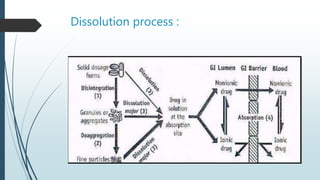
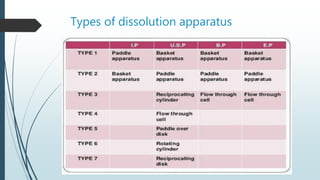
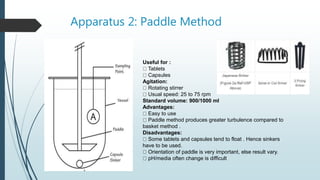
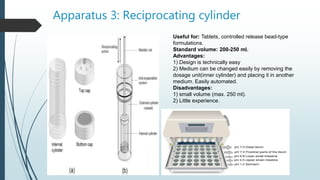
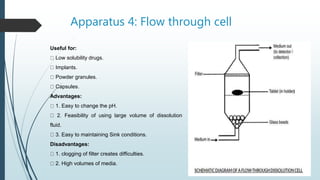
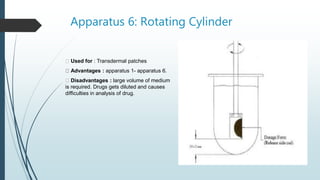
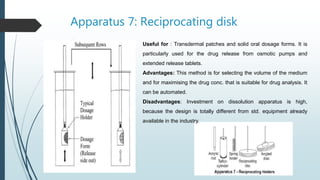
This document discusses dissolution, which is the process by which a solid substance solubilizes in a solvent. It defines dissolution rate and introduces the Noyes-Whitney equation. It then describes 7 types of dissolution apparatus used in compendial methods for testing drug dissolution, including rotating basket, paddle, reciprocating cylinder, and flow through cell. Key factors that affect dissolution rate are also outlined, such as drug properties, formulation components, processing methods, apparatus parameters, and test conditions.