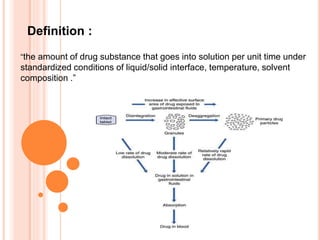
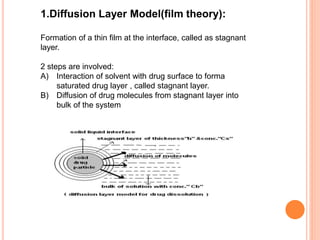
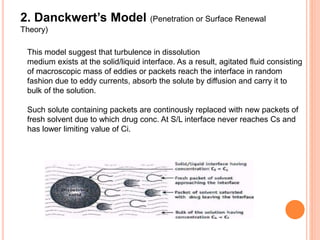
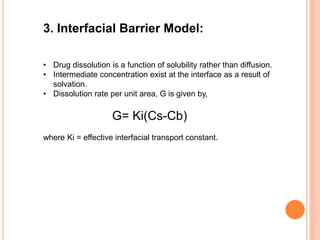
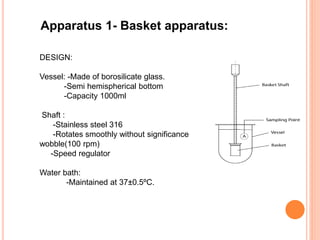
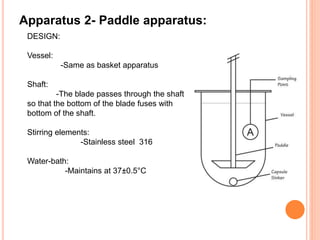
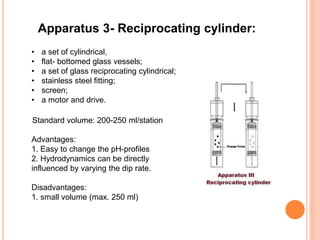
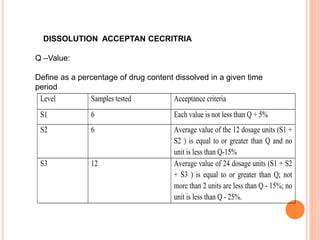
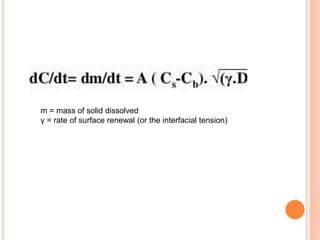The document discusses dissolution testing of pharmaceutical solid dosage forms. It defines dissolution as the amount of drug substance that goes into solution per unit time under standardized conditions. Dissolution testing is important for quality control to ensure uniform drug release and bioavailability. The key mechanisms of dissolution are the diffusion layer model, Danckwert's model, and the interfacial barrier model. Factors that influence dissolution include apparatus parameters, drug properties, and dosage form composition. Common apparatus are the basket, paddle, and flow-through cell methods. Acceptance criteria and methods to enhance dissolution through nanonization or changes to formulation are also covered.