The document discusses the evaluation of parenteral products. It provides an overview of parenterals, including their routes of administration and quality control tests. Key points covered include:
1) Parenterals are sterile solutions or suspensions administered outside the intestines, such as injections.
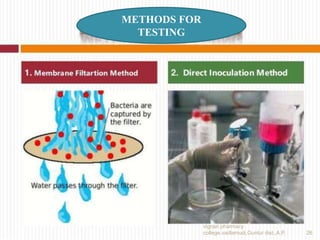
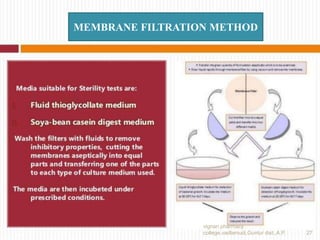
2) Quality control tests evaluate sterility, pyrogens, particulates, weight variation, and closure integrity.
3) Common tests include the leaker test, bacterial endotoxin test, and rabbit pyrogen test.