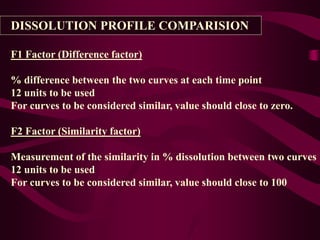
- Dissolution testing seeks to relate in vitro dissolution to in vivo drug absorption and bioavailability.
- The Biopharmaceutics Classification System categorizes drugs based on their solubility and permeability properties to determine the rate-limiting step of absorption.
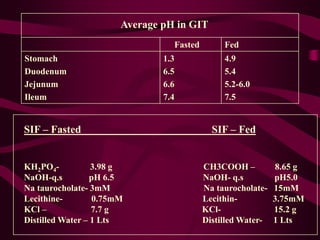
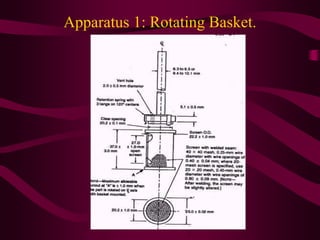
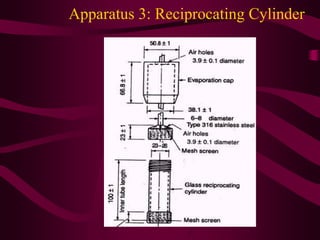
- Procedures for dissolution testing must account for factors like pH, surfactants, and apparatus to mimic conditions in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Diss